1.安装ansible eple源
cat <<eof>>/etc/yum.repos.d/my.repo
[epel]
name=epel
baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/epel/7Server/x86_64/
enable=1
gpgcheck=0
eof
yum -y install ansible 安装2.安装ansible 常用帮助
ansible-doc -h #列出相关榜示
[root@4cd65df9495a /]# ansible-doc -l | grep yum#用于列出某个模块
[root@4cd65df9495a /]# ansible-doc -s yum #获取参数
-C #不对远程主机做出一些改变,而是预测某些可能发生的改变
-f #指定并行处理的进程数量,默认为5个
--list-hosts#不会执行任何操作,而是列出匹配到的主机列表
-m#指定要执行的模块名,默认的模块为"command"
-k #密码
--syntax-check #检查语法3.andible.cfg配置参数
Ansible有很多配置参数,以下是几个默认的配置参数:
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts#inventory的位子
library = /usr/share/my_modules/#模块的目录
forks = 5
sudo_user = root
remote_port = 22
host_key_checking = False#设置是否检查SSH主机的密钥
timeout = 20#设置SSH连接的超时间隔,单位是秒
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log4.设置互信任配置
略
5.inventory 用于定义ansible要管理的主机
cat -n /etc/ansible/hosts
192.168.100.59:22
192.168.100.60 ansible_ssh_pass='123456' ansible_ssh_port=22
[nginx]#分组
192.168.100.5[7:9]
[nginx:vars]#vars主机变量
ansible_ssh_pass='123456'
[webservers:children]#创建webservers组里面包含nginx组
nginx
ansible_ssh_user: ssh登录的用户名。默认为root。
ansible_ssh_pass: ssh登录远程用户时的认证密码。
ansible_ssh_private_key_file: ssh登录远程用户时的认证私钥。(?)6.ansible 常用模块总结
command和shell
默认ansible使用的模块是command,即可以执行一些shell命令。shell和command的用法基本一样
command不能解析变量(如$HOME)和某些操作符("<", ">", "|", ";"以及"&")
ansible-doc -s shell
- name: Execute commands in nodes.
action: shell
chdir # 在执行命令前,先cd到指定的目录下
creates # 用于判断命令是否要执行。如果指定的文件(可以使用通配符)存在,则不执行。
removes # 用于判断命令是否要执行。如果指定的文件(可以使用通配符)不存在,则不执行。案例
ansible db -m shell -a "echo '123456' | passwd --stdin alex"#设置alex密码
ansible db -m shell -a "creates=/tmp pwd"#tmp存在所以跳过
ansible db -m shell -a "creates=/tmp2 pwd"#tmp不存在执行
ansible db -m shell -a "removes=/tmp2 pwd"#不存在 不会执行
ansible db -m shell -a "removes=/tmp pwd"#存在执行script 执行本地文件
- chdir 切换目录,编译安装
- creates 判断是否存在,如果存在,就不执行被控机
- removes 判断是否存在,如果存在,就执行案例
ansible db -m script -a "1.sh" #执行本地文件
ansible db -m script -a "creates=/root/11.sh /root/1.sh"#判断被控机上是否存在11.sh 不存在就执行
ansible db -m script -a "removes=/root/1.sh /root/1.sh"#判断被控制上是否存在 存在就执行copy 将本地文件复制远程机器
- backup#创建一个备份文件 以时间戳几位
- content#直接往里面写内容
- scr#源地址
- dest#目标地址
- owner#属主
- group#属组
- follow=[yes|no] # 是否追踪到链接的源文件
- mode#权限案例
ansible db -m copy -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/f"#把fstabl复制远控主机/tmp/f 多次执行不改变 不会覆盖
ansible db -m copy -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/f backup=yes"#以文件名加时间戳的方式 备份远控主机文件
ansible db -m copy -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/f backup=yes owner=sshd group=sshd mode=644"#设置下属主权限
ansible db -m copy -a "src=/etc/init.d dest=/tmp"#复制整个目录到tmp 没加/就是整个目录
ansible db -m copy -a "src=/etc/init.d/ dest=/tmp"#复制整个目录下所有的文件到tmp目录下
ansible db -m copy -a "content='11111' dest=/tmp/b"#往被控端写内容 会覆盖
file管理文件、目录的属性,也可以创建文件或目录。
- path #指定待操作的文件,可使用别名'dest'或'name'来替代path
- ower#属主
- group#属组
- mode#权限
- src #创建链接时使用,指定链接的源文件
- state # directory:如果目录不存在则递归创建
# file:文件不存在时,不会被创建(默认值)
# touch:touch由path指定的文件,即创建一个新文件,或修改其mtime和atime
# link:修改或创建软链接
# hard:修改或创建硬链接
# absent:目录和其中的文件会被递归删除,文件或链接将取消链接状态案例
ansible db -m file -a "path=/tmp/alex1 state=directory owner=xiaoqiang"#创建alex目录 指定属主
ansible db -m file -a "path=/tmp/alex1.txt state=touch"#创建文件
ansible db -m file -a "path=/tmp/yum src=/var/log/yum.log state=link"#创建软链接 链接是被控制自己的
ansible db -m file -a "path=/tmp/yum state=absent"#删除被控机软链接fetch拉取文件到本地
从远程主机将文件拉取到本地端,存储时使用主机名作为目录树,且只能拉取文件不能拉取目录。
- dest 目标地址
- src 源地址ansible db -m fetch -a "src=/var/log/yum.log dest=/tmp"#拉取被控主机yum.log到tmp并以主机ip地址或者主机名为目录,并且保留了原来的目录结构yum模块安装
- name#包名
- state
install
remove
disablerepo #禁用某个源
enablerepo #启用某个源案例
yum grouplist #查包组信息
ansible db -m yum -a "name=dos2unix"#安装doc2unix
ansible db -m yum -a "name=dos2unix,nginx"#安装多个包
ansible db-m yum -a "name='@Development Tools'"#安装组
ansible db -m yum -a "name=nginx state=absent" #卸载
[root@7065dc05e37c tmp]# rpm -q nginx
nginx-1.12.2-2.el7.x86_64
pip模块安装
pip freeze > a.txt #将本地环境导出
pip install -r a.txt #安装所有的包
pip list #查看所有的包
pip uninstall flask #卸载
- cddir#切换目录
- name#包名
- requirements #导出的文件
- virtualenv #虚拟环境ansible db -m pip -a "name=flask"service模块
ps -ef|grep nginx #查看进程
ss -tnlp # 查看端口信息
systemctl start nginx # centos7启动nginx
service nginx start # centos6启动nginx
systemctl enable nginx # centos7 开机自启动
chkconfig nginx on # centos6开机自启动案例
ansible web -m service -a 'name=nginx state=started' # 启动nginx
ansible web -m service -a 'name=nginx state=stopped' # 关闭nginx
ansible web -m service -a 'name=nginx state=started enabled=yes' # 设置开机自启动docker run --privileged -ti --name test1 centos /usr/sbin/init #如果用docker 需要加privileged 特权 据说7.2镜像已经解决了这个问题
cron计划任务
* * * * * job
分 时 日 月 周 任务
0 */2 * * * job 每隔两个小时
0 12,13 * * * job 12点和13点
0 12-17 * * * job 12点到17点
0 12-17/2 * * 1,3,6,0 周1,周3,周6,周7 12点到17点每隔两个小时
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/crontab
crontab -e # 编辑计划任务
crontab -l # 查看计划任务
crontab -r # 删除计划任务参数
- minute #分钟
- hour #小时
- day #天
- month #月
- weekday #周
- disabled #禁用crontab 表现形式加#
- name #名称
- user #用户例子
ansible db -m cron -a "minute=12 name=touchfile job='touch /tmp/xiaoqiang'"#每个小时12分执行 创建touch /tmp/xiaoqiang'
ansible db -m cron -a "name=touchfile state=absent"#删除
absible db -m cron -a "minute=12 name=touchfile2 job='touch /tmp/xiaoqiang.txt' disabled=yes"#注释user模块
用户:
管理员 root 0
普通用户
系统用户 不能登录 1-999 centos7 1-499 centos6
登录用户 可以登录 1000-65535 centos7 500-65535 centos6
用户组:
管理员组 root 0
系统用户组 1-999 centos7 1-499 centos6
登录用户组 1000-65535 centos7 500-65535 centos6
[root@localhost ~]# useradd -h #查看useradd的参数
-d #指定用户的家目录
-g #指定用户的组
-G #执行用户的附加组
-s #指定登录后使用的shell
-r #创建一个系统用户
useradd -r wusir #创建系统用户, 从999倒序
useradd -s /sbin/nologin alexsb #创建的是普通用户,从1000开始升序
useradd -d /opt/alexsb2 alexsb2 #创建用户时指定用户的家目录
useradd -u 3000 alexsb6 # 创建用户并指定用户的uid
userdel alex #删除用户
userdel -r alexsb2 #删除用户并删除用户的家目录
groupadd yuchao #创建用户组
groupdel yuchao #删除用户组- group #组
- groups#附加组
- home#家目录
- name#用户名
- password#密码
- remove#当remove=yes 删除用户且删除用户家目录
- shell#用户登陆后使用的shell
- system#创建一个系统用户
- uid#用来指定用户的id
- state#状态例子
ansible db -m user -a "name=alex10 shell=/sbin/nologin home=/opt/alex10 uid=3000 groups=root"#创建一个用户 指定 home附加组和uid
ansible db -m user -a 'name=alex10 state=absent remove=yes'#删除一个用户 并删除家目录
ansible db -m user -a 'name=alex10 state=absent'#删除用户不删除家目录group模块
groupadd
-g 设置id
-r 系统组
超级管理员组 root 0
普通组
系统组 1-999 centos7 1-499 centos6 从大到小
登录用户组 1000-65535 centos7 500-65535 centos6
从小到大
查看
tail /etc/group- git #组的id
- name#组名
- system#系统组例子
ansible db -m group -a 'name=wulaoshi system=yes' #创建系统组
ansible db -m group -a 'name=wulaoshi state=absent' # 删除组playbook
yaml 或yml后缀结尾
json
- 字典 key:value
- 列表 [] \-
```shell
- alex
- wusir
- yantao
- yuchao
[alex,wusir,yantao,yuchao]
-C, --check #白跑,执行但是不会有结果
--list-hosts #列出符合的主机
-f FORKS, --forks=FORKS #做并发
--syntax-check #检查语法
ansible-playbook --syntax-check
-k, --ask-pass #输入密码
- hosts: web #主机列表
tasks: #任务
- name: creategroup #任务名称
group: name=alex10 #模块名:参数
- name: cretaeuser #任务名称
user: name=wusir10 #模块名:参数
单个playbook
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: createuser
user: name=alex20 home=/opt/alex20 uid=4000多个playbook
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: createuser
user: name=alex20 home=/opt/alex20 uid=4000
- name: copyfile
copy: src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/fs
幂等性 没更改不管执行多少次,得到的结果都是一样的
传参第一种方式
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: create{{user}}
user: name={{user}}
ansible-playbook -e user=wusir20 p3.yml传参第二种方式
在配置文件中
[web]
192.168.226.[101:102] user=alex30
192.168.226.104 user=alex100传参第三种方式
在配置文件中
[web:vars]#表示组的参数
user=alex31传参第四种方式
- hosts: web
vars:
- user: alex32
tasks:
- name: create{{user}}
user: name={{user}}传参第五种方式
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: yum
yum: name=bc
- name: sum
shell: echo 11+22|bc
register: user
- name: echo
shell: echo {{user.stdout}} > /tmp/echo.txt
- name: create{{user.stdout}}
user: name=alex{{user.stdout}}优先级
-e > playbook > hosts
setup 收集模块
ansible db -m setup
ansible db -m setup -a 'filter="*ipv4*"' #过滤某个
ansible_all_ipv4_addresses #所有的ipv4地址
ansible_all_ipv6_addresses #所有的ipv6地址
ansible_architecture #系统的架构
ansible_date_time #系统时间
ansible_default_ipv4 #默认的ipv4地址
address ip地址
alias 网卡名称
broadcast 广播地址
gateway 网关
netmask 子网掩码
network 网段
ansible_default_ipv6 #默认的ipv6地址
ansible_device_links #系统的磁盘信息
ansible_distribution #系统名称
ansible_distribution_file_variety #系统的基于公司
ansible_distribution_major_version #系统的主版本
ansible_distribution_version #系统的全部版本
ansible_dns #系统的dns 默认udp 端口53
ansible_domain #系统的域 ldap
ipv4 #ipv4地址
ansible_env #系统的环境
ansible_fqdn #系统的完整主机名
ansible_hostname #系统的简写主机名
ansible_kernel #系统的内核版本
ansible_machine #系统的架构
ansible_memtotal_mb #系统的内存
ansible_memory_mb #系统的内存使用情况
ansible_mounts #系统的挂载信息
ansible_os_family #系统家族
ansible_pkg_mgr #系统的包管理工具
ansible_processor #系统的cpu
ansible_processor_cores #每颗cpu的核数
ansible_processor_count #cpu的颗数
ansible_processor_vcpus #cpu的个数=cpu的颗数*每颗cpu的核数
ansible_python #系统python信息
ansible_python_version #系统python的版本
ansible_system #系统名字tags 单独执行某一条指令
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: install
yum: name=redis
- name: copyfile
copy: dest=/etc/redis.conf src=/etc/redis.conf
tags: copy
- name: start
service: name=redis state=started
ansible-playbook -t copy p7.yml #只执行copyhandlers 触发
- hosts: db
tasks:
- name : install
yum : name=redis
notify: restart
handlers:
- name : restart#此name名称和notify后面的名称保持一致
service: name=redis state=startedtemplate
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: installredis
yum: name=redis
- name: copyfile
template: src=/etc/redis.conf dest=/etc/redis.conf
- name: start
service: name=redis state=started
#在控制端conf中 吧bind修改成 以下
配置文件: bind {{ ansible_default_ipv4.address }}when 条件判断
- hosts: db
tasks:
- name: createfile
copy: content='111111111111' dest=/tmp/a.txt
when: a=='1'
- name: createfile
copy: content='22222222222' dest=/tmp/a.txt
when: a=='2'
ansible-playbook -e 'a="3"' when.yml
- hosts: db
tasks:
- name: copy
copy: content='6666666666' dest=/tmp/6.txt
when: ansible_distribution_major_version=="6"
- name: copy
copy: content='777777777' dest=/tmp/7.txt
when: ansible_distribution_major_version=="7"with_items循环
- hosts: db
tasks:
- name: createuser
user: name={{item}}
with_items:
- alex50
- wuser50
- taibai50嵌套循环
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: crateuser
user: name={{item.name}} group={{item.group}}
with_items:
- {"name":alex52,"group":alex60}
- {"name":wusir52,"group":wusir60}
- {"name":taibai52,"group":taibai60}yuml定时任务
- hosts:db
tasks:
- name: cron
cron: hour=02 minute=30 job='tar zcf `date +%F`_etc.tar.gz /etc'nginx基于uwsgi部署Django回顾
1.安装nginx
yum install -y nginx(需要epel源)2.安装uwsgi
yum groupinstall "Development tools"
yum install zlib-devel bzip2-devel pcre-devel openssl-devel ncurses-devel sqlite-devel readline-devel tk-devel python-devel
pip install uwsgi3.安装django
pip install django==1.114.创建django项目
#/data 目录下创建mysite项目
django-admin startproject mysite5.创建app
python manage.py startapp app016.修改mysite/settings.py
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']7.关闭防火墙
关闭内置防火墙selinux
#暂时停止selinxu
setenforce 0
#永久关闭selinux
vi /etc/selinux/conf
修改如下行
SELINUX=enforcing
重启机器,使得selinx永久关闭关闭软件防火墙
iptables -F #清空防火墙规则
systemctl stop firewalld #关闭软件防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld #删除iptables的开机自启8、uwsgi配置文件
uwsgi支持ini、xml等多种配置方式,本文以 ini 为例, 在/etc/目录下新建uwsgi.ini,添加如下配置:
#三种配置方法可任选其中一种,选择哪种则将哪种的注释打开即可
[uwsgi]
http = 0.0.0.0:8000 #第一种配置方法
#socket = 0.0.0.0:8000 #第二种配置方法
#the local unix socket file than commnuincate to Nginx
#socket = /data/mysite/mysite.socket #第三种配置方法
# the base directory (full path)
chdir = /data/mysite
# Django's wsgi file
wsgi-file = mysite/wsgi.py
# maximum number of worker processes
processes = 4
#thread numbers startched in each worker process
threads = 2
# clear environment on exit
vacuum = true
daemonize = /data/mysite/uwsgi.log
py-autoreload=1第一种使用http = 0.0.0.0:8000,对应nginx配置文件如下:
vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
location / {
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
}第二种使用socket = 0.0.0.0:8000,对应nginx配置文件如下:
vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
location / {
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8000;
}第三种使用socket = /data/mysite/mysite.socke,对应nginx配置文件如下:
vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
location / {
include /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass unix:/data/mysite/mysite.socket;
}启动uwsgi
uwsgi --ini /etc/uwsgi.ini启动nginx
systemctl start nginxansible之roles
之前我们已经了解tasks和handlers,那怎么组织playbook才是最好的方式 用roles
Roles一个已知文件结构 自动加载vars files tasks handlers,基于roles对内容进行分组,使得我们可以与其他用户分享roles
文件夹里面是要创建的每一个角色,每一个角色一个文件夹
每一个角色里面都有tasks(必须的),templates,files,handlers,vars目录
#roles文件目录树参考如下:
--roles文件夹
--角色1文件夹
--templates
--files
--tasks
--main.yml
--vars
--handlers
--main.yml
--角色2文件夹
--templates
--files
--tasks
--main.yml
--vars
--handlers
--main.ymlroles/nginx/
├── files -- 静态文件
│ └── c.txt
├── handlers -- 触发的任务
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks -- 任务(必须的)
│ ├── copyfile.yml
│ ├── install.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ └── start.yml
├── templates -- 动态文件,需要传递参数
│ └── nginx.conf
└── vars -- 变量
└── main.yml
查找顺序
- 主文件看到roles,就回去roles目录下面找对应的目录
- 先去tasks目录里面找main.yml文件,如果遇到import_task则加载任务
- 如果遇到了template,则去templates目录里面找文件
- 如果遇到了copy,则去files目录里面找文件
- 如果遇到了变量,则去vars目录里面找main.yml文件
- 如果遇到了notify,则去handlers目录里面找main.yml文件
setenforce 0
还可以在剧本之前使用
wsgi是用nginx的 install.yml
ansible_playbooks
roles文件夹
nginx文件
files文件
handlers文件
main.yml
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=reloaded
tasks文件
install.yml
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: confignginx
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify:
- restart nginx
- name: start
service: name=nginx state=started
main.yml
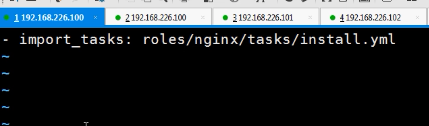
- import_tasks: install.yml
templates文件
nginx.conf.j2
vars文件
nginx.yml
练习 用roles 载安装nginx+uwsgi+mariadb + redis的目录框架
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4335502/blog/3549660

