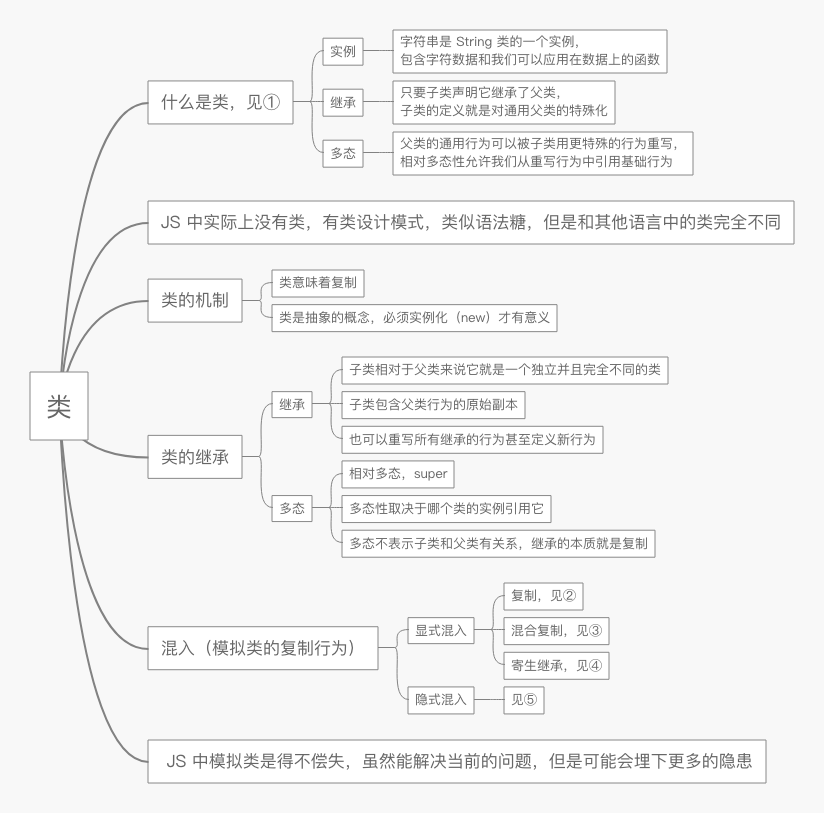
① 什么是类,描述了一种代码的组织结构,一种在软件中对真实世界中问题领域的建模方法
②
// 非常简单的 mixin() 例子
function mixin(sourceObj, targetObj) {
for (var key in sourceObj) {
// 只会在不存在的情况下复制
if (!(key in targetObj)) {
targetObj[key] = sourceObj[key]
}
}
return targetObj;
}
var Vehicle = {
engines: 1,
ignition: function() {
console.log('Turning on my engine.');
},
drive: function() {
this.ignition();
console.log('Steering and moving forward!');
}
}
var Car = mixin(Vehicle, {
wheel: 4,
drive: function(){
Vehicle.drive.call(this);
console.log('Rolling on all ' + this.wheel + ' wheels!');
}
})
③
// 另一种混入函数,可能有重写风险
function mixin(sourceObj, targetObj) {
for (var key in sourceObj) {
targetObj[key] = sourceObj[key];
}
return targetObj;
}
var Vehicle = {
// ...
}
// 首先创建一个空对象并把 Vehicle 对内容复制进去
var Car = mixin( Vehicle, {} );
// 然后把新内容复制到 Car 中
mixin({
wheels: 4,
drive: function() {
// ...
}
}, Car)
④
// 传统的 JS 类,Vehicle
function Vehicle() {
this.engines = 1;
}
Vehicle.prototype.ignition = function () {
console.log('Turning on my engine.');
}
Vehicle.prototype.drive = function () {
this.ignition();
console.log('Steering and moving forward!');
}
// 寄生类 Car
function Car() {
// 首先, Car 是一个 Vehicle
var car = new Vehicle();
// 接着我们对 Car 进行定制
car.wheels = 4;
// 保存到 Vehicle::drive() 的特殊引用
var vehDrive = car.drive;
// 重写 Vehicle::drive()
car.drive = function() {
vehDrive.call(this);
console.log('Rolling on all ' + this.wheels + ' wheels!');
}
return car;
}
var myCar = new Car()
myCar.drive();
⑤
var Something = {
cool: function () {
this.greeting = 'Hello World';
this.count = this.count ? this.count + 1 : 1;
}
}
Something.cool();
Something.greeting; // 'Hello World'
Something.count; // 1
var Another = {
cool: function() {
// 隐式把 Something 混入 Another
Something.cool.call(this);
}
};
Another.cool();
Another.greeting; // 'Hello World'
Another.count; // 1
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/wzndkj/p/12657605.html