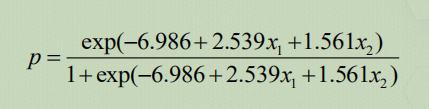转专业意向调查
问题描述
0 导入相关库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import metrics # 评估
import statsmodels.api as sm
1 加载数据
df = pd.read_csv('Regression/Regression7/sampling_survey.csv')
df.info()
features = ['x1', 'x2']
labels = ['y']
X = sm.add_constant(df[features])
y = df[labels]
2 模型拟合
model = sm.Logit(y, X)
result = model.fit()
print(result.summary())

2.1 拟合结果
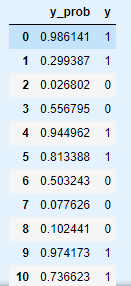
# 计算概率
y_prob = result.predict(X)
y_prob = pd.DataFrame(y_prob, columns=['y_prob'])
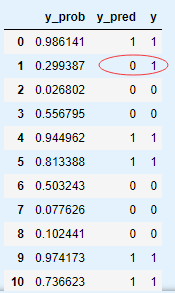
y_prob
y_prob.join(df['y'])
2.2 判别(阈值p=0.6)
# 预测因变量归类
alpha=0.6 #设定阈值
y_pred = y_prob.apply(lambda x: 1 if x[0] > alpha else 0, axis=1)
y_pred = pd.DataFrame(y_pred, columns = ['y_pred'])
y_prob.join(y_pred).join(df['y'])
3 评估
3.1 混淆矩阵
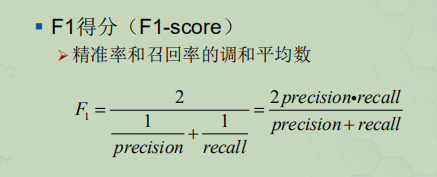
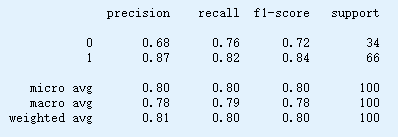
计算分类各评估指标
confusion=metrics.confusion_matrix(y,y_pred) # 计算混淆矩阵
print(metrics.classification_report(y,y_pred)) # 分类情况汇总
回归结果
from matplotlib import font_manager
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
font_dirs = ['/root/notebooks', ] # 字体所在目录
font_files = font_manager.findSystemFonts(fontpaths = font_dirs) # 寻找可用字体
# print(font_files)
font_list = font_manager.createFontList(font_files) # 创建字体查找列表
# print(font_list)
font_manager.fontManager.ttflist.extend(font_list) # 扩展字体列表
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'YaHei Consolas Hybrid' # 设置字体样式
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = '16' # 设置字体大小
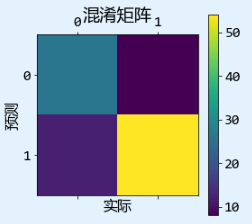
混淆矩阵画图
plt.matshow(confusion)
plt.title('混淆矩阵')
plt.colorbar()
plt.ylabel('预测')
plt.xlabel('实际')
plt.show()
3.2 ROC权曲线 & AUC计算
fpr, tpr, threshold = metrics.roc_curve(y, y_prob)
ROC_data=np.c_[fpr,tpr,threshold]
ROC_data=pd.DataFrame(ROC_data)
ROC_data.columns=['fpr','tpr','threshold']
auc = metrics.auc(fpr, tpr)
画ROC曲线图
# 创建一个图形框
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6), dpi=80)
# 在图形框里只画一幅图
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.set_title("%s" % "ROC曲线")
ax.set_xlabel("False positive rate")
ax.set_ylabel("True positive rate")
ax.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], "r--")
ax.set_xlim([0, 1])
ax.set_ylim([0, 1])
ax.plot(fpr, tpr, "k", label="%s; %s = %0.2f" % ("ROC曲线",
"AUC", auc))
ax.fill_between(fpr, tpr, color="grey", alpha=0.6) # 区间
legend = plt.legend(shadow=True)
plt.show()

4 Sklearn回归
4.1 sklearn回归#1
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
trainSet, testSet = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, random_state=2020)
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(trainSet[features], trainSet[labels])
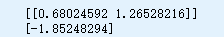
print(model.coef_)
print(model.intercept_)
sklearn回归#2
调参数:
1.test_size: 数据集(训练集&测试集比例)
2.C: (正则化参数)
trainSet, testSet = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.05, random_state=2020)
model = LogisticRegression(C=500)
model.fit(trainSet[features], trainSet[labels])
print(model.coef_)
print(model.intercept_)

4.3 交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
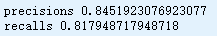
precisions = cross_val_score(model, trainSet[features], trainSet[labels], cv=5, scoring='precision')
print('precisions', np.mean(precisions))
recalls = cross_val_score(model, trainSet[features], trainSet[labels], cv=5, scoring='recall')
print('recalls', np.mean(recalls))
来源:CSDN
作者:喝醉酒的小白
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hezuijiudexiaobai/article/details/104777452