前言
游戏开发中,经常在玩家进入游戏的时候进行必要的信息初始化,往往这个初始化信息数据包是相对来说还是比较大的,一般在30-40kb左右,还是有必要进行压缩一下再发送消息,刚好前段时间看过,里面列举了一些常用的压缩算法,如下图所示: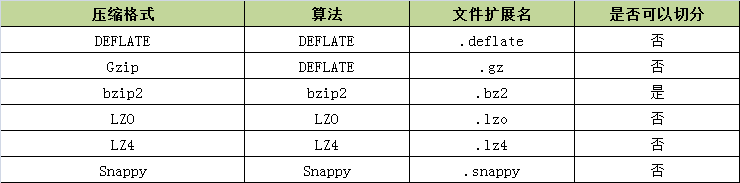
是否可切分表示是否可以搜索数据流的任意位置并进一步往下读取数据,这项功能在Hadoop的MapReduce中尤其适合。
下面对这几种压缩格式进行简单的介绍,并进行压力测试,进行性能比较
DEFLATE
DEFLATE是同时使用了LZ77算法与哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding)的一个无损数据压缩算法,DEFLATE压缩与解压的源代码可以在自由、通用的压缩库zlib上找到,zlib官网:http://www.zlib.net/
jdk中对zlib压缩库提供了支持,压缩类Deflater和解压类Inflater,Deflater和Inflater都提供了native方法
private native int deflateBytes(long addr, byte[] b, int off, int len,
int flush); private native int inflateBytes(long addr, byte[] b, int off, int len)
throws DataFormatException;所有可以直接使用jdk提供的压缩类Deflater和解压类Inflater,代码如下:
public static byte[] compress(byte input[]) {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Deflater compressor = new Deflater(1);
try {
compressor.setInput(input);
compressor.finish();
final byte[] buf = new byte[2048];
while (!compressor.finished()) {
int count = compressor.deflate(buf);
bos.write(buf, 0, count);
}
} finally {
compressor.end();
}
return bos.toByteArray();
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] input) throws DataFormatException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Inflater decompressor = new Inflater();
try {
decompressor.setInput(input);
final byte[] buf = new byte[2048];
while (!decompressor.finished()) {
int count = decompressor.inflate(buf);
bos.write(buf, 0, count);
}
} finally {
decompressor.end();
}
return bos.toByteArray();
}可以指定算法的压缩级别,这样你可以在压缩时间和输出文件大小上进行平衡。可选的级别有0(不压缩),以及1(快速压缩)到9(慢速压缩),这里使用的是以速度为优先。
gzip
gzip的实现算法还是deflate,只是在deflate格式上增加了文件头和文件尾,同样jdk也对gzip提供了支持,分别是GZIPOutputStream和GZIPInputStream类,同样可以发现GZIPOutputStream是继承于DeflaterOutputStream的,GZIPInputStream继承于InflaterInputStream,并且可以在源码中发现writeHeader和writeTrailer方法:
private void writeHeader() throws IOException {
......
}
private void writeTrailer(byte[] buf, int offset) throws IOException {
......
}具体的代码实现如下:
public static byte[] compress(byte srcBytes[]) {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
GZIPOutputStream gzip;
try {
gzip = new GZIPOutputStream(out);
gzip.write(srcBytes);
gzip.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return out.toByteArray();
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
try {
GZIPInputStream ungzip = new GZIPInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int n;
while ((n = ungzip.read(buffer)) >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return out.toByteArray();
}bzip2
bzip2是Julian Seward开发并按照自由软件/开源软件协议发布的数据压缩算法及程序。Seward在1996年7月第一次公开发布了bzip2 0.15版,在随后几年中这个压缩工具稳定性得到改善并且日渐流行,Seward在2000年晚些时候发布了1.0版。更多wikibzip2
bzip2比传统的gzip的压缩效率更高,但是它的压缩速度较慢。
jdk中没有对bzip2实现,但是在commons-compress中进行了实现,maven引入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-compress</artifactId>
<version>1.12</version>
</dependency>具体的代码实现如下:
public static byte[] compress(byte srcBytes[]) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
BZip2CompressorOutputStream bcos = new BZip2CompressorOutputStream(out);
bcos.write(srcBytes);
bcos.close();
return out.toByteArray();
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
try {
BZip2CompressorInputStream ungzip = new BZip2CompressorInputStream(
in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
int n;
while ((n = ungzip.read(buffer)) >= 0) {
out.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return out.toByteArray();
}下面的介绍的lzo,lz4以及snappy这3中压缩算法,均已压缩速度为优先,但压缩效率稍逊一筹。
lzo
LZO是致力于解压速度的一种数据压缩算法,LZO是Lempel-Ziv-Oberhumer的缩写。这个算法是无损算法,更多wikiLZO
需要引入第三方库,maven引入:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.anarres.lzo</groupId>
<artifactId>lzo-core</artifactId>
<version>1.0.5</version>
</dependency>具体实现代码:
public static byte[] compress(byte srcBytes[]) throws IOException {
LzoCompressor compressor = LzoLibrary.getInstance().newCompressor(
LzoAlgorithm.LZO1X, null);
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
LzoOutputStream cs = new LzoOutputStream(os, compressor);
cs.write(srcBytes);
cs.close();
return os.toByteArray();
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
LzoDecompressor decompressor = LzoLibrary.getInstance()
.newDecompressor(LzoAlgorithm.LZO1X, null);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ByteArrayInputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
LzoInputStream us = new LzoInputStream(is, decompressor);
int count;
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
while ((count = us.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
}lz4
LZ4是一种无损数据压缩算法,着重于压缩和解压缩速度更多wikilz4
maven引入第三方库:
<dependency>
<groupId>net.jpountz.lz4</groupId>
<artifactId>lz4</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>具体代码实现:
public static byte[] compress(byte srcBytes[]) throws IOException {
LZ4Factory factory = LZ4Factory.fastestInstance();
ByteArrayOutputStream byteOutput = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
LZ4Compressor compressor = factory.fastCompressor();
LZ4BlockOutputStream compressedOutput = new LZ4BlockOutputStream(
byteOutput, 2048, compressor);
compressedOutput.write(srcBytes);
compressedOutput.close();
return byteOutput.toByteArray();
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
LZ4Factory factory = LZ4Factory.fastestInstance();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
LZ4FastDecompressor decompresser = factory.fastDecompressor();
LZ4BlockInputStream lzis = new LZ4BlockInputStream(
new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes), decompresser);
int count;
byte[] buffer = new byte[2048];
while ((count = lzis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
lzis.close();
return baos.toByteArray();
}snappy
Snappy(以前称Zippy)是Google基于LZ77的思路用C++语言编写的快速数据压缩与解压程序库,并在2011年开源。它的目标并非最大压缩率或与其他压缩程序库的兼容性,而是非常高的速度和合理的压缩率。更多wikisnappy
maven引入第三方库:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.xerial.snappy</groupId>
<artifactId>snappy-java</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2.6</version>
</dependency>具体代码实现:
public static byte[] compress(byte srcBytes[]) throws IOException {
return Snappy.compress(srcBytes);
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) throws IOException {
return Snappy.uncompress(bytes);
}压力测试
以下对35kb玩家数据进行压缩和解压测试,相对来说35kb数据还是很小量的数据,所有以下测试结果只是针对指定的数据量区间进行测试的结果,并不能说明哪种压缩算法好与不好。
测试环境:
jdk:1.7.0_79
cpu:i5-4570@3.20GHz 4核
memory:4G
对35kb数据进行2000次压缩和解压缩测试,测试代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("player.dat"));
FileChannel channel = fis.getChannel();
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) channel.size());
channel.read(bb);
byte[] beforeBytes = bb.array();
int times = 2000;
System.out.println("压缩前大小:" + beforeBytes.length + " bytes");
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] afterBytes = null;
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
afterBytes = GZIPUtil.compress(beforeBytes);
}
long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("压缩后大小:" + afterBytes.length + " bytes");
System.out.println("压缩次数:" + times + ",时间:" + (endTime1 - startTime1)
+ "ms");
byte[] resultBytes = null;
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
resultBytes = GZIPUtil.uncompress(afterBytes);
}
System.out.println("解压缩后大小:" + resultBytes.length + " bytes");
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("解压缩次数:" + times + ",时间:" + (endTime2 - startTime2)
+ "ms");
}代码中的GZIPUtil根据不同的算法进行替换,测试结果如下图所示:

分别对压缩前大小、压缩后大小、压缩时间、解压缩时间、cpu高峰进行了统计
总结
从结果来看,deflate、gzip和bzip2更关注压缩率,压缩和解压缩时间会更长;lzo,lz4以及snappy这3中压缩算法,均已压缩速度为优先,压缩率会稍逊一筹;lzo,lz4以及snappy在cpu高峰更低一点。因为在容忍的压缩率之内,我们更加关注压缩和解压缩时间,以及cpu使用,所有最终使用了snappy,不难发现snappy在压缩和解压缩时间以及cpu高峰都是最低的,并且在压力率上也没有太多的劣势。
个人博客:codingo.xyz
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/159239/blog/805427