相关概念
缓冲区Buffer
Buffer是一个对象,它包含一些要写入或者要读出的数据。在NIO库中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的。缓冲区实质上是一个数组,最常用的缓冲区是ByteBuffer。通道 Channel
通道像一个自来水管一样,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入。其和流的区别是,流只能在一个方向上移动,而通道可以用于读、写或者二者同时进行。多路复用器 Selector
多路复用器提供选择就绪的任务的能力。简单来说Selector会不断的轮询注册在其上的Channel。
NIO服务端时序图

- 打开ServerSocketChannel,用于监听客户端的连接,它是所有客户端连接的父通道。
- 绑定监听的端口,设置为非阻塞模式
- 创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程
- 将ServerSocketChannel注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器Selector上,监听ACCEPT事件
- 多路复用器在线程run方法的无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key
- 多路复用器监听到有新的客户端接入,处理新的接入请求,完成TCP三次握手,建立物理链路。
- 设置客户端链路为非阻塞模式。
- 将新接入的客户端连接注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器上,监听读操作,读取客户端发送的网络消息。
- 异步读取客户端请求消息到缓冲区
- 对ByteBuffer进行编解码,如果有半包消息指针reset,继续读取后续的报文,将解码成功的消息封装成Task,投递到业务线程池中,进行业务逻辑编排。
- 将POJO对象encode成ByteBuffer,调用SocketChannel异步写入接口,将消息异步发送给客户端。
NIO改造后的TimeServer
public class TimeServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length >0){
try{
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
}catch (NumberFormatException e){
}
}
MultiplexerTimeServer timeServer = new MultiplexerTimeServer(port);
new Thread(timeServer).start();
}
}
其中,我们创建了一个MultiplexerTimeServer的多路复用类,它是一个独立的线程,负责轮询多路复用器Selector,其代码如下:
public class MultiplexerTimeServer implements Runnable{
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public MultiplexerTimeServer(int port){
try {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port),1024);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
public void stop(){
this.stop = true;
}
public void run() {
while (!stop){
try{
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (iterator.hasNext()){
key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
try {
handleInput(key);
}catch (Exception e){
if (key != null){
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isValid()){
if (key.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
if (key.isReadable()){
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes>0){
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
String curentTime = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(body)?new Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()
).toString():"BAD ORDER";
doWrite(sc,curentTime);
}else if(readBytes<0){
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
}
}
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel channel,String response) throws IOException {
if (response != null && response.trim().length()>0){
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
channel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
NIO客户端时序图
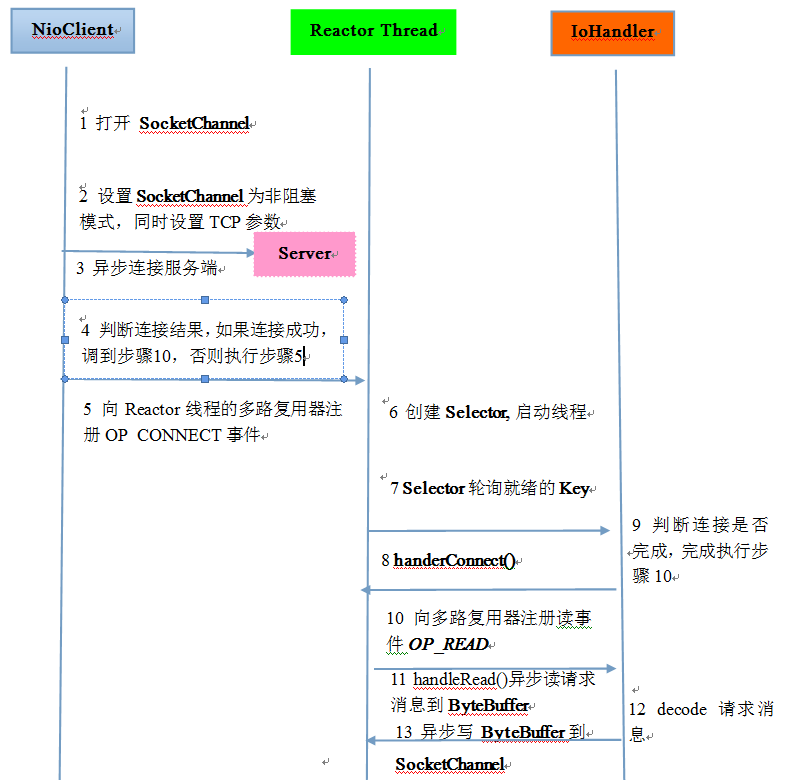
- 打开SocketChannel,绑定客户端本地地址
- 设置SocketChannel为非阻塞模式,同时设置客户端连接的TCP参数
- 异步连接服务端
- 判断是否连接成功,如果连接成功,则直接注册读状态未到多路复用器中。
- 向Reactor线程的多路复用器注册OP_CONNECT状态位,监听服务端的TCP ACK应答。
- 创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器启动线程
- 多路复用器在线程run方法的无限循环体中轮询准备就绪的Key
- 接受connect事件进行处理
- 判断连接成功,如果连接成功,注册读事件到多路复用器
- 注册读事件到多路复用器
- 异步读客户端请求到缓冲区
- 对ByteBuffer进行编解码,如果有半包消息接受缓冲区Reset,继续读取后续的报文,将解码成功的消息封装成Task,投递到业务线程池中,进行业务逻辑编排。
NIO改造后 TimeClient
public class TimeClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
}
new Thread(new TimeClientHandle("127.0.0.1",port)).start();
}
}
与之前不同的地方在于通过创建TimeClientHandle线程来处理异步连接和读写操作 ,因此下面我们看看TimeClientHandle的实现。
public class TimeClientHandle implements Runnable{
private String host;
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public TimeClientHandle(String host, int port) {
this.host = host == null ? "127.0.0.1":host;
this.port = port;
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
public void run() {
try {
doConnect();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
while (!stop){
try{
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()){
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try{
handleInput(key);
}catch (Exception e){
if (key != null){
key.cancel();
if (key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isValid()){
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (key.isConnectable()){
if (sc.finishConnect()){
sc.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(sc);
}else{
System.exit(1);
}
}
if (key.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0){
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(body);
this.stop = true;
}else if(readBytes < 0){
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}else{
}
}
}
}
private void doConnect() throws IOException {
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host,port))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(socketChannel);
}else{
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
private void doWrite(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
sc.write(writeBuffer);
if (!writeBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println("succeed");
}
}
}
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/junjiang3/p/10164513.html