Flask is a microframework for Python based on Werkzeug, Jinja 2 and good intentions.
我们的目标是通过Flask实现一个简单的web系统,系统需要用户登录,未登录用户无法访问授权页面,因此,我们定义页面如下:
- index.html默认首页,需要登录授权访问
- login.html登录页,输入用户名和密码
- error.html, 40X.html 错误页,显示错误信息
- detail.html详情页,需要登录授权访问
未使用Flask-Login模块进行会话管理时,我们可以通过简单的session控制来实现基本的授权访问控制
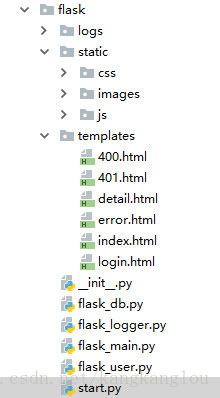
这是基本的代码组织结构:
- 前台页面登录页面代码如下:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>用户登录</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/styles.css') }}"/>
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='images/favicon.ico')}}"/>
</head>
<body>
<div class="htmleaf-container">
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="container">
<h1>Welcome</h1>
<form class="form" method="post" action="/" onsubmit="return doLogin();">
<input type="text" placeholder="Username" name="username" id="username">
<input type="password" placeholder="Password" name="password" id="password">
<button type="submit" id="login-button">Login</button>
</form>
</div>
<ul class="bg-bubbles">
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<script src="{{ url_for('static', filename='js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js') }} " type="text/javascript"></script>
<script>
function doLogin() {
var login = false;
$.ajax({
url: '/login',
data: "username=" + $("#username").val() + "&password=" + $("#password").val(),
type: 'POST',
contentType: 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
async: false,
success: function (d) {
var status = d.status;
if (status != undefined && status != '') {
if (status == "-1") {
alert("认证异常");
login = false;
} else {
login = true;
}
} else {
alert("用户名或密码错误!");
login = false;
}
}
});
return login;
}
</script>
<div style="text-align:center;margin:50px 0; font:normal 14px/24px 'MicroSoft YaHei';color:#000000">
<h1>管理后台</h1>
</div>
</body>注意,加载css和js的写法,通过url_for加载static目录下对应的文件
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/styles.css') }}"/>
<script src="{{ url_for('static', filename='js/jquery-2.1.1.min.js') }} " type="text/javascript"></script>- 路由由方法login:
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
logger.debug("login post method")
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
if username == 'admin' and password == 'admin123':
session['username'] = username
session['password'] = password
resp = make_response(render_template('index.html', name=username))
resp.set_cookie('username', username)
# return resp
return jsonify({'status': '0', 'errmsg': '登录成功!'})
else:
# return redirect(url_for('error'))
return jsonify({'status': '-1', 'errmsg': '用户名或密码错误!'})
logger.debug("login get method")
return render_template('login.html')
注意:为了简单期间,我们将用户名和密码直接限定为固定值,后续,我们会有专门章节介绍数据库读取方式
if username == 'admin' and password == 'admin123':- 路由方法index
通过session判断用户是否登录:
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def index():
logger.debug("index page")
logger.debug("cookie name %s" % request.cookies.get('username'))
if 'username' in session:
logger.debug("login user is %s" % flask_login.current_user)
logger.debug('Logged in as %s' % escape(session['username']))
return render_template('index.html', name=session['username'])
else:
logger.debug("you are not logged in")
return render_template('login.html')至此,我们完成了一个简单的web应用,后续,我们介绍如何使用Flask-Login进行会话管理
来源:CSDN
作者:__HelloWorld__
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/kangkanglou/article/details/79006501