2019-2020 Russia Team Open, High School Programming Contest (VKOSHP 19) D题
题意:给你一个N*M的图,起点是(1,1),终点是(N,M),然后每次我们可以选择往下走或者是往右走,每次你自己输入一种走法之后,测评机会告诉你,你有Q个点是走的正确的,并且告诉你这Q个点,然后要求的是你10次以内找到正确的答案,并且输出。
思路:
首先,突破点一定是这个10次操作和N和M都是小于等于1000的这个范围限制,这是硬生生的逼着我们往
 来想啊!
来想啊!
那么,我们不如这么走!
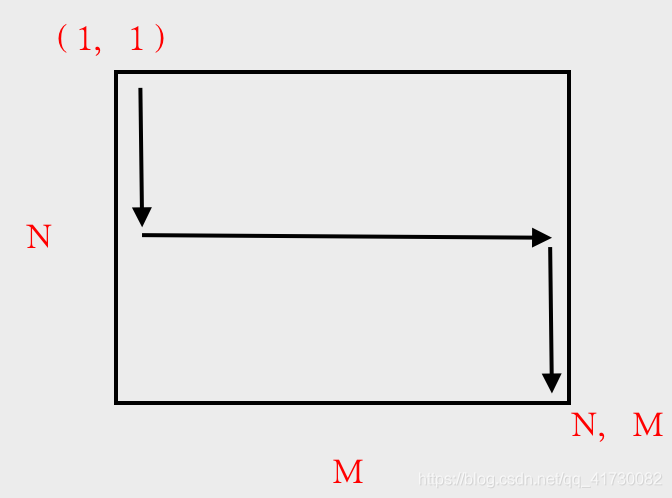
这样,有怎样的性质呢?
我们从
 走到
走到 ,再走到
,再走到 ,最后走到
,最后走到 的位置,我们是不是能保证至少有三个结点是正确的,因为中间的那条链肯定会被经过一次,左边链和右边链都会至少被经历过一次,并且被经历的点,在对应的链上是一定连续的。
的位置,我们是不是能保证至少有三个结点是正确的,因为中间的那条链肯定会被经过一次,左边链和右边链都会至少被经历过一次,并且被经历的点,在对应的链上是一定连续的。
我们假设红色链是正确的经过点:

那么,我们似乎就可以确定对应的位置关系了。
红色的,一定是正确的解,那么我们会围出来两个小方块,这两个小方块内的点的路线还是未知的。
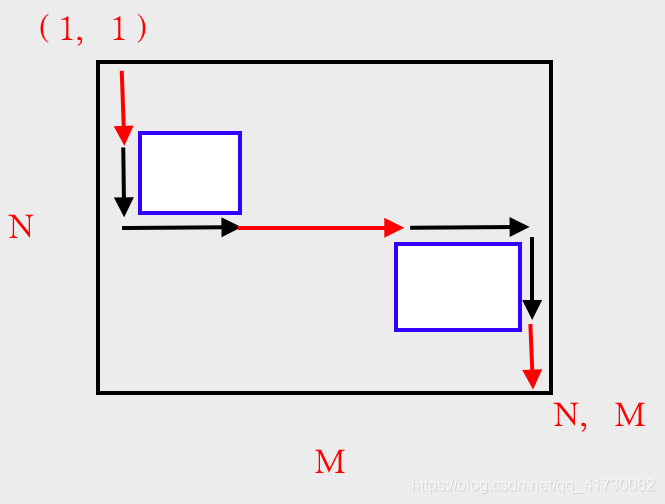
那么,我们不断的去查看这样的小方块不就是可以的嘛!
并且,这样每次都是一个二分的过程,我们能保证N能很快的降到长度1,然后如果现在一个矩形的长度为1,不就是代表只有唯一路径了嘛!所以只要唯一确定就是可以了的。
然后就是一些代码能力的考验了。
对了,交互问题要用cin和cout,给缓冲用的,不然会返回一个神奇的玩意儿。![]()
(我的代码其实不长,很多都是打注释的~QAQ)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <limits>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#define lowbit(x) ( x&(-x) )
#define pi 3.141592653589793
#define e 2.718281828459045
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define HalF (l + r)>>1
#define lsn rt<<1
#define rsn rt<<1|1
#define Lson lsn, l, mid
#define Rson rsn, mid+1, r
#define QL Lson, ql, qr
#define QR Rson, ql, qr
#define myself rt, l, r
#define MP(a, b) make_pair(a, b)
#define Min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c))
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int uit;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxN = 1e3 + 7;
int N, M;
bool mp[maxN][maxN] = {false};
struct node
{
int sx, sy, ex, ey;
node(int a=0, int b=0, int c=0, int d=0):sx(a), sy(b), ex(c), ey(d) {}
};
vector<node> vt, now;
char ch[30000];
int _Index, all_sx, all_sy;
void path_did(int las_ex, int las_ey, int now_sx, int now_sy)
{
while(las_ex ^ now_sx)
{
ch[++_Index] = 'D';
las_ex++;
}
while(las_ey ^ now_sy)
{
ch[++_Index] = 'R';
las_ey++;
}
}
void solve(int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey)
{
int mid_x = (sx + ex) / 2;
while(sx ^ mid_x)
{
ch[++_Index] = 'D';
sx++;
}
while(sy ^ ey)
{
ch[++_Index] = 'R';
sy++;
}
while(sx ^ ex)
{
ch[++_Index] = 'D';
sx++;
}
}
void update(int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey)
{
int mid_x = (sx + ex) / 2;
int x1 = sx, y1 = sy + 1, x2 = sx, y2 = sy + 1;
while(sx <= mid_x && mp[sx][sy])
{
x1 = sx; y1 = sy + 1;
sx++;
}
if(x1 == mid_x) //第一条链向下去都是勾勾点,可以进入转角
{
x1 = mid_x + 1; y1 = sy;
while(sy <= ey && mp[mid_x][sy])
{
x1 = mid_x + 1; y1 = sy;
sy++;
}
if(y1 == ey) //又可以进入下一个转角的情况
{
for(int i=x1; i<=ex; i++) mp[i][ey] = true;
return;
}
x2 = ex; y2 = ey - 1;
while(ex >= mid_x && mp[ex][ey])
{
x2 = ex; y2 = ey - 1;
ex--;
}
if(x1 == x2 || y1 == y2)
{
if(x1 == x2) for(int i=y1; i<=y2; i++) mp[x1][i] = true;
else for(int j=x1; j<=x2; j++) mp[j][y1] = true;
}
else vt.push_back(node(x1, y1, x2, y2));
}
else //第一条链就不可以进入转角,在转角之前就断了连续
{
for(int i=sy; i<=ey; i++)
{
if(mp[mid_x][i])
{
x2 = mid_x - 1;
y2 = i;
break;
}
}
if(x1 == x2 || y1 == y2)
{
if(x1 == x2) for(int i=y1; i<=y2; i++) mp[x1][i] = true;
else for(int j=x1; j<=x2; j++) mp[j][y1] = true;
}
else vt.push_back(node(x1, y1, x2, y2));
sx = mid_x; //接下去就是要看下面的再分裂是否也有这样的矩形块,起点块就是变成了中间链
for(int i=sy; i<=ey; i++)
{
if(mp[mid_x][i])
{
sy = i;
break;
}
}
x1 = mid_x + 1; y1 = sy;
while(sy <= ey && mp[mid_x][sy])
{
x1 = mid_x + 1; y1 = sy;
sy++;
}
if(y1 == ey) //又可以进入下一个转角的情况
{
for(int i=x1; i<=ex; i++) mp[i][ey] = true;
return;
}
x2 = ex; y2 = ey - 1;
while(ex >= mid_x && mp[ex][ey])
{
x2 = ex; y2 = ey - 1;
ex--;
}
if(x1 == x2 || y1 == y2)
{
if(x1 == x2) for(int i=y1; i<=y2; i++) mp[x1][i] = true;
else for(int j=x1; j<=x2; j++) mp[j][y1] = true;
}
else vt.push_back(node(x1, y1, x2, y2));
}
}
inline bool In_Map(int x, int y) { return x <= N && y <= M; }
inline void Prit()
{
// printf("! ");
cout << "! ";
int x = 1, y = 1;
while(x ^ N || y ^ M)
{
if(In_Map(x + 1, y) && mp[x + 1][y])
{
x++;
// printf("D");
cout << "D";
}
else
{
y = y + 1;
// printf("R");
cout << "R";
}
}
// printf("\n");
cout << endl;
}
inline void init()
{
_Index = 0;
vt.clear();
all_sx = 1; all_sy = 1;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
cin >> N >> M;
if(N == 1 || M == 1) //特殊的只有一条链的情况
{
// printf("! ");
cout << "! ";
int sx = 1, sy = 1;
while((sx ^ N) || (sy ^ M))
{
if(sx ^ N)
{
// printf("D");
cout << "D";
sx++;
}
else
{
// printf("R");
cout << "R";
sy++;
}
}
// printf("\n");
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
mp[1][1] = mp[N][M] = true;
int oper = 10, len;
vt.push_back(node(1, 1, N, M));
while(oper --) //此时我们需要进行询问
{
now = vt;
init();
len = (int)now.size();
for(int i=0, sx, sy, ex, ey; i<len; i++) //我们先把需要输出的路径给整出来
{
sx = now[i].sx; sy = now[i].sy;
ex = now[i].ex; ey = now[i].ey;
mp[sx][sy] = mp[ex][ey] = true;
path_did(all_sx, all_sy, sx, sy);
all_sx = ex; all_sy = ey;
solve(sx, sy, ex, ey);
}
path_did(all_sx, all_sy, N, M);
// printf("? ");
cout << "? ";
// for(int i=1; i<=_Index; i++) printf("%c", ch[i]);
for(int i=1; i<=_Index; i++) cout << ch[i];
// printf("\n");
cout << endl;
int Q; //scanf("%d", &Q);
cin >> Q;
for(int i=1, xx, yy; i<=Q; i++)
{
// scanf("%d%d", &xx, &yy);
cin >> xx >> yy;
mp[xx][yy] = true;
}
for(int i=0, sx, sy, ex, ey; i<len; i++) //现在,对每个子块进行处理,去划分更小的子块然后继续存入vt中
{
sx = now[i].sx; sy = now[i].sy;
ex = now[i].ex; ey = now[i].ey;
update(sx, sy, ex, ey);
}
len = (int)vt.size();
if(!len)
{
Prit();
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
来源:CSDN
作者:Andres_Lionel
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41730082/article/details/103486434