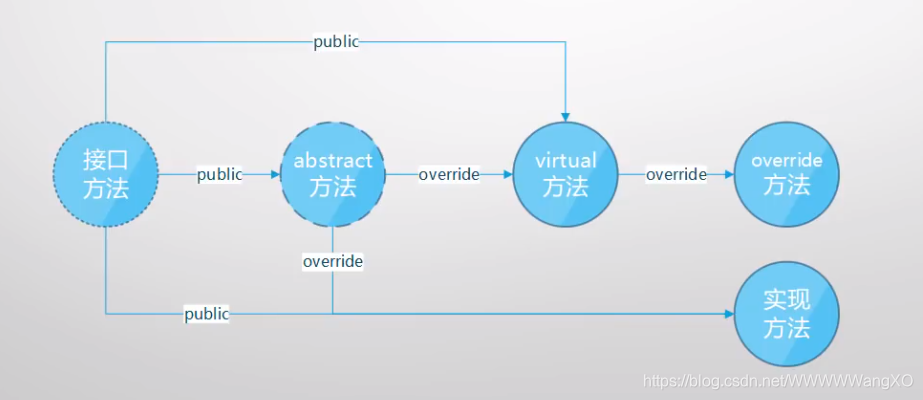
什么是接口和抽象类
- 接口和抽象类都是“软件工业产物”
- 具体类→抽象类→接口:越来越抽象,内部实现的东西越来越少
- 抽象类是未完全实现逻辑的类(可以有字段和非public成员,它们代表了“具体逻辑”),不可被实例化
- 抽象类为复用而生:专门作为基类来使用,也具有解耦功能
- 封装确定的,开放不确定的,推迟到合适的子类中去实现
- 接口是完全未实现逻辑的“类”(“纯虚类”;只有函数成员;成员全部public)
- 接口为解耦而生:“高内聚,低耦合”,方便单元测试
- 接口是一个“协约”,早已为工业生产所熟知(有分工必有协作,有协作必有协约)
- 他们都不能实例化,只能用来声明变量,或引用具体类的实例
为做基类而生的“抽象类”与“开放/关闭原则”
抽象类:
namespace Class
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle v = new RaceCar();
v.Run();
}
}
abstract class Vehicle
{
public abstract void Run();
public void Fill()
{
Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Stopped");
}
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class Tunck:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tunck is running");
}
}
class RaceCar:Car
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("RaceCar is running");
}
}
}
接口:类中全为抽象成员,成员必须为public
namespace Class
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vehicle v = new RaceCar();
v.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Stop();
void Fill();
void Run();
}
//接口相当于纯虚类,类中的成员都是抽象
//abstract class IVehicle
//{
// abstract public void Stop();
// abstract public void Fill();
// abstract public void Run();
//}
abstract class Vehicle:IVehicle
{
public void Fill()//若继承接口 将override去掉 并将继承所有成员 不能少
{
Console.WriteLine("Pay and fill");
}
public void Stop()
{
Console.WriteLine("Stopped");
}
abstract public void Run();
}
class Car:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class Tunck:Vehicle
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tunck is running");
}
}
class RaceCar:Car
{
public override void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("RaceCar is running");
}
}
}
接口与单元测试
- 接口的产生:自底向上(重构),自顶向下(设计)
- C#中接口的实现(隐式,显式,多接口)
- 语言对面向对象的设计的内建支持:依赖反转,接口隔离,开/闭原则等

namespace InterFaceExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] num1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
ArrayList num2 = new ArrayList { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Console.WriteLine(Sum(num1));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(num2));
Console.WriteLine(Avg(num1));
Console.WriteLine(Avg(num2));
}
//int所在的Array类和Arraylist类都继承自IEnumerable接口
//免去了输入类型不同的麻烦
static int Sum(IEnumerable nums)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var n in nums)
{
sum += (int)n;
}
return sum;
}
static int Avg(IEnumerable nums)
{
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
foreach (var n in nums)
{
sum += (int)n;
count++;
}
return sum / count;
}
}
}
*紧耦合实例(Car类紧依赖Engine类)
namespace InterFaceExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Engine engine = new Engine();
Car car = new Car(engine);
car.run(5);
Console.WriteLine(car.Speed);
}
}
class Engine
{
public int RPM { get;private set; }
public void Work(int gas)
{
this.RPM = 1000 * gas;
}
}
class Car
{
private Engine _engine;
public Car(Engine engine)
{
this._engine = engine;
}
public int Speed { get;private set; }
public void run(int gas)
{
_engine.Work(gas);
this.Speed = _engine.RPM / 100;
}
}
}
*低耦合示例:
namespace InterFaceExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//使用接口只需更换类名即可 new PhoneUser(new EricssonPhone());
var v = new PhoneUser(new NokiaPhone());
v.UsePhone();
}
}
class PhoneUser
{
private IPhone _phone;
public PhoneUser(IPhone phone)
{
_phone = phone;
}
public void UsePhone()
{
_phone.Dail();
_phone.PickUp();
_phone.Send();
_phone.Receive();
}
}
interface IPhone
{
void Dail();
void PickUp();
void Send();
void Receive();
}
public class NokiaPhone : IPhone
{
public void Dail()
{
Console.WriteLine("Nokia calling...");
}
public void PickUp()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello!This is Tim!");
}
public void Receive()
{
Console.WriteLine("Nokia Message ring...");
}
public void Send()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
}
}
public class EricssonPhone : IPhone
{
public void Dail()
{
Console.WriteLine("Ericsson calling...");
}
public void PickUp()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello!This is Tim!");
}
public void Receive()
{
Console.WriteLine("Ericsson Message ring...");
}
public void Send()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
}
}
}
依赖反转,测试单元
namespace InterFaceExample
{
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupply());
Console.WriteLine(fan.Work());
}
}
public interface IPowerSupply
{
int GetPower();
}
public class PowerSupply:IPowerSupply
{
public int GetPower()
{
return 100;
}
}
public class DeskFan
{
private IPowerSupply _powerSupply;
public DeskFan(IPowerSupply powerSupply)
{
_powerSupply = powerSupply;
}
public string Work()
{
int power = _powerSupply.GetPower();
if (power <= 0)
{
return "Won't work!";
}
else if (power < 100)
{
return "Slow!";
}else if (power < 200)
{
return "Work fine!";
}
else
{
return "Warning";
}
}
}
}
*依赖反转在测试单元中的应用:
namespace InterfaceExample.Tests
{
public class DeskfanTest
{
[Fact]//测试case
public void PowerLowerThanZero ()
{
var fan = new DeskFan(new PowerSupplyLowerThanZero());
var expected = "Won't work!";
var actual = fan.Work();
Assert.Equal(expected, actual);
}
}
class PowerSupplyLowerThanZero : IPowerSupply
{
public int GetPower()
{
return 0;
}
}
}
*使用Moq进行单元测试:
namespace InterfaceExample.Tests
{
public class DeskfanTest
{
[Fact]//测试case
public void PowerLowerThanZero ()
{
var mock = new Mock<IPowerSupply>();
mock.Setup(ps => ps.GetPower()).Returns(() => 0);
var fan = new DeskFan(mock.Object);
var expected = "Won't work!";
var actual = fan.Work();
Assert.Equal(expected, actual);
}
}
}
接口隔离
接口隔离原则示例1:
Diver类只关注Run()方法,不关注Fire()方法
namespace ISPExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Driver driver = new Driver(new HeavyTank());
driver.Drive();
}
}
class Driver
{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle)
{
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive()
{
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Run();
}
class Car:IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class Tunck:IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tunck is running");
}
}
interface IWeapon
{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank:IWeapon,IVehicle
{
}
class LightTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!");
}
}
class MediumTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!");
}
}
class HeavyTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!!!!");
}
}
}
接口隔离原则示例2:
namespace ISPExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] num1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
ArrayList num2 = new ArrayList { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
var num3 = new ReadOnlyCollection(num1);
Console.WriteLine(Sum(num1));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(num2));
Console.WriteLine(Sum(num3));
}
//若使用ICollection(:IEnumerable)接口 则传入的太胖 只用得着迭代,调用者绝不多要
static int Sum(IEnumerable nums)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var n in nums)
{
sum += (int)n;
}
return sum;
}
}
class ReadOnlyCollection : IEnumerable//自定义迭代器 继承Ienumerable接口
{
private int[] _array;
public ReadOnlyCollection(int[] array)
{
_array = array;
}
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
return new Enumerator(this);
}
public class Enumerator : IEnumerator
{
private ReadOnlyCollection _collection;
private int _head;
public Enumerator(ReadOnlyCollection collection)
{
_collection = collection;
_head = -1;
}
public object Current
{
get
{
object o = _collection._array[_head];
return o;
}
}
public bool MoveNext()
{
if (++_head < _collection._array.Length)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
public void Reset()
{
_head = -1;
}
}
}
}
接口隔离原则示例2:
接口的显示实现;只有把WarmKiller类的实例当作IKiller类型的实例来用的时候,kill()方法才能被调用
namespace ISPExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IKiller killer = new WarmKiller();
killer.kill();
var wk = killer as WarmKiller;
wk.love();
}
}
interface IGentleman
{
void love();
}
interface IKiller
{
void kill();
}
class WarmKiller : IGentleman, IKiller
{
public void love()
{
Console.WriteLine("I will love you forever");
}
void IKiller.kill()
{
Console.WriteLine("Let me kill the enemy");
}
}
}
反射与依赖注入
- 反射:以不变应万变(更松的耦合),给一个对象,不用new操作符,也不知道所给对象是什么静态类型的情况下,能创建出一个同类型的变量
- 反射与接口的结合
- 反射与特性的结合
- 依赖注入:此ID非彼ID,但没有彼ID就没有此ID
*反射简单示例
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace ISPExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ITank tank = new HeavyTank();
var t = tank.GetType();
object o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
MethodInfo FireMI = t.GetMethod("Fire");
MethodInfo RunMI = t.GetMethod("Run");
FireMI.Invoke(o, null);
RunMI.Invoke(o, null);
}
}
class Driver
{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle)
{
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive()
{
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Run();
}
class Car : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class Tunck : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tunck is running");
}
}
interface IWeapon
{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank : IWeapon, IVehicle
{
}
class LightTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!");
}
}
class MediumTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!");
}
}
class HeavyTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!!!!");
}
}
}
*一般使用封装好的反射:依赖注入示例
namespace ISPExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//分割线以上是一次性的注册,在程序启动时注册
var sc = new ServiceCollection();
sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank), typeof(HeavyTank));//将后者注入前者
sc.AddScoped(typeof(IVehicle), typeof(Car));
sc.AddScoped<Driver>();
var sp = sc.BuildServiceProvider();
//=================================================
//分割线以下代表在程序其他地方只要能看到ServiceProvider的地方,都可以这么用,不再用new
ITank tank = sp.GetService<ITank>();
tank.Fire();
tank.Run();
var driver = sp.GetService<Driver>();
driver.Drive();
//优点:在程序大量引用了ITank实例后,系统升级后若Itank对应的实现类不再是HeavyTank
//而是LightTank只需要修改sc.AddScoped(typeof(ITank), typeof(LightTank));
}
}
class Driver
{
private IVehicle _vehicle;
public Driver(IVehicle vehicle)
{
_vehicle = vehicle;
}
public void Drive()
{
_vehicle.Run();
}
}
interface IVehicle
{
void Run();
}
class Car : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Car is running");
}
}
class Tunck : IVehicle
{
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("Tunck is running");
}
}
interface IWeapon
{
void Fire();
}
interface ITank : IWeapon, IVehicle
{
}
class LightTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!");
}
}
class MediumTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!");
}
}
class HeavyTank : ITank
{
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("BOOM!!!!!!");
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("KaKaKa!!!!!!");
}
}
}
*用反射追求更松的耦合:“婴儿车”示例
namespace BabyStoller.App
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var folder = Path.Combine(Environment.CurrentDirectory, "Animals");
var files = Directory.GetFiles(folder);
var animalTypes = new List<Type>();
foreach (var file in files)
{
var assembly = AssemblyLoadContext.Default.LoadFromAssemblyPath(file);
var types = assembly.GetTypes();
foreach (var t in types)
{
if (t.GetMethod("Voice") != null)
{
animalTypes.Add(t);
}
}
}
while (true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < animalTypes.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i + 1}.{animalTypes[i].Name}");
}
Console.WriteLine("=============================");
Console.WriteLine("Please choose animal:");
int index = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (index > animalTypes.Count || index < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("NO such an animal,Try again!");
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("How many times?");
int times = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
var t = animalTypes[index - 1];
var m = t.GetMethod("Voice");
var o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
m.Invoke(o, new object[] { times });
}
}
}
}
添加4个动物库:(cat,sheep,cow也如下)
namespace Animals.lib2
{
public class Dog
{
public void Voice(int times)
{
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Woof!");
}
}
}
}
将生成好的2个dll库放进创建好的Animals文件夹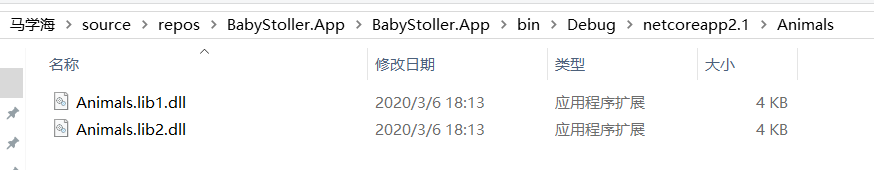
运行结果: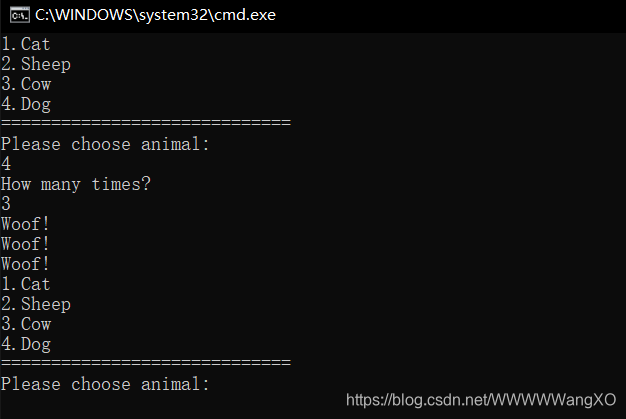
创建对外SDK(IAnimal接口和UnfinishedAttribute类)
namespace BabyStroller.SDK
{
public interface IAnimal
{
void Voice(int times);
}
}
namespace BabyStroller.SDK
{
public class UnfinishedAttribute : Attribute
{
}
}
Build之后回到Animal库中Add Reference到之前的两个库中,继承IAnimal接口
namespace Animals.lib2
{
public class Dog:IAnimal
{
public void Voice(int times)
{
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("Woof!");
}
}
}
}
将更新后的库重新Build,放到Animals文件夹替换之前的库,对原BabyStoller项目进行修改
namespace BabyStoller.App
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var folder = Path.Combine(Environment.CurrentDirectory, "Animals");
var files = Directory.GetFiles(folder);
var animalTypes = new List<Type>();
foreach (var file in files)
{
var assembly = AssemblyLoadContext.Default.LoadFromAssemblyPath(file);
var types = assembly.GetTypes();
foreach (var t in types)
{
if (t.GetInterfaces().Contains(typeof(IAnimal)))
{
var isUnfinished = t.GetCustomAttributes(false).Any(a => a.GetType() == typeof(UnfinishedAttribute));
if (isUnfinished) continue;
animalTypes.Add(t);
}
}
}
while (true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < animalTypes.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{i + 1}.{animalTypes[i].Name}");
}
Console.WriteLine("=============================");
Console.WriteLine("Please choose animal:");
int index = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (index > animalTypes.Count || index < 1)
{
Console.WriteLine("NO such an animal,Try again!");
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine("How many times?");
int times = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
var t = animalTypes[index - 1];
var m = t.GetMethod("Voice");
var o = Activator.CreateInstance(t);
var a = o as IAnimal;
a.Voice(times);
}
}
}
}
来源:CSDN
作者:WWWWWangXO
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/WWWWWangXO/article/details/104669345