对映射文件(mapper.xml说明)
<mapper namespace="com.zy.Dao.UserDao"> //namespace:命名空间
<select id="selectById" resultType="User" parameterType="int"> //id:表示映射文件的sql,将sql语句封装到mappedStatement对象中,所以又叫statement的id,parmeterType(可以不指定):输入类型的参数,如果指定类型是简单类型(int,String等),参数名可以任意
SELECT
*
FROM
t_user
WHERE id = #{id} ;
</select>
</mapper>
MyBatis 使用
增删改查
增
<insert id="insert">
INSERT INTO tb_user (
id,
username,
password,
phone,
email,
created,
updated
)
VALUES
(
#{id},
#{username},
#{password},
#{phone},
#{email},
#{created},
#{update}
)
</insert>
mysql自增主键:返回主键(主键被设置到了传入参数的user上)
<insert id="insetone">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="int"> //order:表示这个方法在插入之后执行
select LAST_INSERT_ID();
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO t_user (username, PASSWORD)
VALUES
(#{username}, #{password});
</insert>
删
<delete id="delete">
DELETE FROM tb_user WHERE id = #{id}
</delete>
改
<update id="update">
UPDATE
tb_user
SET
username = #{username},
password = #{password},
phone = #{phone},
email = #{email},
created = #{created},
updated = #{update}
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>
测试
使用 User user = tbUserDao.getUserById(1); user.setName="dd"; tbUserDao.updata(user);
查
模糊查询
<select id="selectByName" resultType="TbUser">
SELECT
a.id,
a.username,
a.password,
a.phone,
a.email,
a.created,
a.updated AS "update"
FROM
tb_user AS a
WHERE
a.username LIKE CONCAT ('%', #{username}, '%') <!--相当于SQL语句中 a.username LIKE "%zy%"-->
</select>
MyBatis 动态 SQL
注意事项
在 mapper 的动态 SQL 中若出现大于号(>)、小于号(<)、大于等于号(>=),小于等于号(<=)等符号,最好将其转换为实体符号。否则,XML 可能会出现解析出错问题。
特别是对于小于号(<),在 XML 中是绝对不能出现的。否则,一定出错。

if 标签
对于该标签的执行,当 test 的值为 true 时,会将其包含的 SQL 片断拼接到其所在的 SQL 语句中。
本例实现的功能是:查询出满足用户提交查询条件的所有学生。用户提交的查询条件可以包含一个姓名的模糊查询,同时还可以包含一个年龄的下限。当然,用户在提交表单时可能两个条件均做出了设定,也可能两个条件均不做设定,也可以只做其中一项设定。
这引发的问题是,查询条件不确定,查询条件依赖于用户提交的内容。此时,就可使用动态 SQL 语句,根据用户提交内容对将要执行的 SQL 进行拼接。
定义映射文件
为了解决两个条件均未做设定的情况,在 where 后添加了一个“1=1”的条件。这样就不至于两个条件均未设定而出现只剩下一个 where,而没有任何可拼接的条件的不完整 SQL 语句。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lusifer.mybatis.dao.DynamicStudentDao">
<!-- if -->
<select id="selectByIf" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score
FROM
student
WHERE 1 = 1
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name LIKE concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="age != null and age > 0">
AND age > #{age}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>
where 标签
<if/> 标签的中存在一个比较麻烦的地方:需要在 where 后手工添加 1=1 的子句。因为,若 where后的所有 <if/> 条件均为 false,而 where 后若又没有 1=1 子句,则 SQL 中就会只剩下一个空的 where,SQL 出错。所以,在 where 后,需要
添加永为真子句 1=1,以防止这种情况的发生。但当数据量很大时,会严重影响查询效率。
定义映射文件
<!-- where-->
<select id="selectByWhere" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score
FROM
student
<where> //会自动去掉条件中的第一个AND,所以我们就不需要写where 1=1;
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name LIKE concat('%', #{name}, '%') //AND 可以加也可以不加,都会被去掉;
</if>
<if test="age != null and age > 0">
AND age > #{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
示例:模糊查询(组合搜索引擎)
<select id="fuzzysearch" resultType="TbUser">
SELECT <include refid="Usercolumns"/> FROM tbuser As u <where>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
OR u.username LIKE concat('%', #{username}, '%')
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone !=''">
OR u.phone LIKE concat('%', #{phone}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email !=''">
OR u.email LIKE concat('%', #{email}, '%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
示例:模糊查询(单个搜索引擎)
<select id="fuzzysearch" resultType="TbUser">
SELECT <include refid="Usercolumns"/> FROM tbuser As u <where>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
AND u.username LIKE concat('%', #{username}, '%')
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone !=''">
AND u.phone LIKE concat('%', #{phone}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email !=''">
AND u.email LIKE concat('%', #{email}, '%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
choose 标签
该标签中只可以包含 <when/> <otherwise/>,可以包含多个 <when/> 与一个 <otherwise/>。它们联合使用,完成 Java 中的开关语句 switch..case 功能。
本例要完成的需求是,若姓名不空,则按照姓名查询;若姓名为空,则按照年龄查询;若没有查询条件,则没有查询结果。
定义映射文件
<!-- choose -->
<select id="selectByChoose" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score
FROM
student
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name LIKE concat('%', #{name}, '%')
</when>
<when test="age != null and age > 0">
AND age > #{age}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND 1 != 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
foreach 标签(遍历数组)
<foreach/> 标签用于实现对于数组与集合的遍历。对其使用,需要注意:
-
collection表示要遍历的集合类型(或者对象的属性名),这里是数组,即 array。 -
open、close、separator为对遍历内容的 SQL 拼接(注意拼接的含义)。
定义映射文件
动态 SQL 的判断中使用的都是 OGNL 表达式。OGNL 表达式中的数组使用 array 表示,数组长度使用 array.length 表示。
注意:如果传入的直接是一个数组或者集合,下面代码中的名字不能乱写,如果传入一个pojo,pojo对象属性是集合或者数组,那么下面的名字就是属性名;
1、sql:SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE id IN (3,4); open:"(",close:")",separator(分割这些数据)是","

<!-- foreach -->
<select id="selectByForeach" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (2, 4) -->
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score
FROM
student
<if test="array != null and array.length > 0">
WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="array" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id} //如果list<Interget>,#{id}:就是每一个值,如果list<pojo>,#{id}:就是属性
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
如果sql:SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE (id=3 OR id =4); open:"(",close:")",separator(分割这些数据)是"OR"
<select id="selectByForeach" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (2, 4) -->
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score
FROM
student
<if test="array != null and array.length > 0">
WHERE
<foreach collection="array" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator="OR">
id=#{id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
foreach 标签(遍历集合)
遍历集合的方式与遍历数组的方式相同,只不过是将 array 替换成了 list
sql 标签
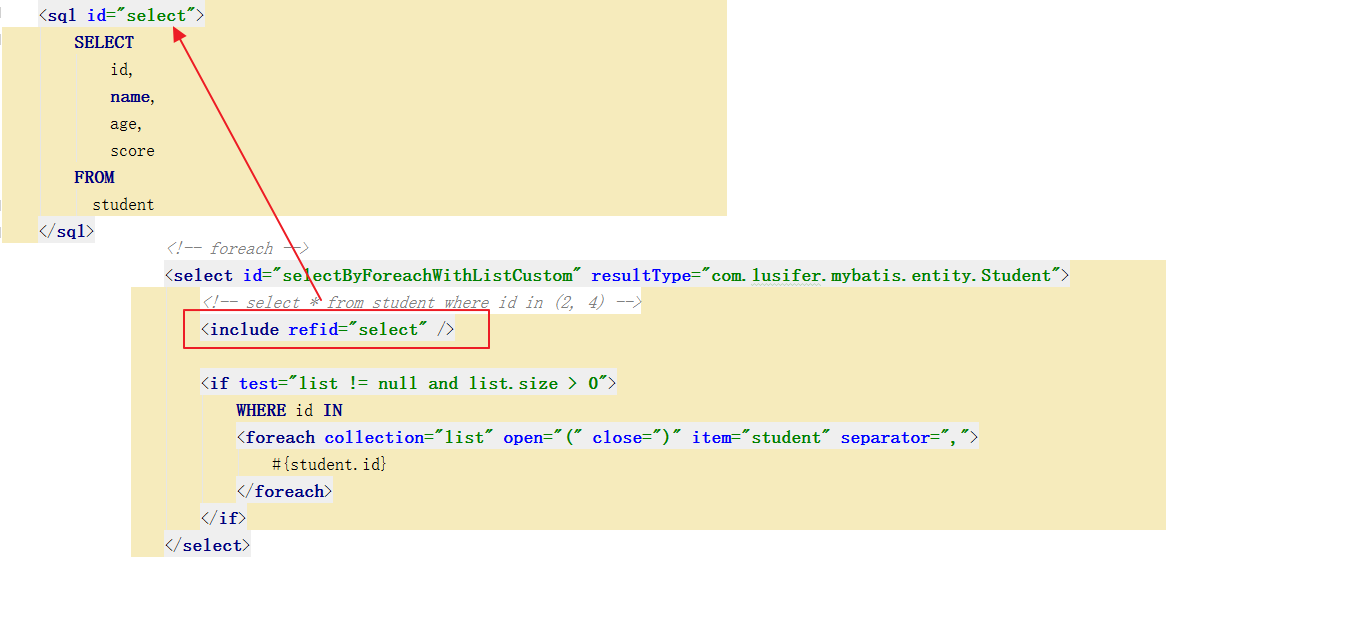
<sql/> 标签用于定义 SQL 片断,以便其它 SQL 标签复用。而其它标签使用该 SQL 片断, 需要使用 <include/> 子标签。该 <sql/> 标签可以定义 SQL 语句中的任何部分,所以 <include/> 子标签可以放在动态 SQL 的任何位置。
修改映射文件
<sql id="select">
SELECT
id,
name,
age,
score //结尾不能有逗号,注意
FROM
student
</sql>
<!-- foreach -->
<select id="selectByForeachWithListCustom" resultType="com.lusifer.mybatis.entity.Student">
<!-- select * from student where id in (2, 4) -->
<include refid="select" /> //如果指定的sql不在同一个Mapper中,那么select前面需要加上指定sql的namespace
<if test="list != null and list.size > 0">
WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="student" separator=",">
#{student.id}
</foreach>
</if>
</select>
补充:
1、#{}和${} 区别
#{}:表示占位符(不可以写成 '#{}'),如果传入的值是一个简单类型(int,String),#{}获得的就是传入的参数值,如果传入的是一个pojo或者hashmap,那么#{}获得的就是这个相应的属性值(例如,传入一个User,#{id},就相当于user.id)
${}:字符串拼接(容器引起sql注入,不建议使用),如果传入参数是一个简单类型,就就必须写成 ${value},否做就是获取传入参数的属性值。
2、resultMap
基础用法;
当我们查询的结果中的字段和pojo中的属性不一致,这就导致返回映射不成功;
我们假设User中的id字段是id_和username_,而数据库中的返回的字段是id和username;
解决方式1:
返回值还是resultType,通过别名,修改查询到的数据字段;
<select id="selectById" resultType="User">
SELECT
id AS id_,
username AS username_
FROM
t_user
WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
方式2
使用resultMap (这种方法不常用,方式1就可以搞定)
<!--id:唯一标识,type:返回的数据类型-->
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User">
<!--<id/>是修改特殊(唯一标识)字段,如果多个字段组成唯一标识,就需要配置多个id-->
<id column="id" property="id_"></id>
<!--<result/>是修改普通的字段-->
<result column="username" property="username_"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="userResultMap">
SELECT
id,
username
FROM
t_user
WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
高级用法1:我们主要利用resultMap将一些字段映射到pojo属性(另一个pojo对象)中的属性;
方式1:不使用association (这个需要sql语句进行连表操作,一次性将多个表的数据都查出来)
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User">
<!--<id/>是修改特殊(唯一标识)字段-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--<result/>是修改普通的字段-->
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<!--用户中关联的订单-->
<result column="order_id" property="order.id"></result>
<result column="ordername" property="order.orderName"></result>
</resultMap>
方式2:使用association(延迟加载,需要的时候在执行额外的sql语句)
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User">
<!--<id/>是修改特殊(唯一标识)字段-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--<result/>是修改普通的字段-->
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<!--用户关联的订单-->
<association property="order" javaType="com.zy.pojo.Order"> //property 是pojo中定义的字段
<id column="order_id" property="id"></id> //相当于order.id
<id column="ordername" property="orderName"></id> //相当于order.orderName
</association>
</resultMap>
高级用法2
一对多查询
比如我们需求,查询user中所有的user_detail数据;
SELECT t_user.*, user_detail.`id` AS user_detail_id, //注意:这需要些别名,防止和id冲突 user_detail.`desc`, user_detail.`user_id` FROM t_user, user_detail WHERE t_user.id=user_detail.`user_id`

使用ResultMap中的<collection />属性,来将数据装载到集合中;
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User">
<!--<id/>是修改特殊(唯一标识)字段-->
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<!--<result/>是修改普通的字段-->
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<!--集合中定义的pojo类型需要使用ofType-->
<collection property="userDetailList" ofType="com.zy.pojo.UserDetail">
<id column="user_detail_id" property="id"></id> //需要有唯一标识
<result column="desc" property="desc"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="select" resultMap="userResultMap">
/*重点:user_detail中的id需要使用别名,防止和user中的id冲突*/
SELECT
t_user.*,
user_detail.`id` AS user_detail_id,
user_detail.`desc`,
user_detail.`user_id`
FROM
t_user,
user_detail
WHERE t_user.id=user_detail.`user_id`
</select>
多对多查询【多个一对多】(就是简单的在集合中套一个集合):注意理解集合中的每一个元素都是一个pojo,相当于给每一个pojo设值
<collection property="userDetailList" ofType="com.zy.pojo.UserDetail">
<collection property=""></collection>
</collection>
补充理解:多对多,本质来说就是一对多,因为分析数据的时候,是按照某一张表(可以看做POJO)分析的,比如说A表和B表,知道一个A对应多个B,ok,我们就够了,如果我们需求从A中获取对应的所有的B,我们就不需要知道B对A是一对一还是一对多,没有意义,如果需求,我们需要从B中获取所有的A,那么我们就可以直接分析B对A的关系了,更不就不需要分析A对B的关系。
我们所谓的多对多是两张表之间的关系,但是真正在进行写sql语句的时候,我们只需要关注一条线,起点A-->终点B。或者A--->B----->C(B的数据放在A存,C的数据放在B存,注意上面的A,B,C,都是POJO)
resultMap的继承,rusultMap可以继承另一个resultMap,然后就不需要写在resultMap中写继承的代码了(注意继承,是全部继承的,如果继承中的某些东西不需要,那么就不要继承了)
<resultMap id="userResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User" extends="xx">
3.延迟加载
延迟加载:先从单表查询,需要是在从关联表去关联查询,大大提高数据库性能,如果我们不使用下面案例这个框架,用最简单的方法实现延迟加载本质,就是假如我们只需要用户表中的数据,不需要订单表中的数据,我们就写一个sql查询用户表数据即可,如果突然又需要user表中关联的order信息,我们就在用之前user查询的结果在去查询order信息,这就是延迟加载的本质。
resultMap中的association,collection 可以实现延迟加载
环境配置
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> <setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
Mapper.xml
<!--根据用户信息查询订单,如果不需要,dao可以不用写接口-->
<select id="selectOrderById" resultType="com.zy.pojo.Order">
select * FROM u_order where id=#{id};
</select>
<!--延迟加载resultMap-->
<resultMap id="orderUserResultMap" type="com.zy.pojo.User">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<!--
对订单信息进行延迟加载,用户关联order(订单),所以user对order,是一对一,所以我们使用association
select:指定我们延迟加载需要执行的sql语句(statement Id),这个select可以不用再dao写接口(如果不需要的话)
column:通过数据库查询出来的user信息中得order_id列(所以sql语句中查询的字段不能将order_id字段忽略掉),order_id数据会被传入selectOrderById中
-->
<association property="order" select="selectOrderById" column="order_id">
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--查询用户关联的相关订单-->
<select id="selectUserById" resultMap="orderUserResultMap">
SELECT * FROM t_user where id=#{id};
</select>
dao
public interface UserDao {
public User selectUserById(int id);
}
测试
@Test
public void userTest(){
//注意如果是Debug模式测试,延迟加载就会失效(Debug会直接将order数据查询出来赋值给user)
User user = userDao.selectUserById(3);
System.out.println(user.getId());
System.out.println("------------------------");
/*当执行下面的语句的时候,控制台才出现查询订单的sql,所有如果不是必要,不要打印user,一旦打印了,延迟加载的sql也会被执行(原因需要获得user所有的信息)*/
System.out.println(user.getOrder());
}
4.查询缓存
Mybatis提供了查询缓存,用于减轻数据库压力,提高数据库性能
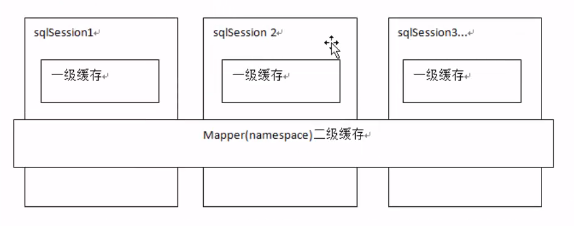
Mybatis提供了一级缓存和二级缓存
为什么使用缓存?
如果sql对应的数据在缓存中存在,那么我们就不需要在查询数据库了,直接将缓存中的数据返回给用户。提高系统的性能
4.1 一级缓存(默认开启)
一级缓存:是Sqlsession级别的缓存。在操作数据库时需要构造soglsession对象,在对象中有一个localCache,他是一个(HashMap)用于存储缓存数据。HaspMap的key就是封装了namespace和statement id 以及拼接好了的sql,value是缓存的数据;
不同的sglsession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互相不影响的。
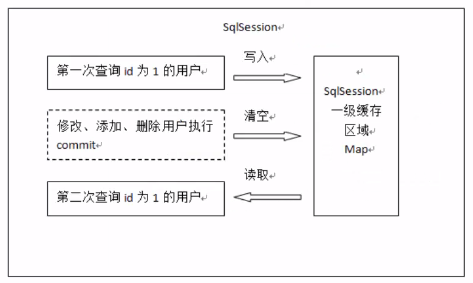
原理:第一次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库查询用户信息。得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中。如果sqlsession去执行commit 操作(执行插入、更新、删除),清空Sqlsession中的一级缓存,这样做的目的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。第二次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有d为1的用户信息,缓存中有,直接从缓存中获取用户信息。没有就去读取数据库,然后将数据写入一级缓存。
测试一级缓存
我使用的是sping整合mybatis,这样sqlsession自动生成的,我测试的时候,每次执行完毕sql后,通过打印日志看到sqlsession就会自动关闭,下一个请求后,就又自动生成一个sqlsession,所以每次的sqlsession都不一样,这样的话,就利用不了一级缓存了,因为一级缓存是在一个sqlsession里面。但是我们开启事务后,就可以利用一级缓存了。原因是开启事务后,事务控制在service(mvc三层结构),当调用service方法后,就开启了事务,会创建一个sqlsession,并且整个service方法这个过程中都是使用的这一个sqlsession。但是一旦service方法执行完毕,sqlsession就关闭了。所以一级缓存时间很短的,service方法调用完毕后,就清空了。如果我们就需要使用二级缓存长时间缓存数据。
参考spring一级缓存的详细说明:https://blog.csdn.net/ctwy291314/article/details/81938882
4.2 二级缓存(默认不开启)
二级缓存:是mapper级别的缓存,多个Sqlsession.去操作同一个Mapper的sql语句,多个Sqlsession.可以共用一个二级缓存,二级缓存是跨Sqlsession的
二级缓存应用场景:1、对访问的请求次数多,但是查询的结果的实时性不高的数据。,2、像一些特别耗时的统计分析sql(查询一条sql可能要几十分钟),实现方法:(设置flushInterval,每隔一段时间,自动清空缓存)
二级缓存局限性?二级缓存对细粒度的数据级别的缓存实现不好,比如,一大批用户查询了1万条的商品信息,放在缓存中,但是某一个商品信息被修改了,就会造成缓存数据被清空,1万条数据清空。
所以我们需要是,改了哪一个商品,就把那一个商品的缓存数据改变,Mybatis实现不了这种需求,需要我们手动实现业务层缓存,就是所谓的三级缓存(概念)。
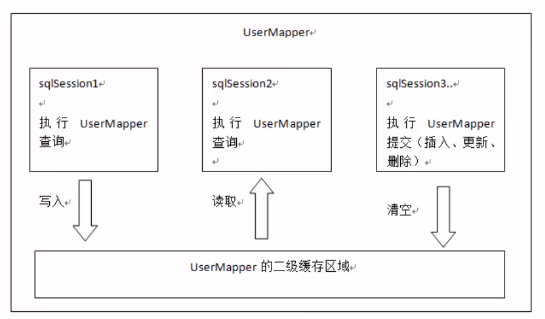
二级缓存区的划分?
是按照namespace划分的(也就是按照dao接口,namespace就是dao接口的全限定路径):每一个namespace有自己的二级缓存空间。不同的sqlsession访问同一个namespace,才数据共享。
比如下面两个dao,sqlsession之后访问同一个dao中相同或者不同的方法,才会共享二级缓存(依旧是HashMap存储数据)。如果mapper文件的namespace(命名空间)一样,那样,他们就可以共享一个mapper缓存。
为什么要划分呢?我自己也不太理解,把所有的数据都放到一个缓存空间不一样吗?等到后续的查阅资料。
UserDao
@Repository
public interface UserDao {
public User selectUserById(int id);
public List<User> selectAllUser(int id);
}
OrderDao
@Repository
public interface OrderDao {
public Order selectOrderById(int id);
}
使用二级缓存
开启二级缓存
1、mybtis-config.xml
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> //设置为true
2、mapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.zy.Dao.UserDao">
<cache></cache> //开启缓存(UserDao调用的所有的方法,公用这一个二级缓存)
</mapper>
3、将查询的pojo实现序列化接口
测试:模拟多个sqlsession;缓存是长时间存在内存中的。
public void sqlsession(UserDao userDao){
User user = userDao.selectUserById(3);
System.out.println(user.getId());
}
public void sqlsession2(UserDao userDao){
User user = userDao.selectUserById(3); //只有调用同一个方法,传入同一个参数,用同一个namespace,sql才会一样,此时就不会再去查询数据库了(如果没有执行增删改操作)
System.out.println(user.getId());
}
//注意测试的时候不用开启事务,否则就使用了一级缓存了(同一个sqlsession),测试不出来结果了
//@Transactional
@Test
public void userTest(){
new DemoTest().sqlsession(userDao); //当调用这个方法结束后,sqlsession就自动关闭了(注意:一定需要关闭,否则查询的数据不会写入到二级缓存中)
new DemoTest().sqlsession2(userDao);
}
补充
<select id="select" resultMap="userResultMap" useCache="false"> //表示这个查询禁用二级缓存 <insert id="" flushCache="true"></insert> //表示刷新缓存(清空缓存),一般插入数据后,都是需要刷新的,所有默认就是true <cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache" flushInterval="30"></cache> //type:使用第三方缓存(ehcache),flushInterval:设置刷新频率(单位应该是秒,不太清楚)
Mybatis逆向工程
mybatis需要程序员自己编写sql语句,mybatis官方提供逆向工程,可以针对单表自动生成mybatis执行所需要的代码(mapper.java、mapper.xml、pojo…),可以让程序员将更多的精力放在繁杂的业务逻辑上。
通过数据库生成java代码
使用方法:参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanxiaoge/p/11043295.html
Mybatis整合ehcache
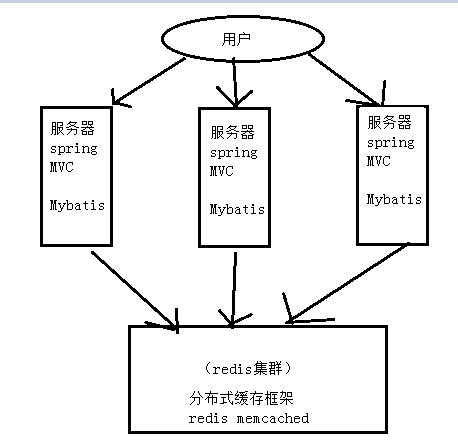
Mybatis实现不了分布式缓存,即使不谈分布式,Mybatis也不适用于做数据缓存,所以必须和其他框架整合,对缓冲的数据进行额外处理,保证对内存空间利用率,而Mybatis仅仅就是简单的将数据存放到内存中,没有对他们进行修饰。
ehcache:分布式缓存框架,如果不用分布式缓存,可以就需要每台服务器都需要保存用户登录的所有的数据。而ehcache可以对缓存数据进行集中管理。
额外的分布式缓存框架:redis,memcached
整合方法
Mybatis提供了一个cache接口,如果需要实现自己的缓存逻辑,就实现擦车接口开发即可;(MyBatis无论和那个缓存框架整和,第一反应就行想这个cache接口)
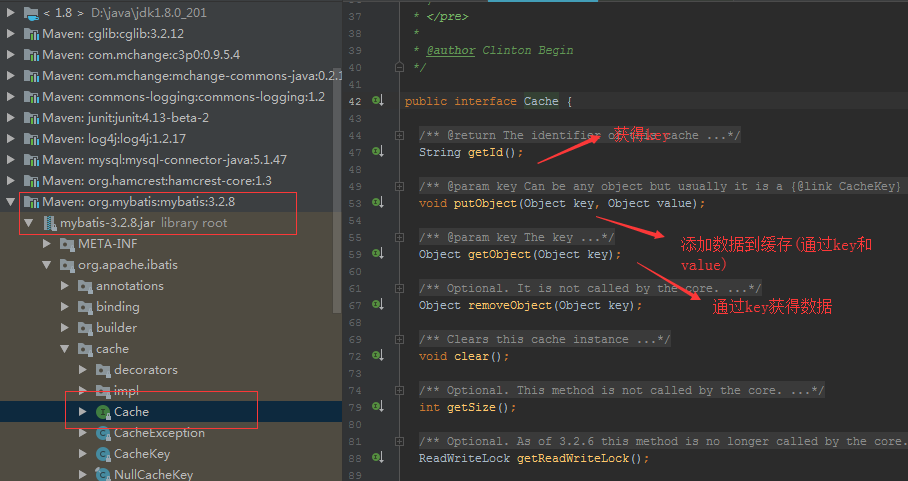
Mybatis中的默认实现类;(可以仿照他自己写一个类,继承cache接口即可)

Mybatis和ehcache整合,Mybatis 和 ehcache整合包中提供了一个cache接口的实现类型。
导入jar包,获取这个实现类
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
mapper.xml配置
<mapper namespace="com.zy.Dao.OrderDao">
<!--type默认类型就是PerpetualCache-->
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"></cache> //ehcache还有其他的cache实现类
</mapper>
配置ehcache配置文件(ehcache.xml,Hibernate可以修改文件位置,Mybatis不知道怎么修改)
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<!--IDEA:xsi如果报红 打开settings->languages&frameworks->Ignored schemas and dtds ,添加地址 http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd-->
<diskStore path="F:\testehcache" />
<!--
以下属性是必须的:
maxElementsInMemory:在内存中缓存的element的最大数目
maxElementsOnDisk : 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大
eternal : 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效,如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds,timeToLiveSeconds判断
overflowToDisk : 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上
以下属性是可选:
timeToIdleSeconds : 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时,这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大
timeToLiveSeconds : 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大
diskPersistent - 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小.默认是30MB.每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区.
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds - 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每个120s,相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy - 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出)
-->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
Mybatis编写插件
mybatis四大对象指的是:executor,statementHandler,parameterHandler和resultHandler对象。这四个对象在sqlSession内部共同协作完成sql语句的执行,同时也是我们自定义插件拦截的四大对象。
Mybatis实现乐观锁
首先数据表需要自已定义一个version表
插入操作(初始值设置0)
INSERT INTO employee(VERSION) VALUES(0)
更新操作,必须要有一个AND VERSION = #{version},#{version},是更新的时候先获取版本号
UPDATE employee SET VERSION = VERSION+1 WHERE id = 1 AND VERSION = #{version};