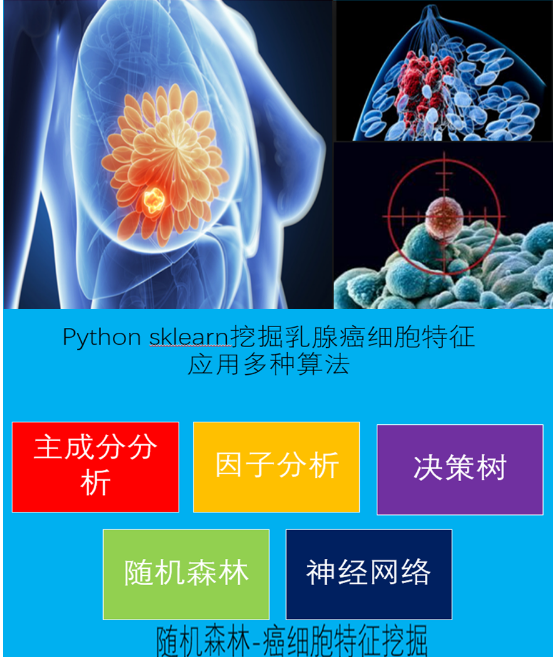
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频,包含数据预处理scale)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
数据预处理方法包括scale,normalization,Binarizer
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Apr 14 09:09:41 2018
@author:Toby
standardScaler==features with a mean=0 and variance=1
minMaxScaler==features in a 0 to 1 range
normalizer==feature vector to a euclidean length=1
normalization
bring the values of each feature vector on a common scale
L1-least absolute deviations-sum of absolute values(on each row)=1;it is insensitive to outliers
L2-Least squares-sum of squares(on each row)=1;takes outliers in consideration during traing
"""
from sklearn import preprocessing
import numpy as np
data=np.array([[2.2,5.9,-1.8],[5.4,-3.2,-5.1],[-1.9,4.2,3.2]])
bindata=preprocessing.Binarizer(threshold=1.5).transform(data)
print('Binarized data:',bindata)
#mean removal
print('Mean(before)=',data.mean(axis=0))
print('standard deviation(before)=',data.std(axis=0))
#features with a mean=0 and variance=1
scaled_data=preprocessing.scale(data)
print('Mean(before)=',scaled_data.mean(axis=0))
print('standard deviation(before)=',scaled_data.std(axis=0))
print('scaled_data:',scaled_data)
'''
scaled_data: [[ 0.10040991 0.91127074 -0.16607709]
[ 1.171449 -1.39221918 -1.1332319 ]
[-1.27185891 0.48094844 1.29930899]]
'''
#features in a 0 to 1 range
minmax_scaler=preprocessing.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1))
data_minmax=minmax_scaler.fit_transform(data)
print('MinMaxScaler applied on the data:',data_minmax)
'''
MinMaxScaler applied on the data: [[ 0.56164384 1. 0.39759036]
[ 1. 0. 0. ]
[ 0. 0.81318681 1. ]]
'''
data_l1=preprocessing.normalize(data,norm='l1')
data_l2=preprocessing.normalize(data,norm='l2')
print('l1-normalized data:',data_l1)
'''
[[ 0.22222222 0.5959596 -0.18181818]
[ 0.39416058 -0.23357664 -0.37226277]
[-0.20430108 0.4516129 0.34408602]]
'''
print('l2-normalized data:',data_l2)
'''
[[ 0.3359268 0.90089461 -0.2748492 ]
[ 0.6676851 -0.39566524 -0.63059148]
[-0.33858465 0.74845029 0.57024784]]
'''数据处理——One-Hot Encoding
一、One-Hot Encoding
One-Hot编码,又称为一位有效编码,主要是采用
 位状态寄存器来对
位状态寄存器来对
 个状态进行编码,每个状态都由他独立的寄存器位,并且在任意时候只有一位有效。
个状态进行编码,每个状态都由他独立的寄存器位,并且在任意时候只有一位有效。
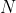 位状态寄存器来对
位状态寄存器来对
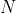 个状态进行编码,每个状态都由他独立的寄存器位,并且在任意时候只有一位有效。
个状态进行编码,每个状态都由他独立的寄存器位,并且在任意时候只有一位有效。
在实际的机器学习的应用任务中,特征有时候并不总是连续值,有可能是一些分类值,如性别可分为“male”和“female”。在机器学习任务中,对于这样的特征,通常我们需要对其进行特征数字化,如下面的例子:
有如下三个特征属性:
- 性别:["male","female"]
- 地区:["Europe","US","Asia"]
- 浏览器:["Firefox","Chrome","Safari","Internet Explorer"]
二、One-Hot Encoding的处理方法
对于上述的问题,性别的属性是二维的,同理,地区是三维的,浏览器则是思维的,这样,我们可以采用One-Hot编码的方式对上述的样本“["male","US","Internet Explorer"]”编码,“male”则对应着[1,0],同理“US”对应着[0,1,0],“Internet Explorer”对应着[0,0,0,1]。则完整的特征数字化的结果为:[1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1]。这样导致的一个结果就是数据会变得非常的稀疏。
https://study.163.com/provider/400000000398149/index.htm?share=2&shareId=400000000398149( 欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章)
机器学习项目合作QQ:231469242
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/u/4313381/blog/4009158