combineAll
组合多个流, 每次有一个流更新时, 发出所有流最新值的数组
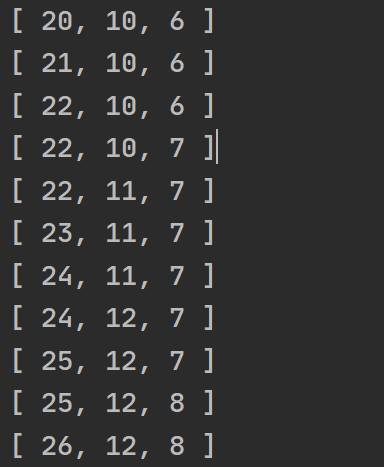
const source$ = of(200, 400, 600)
source$.pipe(
map(v => interval(v)),
combineAll()
).subscribe(console.log)combineLatest
由rxjs导入, 和combineAll作用一样, 用于组合最新的观察值
const {combineLatest, interval, of} = require('rxjs')
const {map} = require('rxjs/operators')
const source1$ = interval(200)
const source2$ = interval(400)
const source3$ = interval(600)
// 可传入数组或者参数式逐个传入
// combineLatest(source1$, source2$, source3$).subscribe(console.log)
combineLatest([source1$, source2$, source3$]).subscribe(console.log)
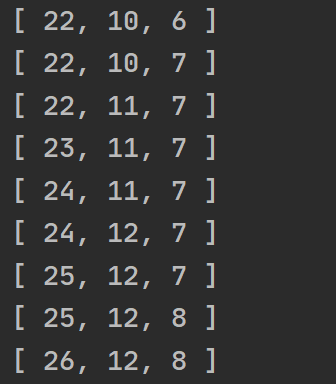
concat / concatAll
串行连接流, 只有当前面的流完成后, 才会从继续后面的流中继续取数据

const {interval, of, concat} = require('rxjs')
const {map, concatAll, take} = require('rxjs/operators')
const source1$ = interval(200).pipe(take(3))
const source2$ = interval(400).pipe(take(3), map(v => 'v' + v))
concat(source1$, source2$).subscribe(console.log)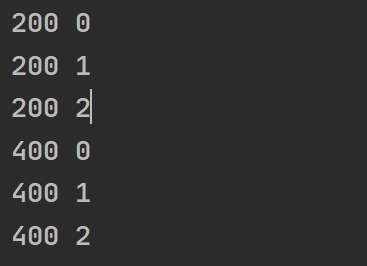
of(200, 400).pipe(
map(v => interval(v).pipe(map(x => v + ' ' + x), take(3))),
concatAll()
).subscribe(console.log)concatMap
改写上面的例子, 在做串行连接之前先进行map映射, 返回一个新的流
of(200, 400).pipe(
concatMap(v => interval(v).pipe(map(x => v + ' ' + x), take(3)))
).subscribe(console.log)concatMapTo
将所有值映射为固定值
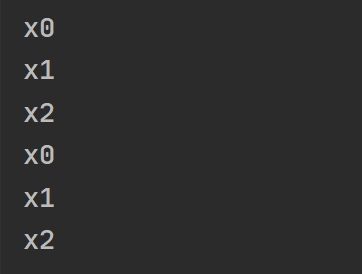
of(200, 400).pipe(
concatMapTo(interval(100).pipe(map(x => 'x' + x), take(3)))
).subscribe(console.log)
exhaust
已经开始的流, 必须完成后才会去启动, 并且在数据期间的流不会启动
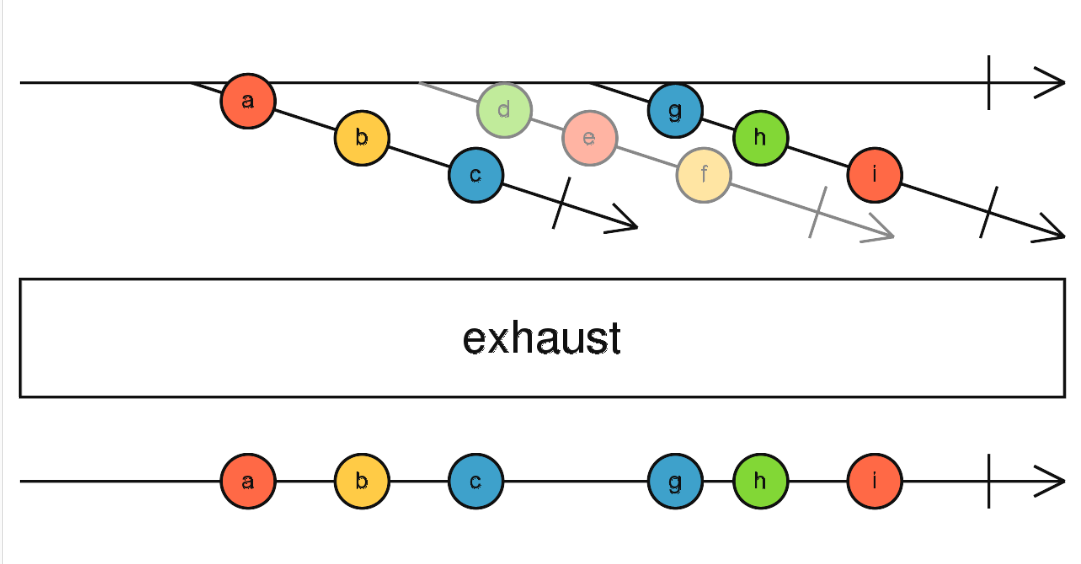
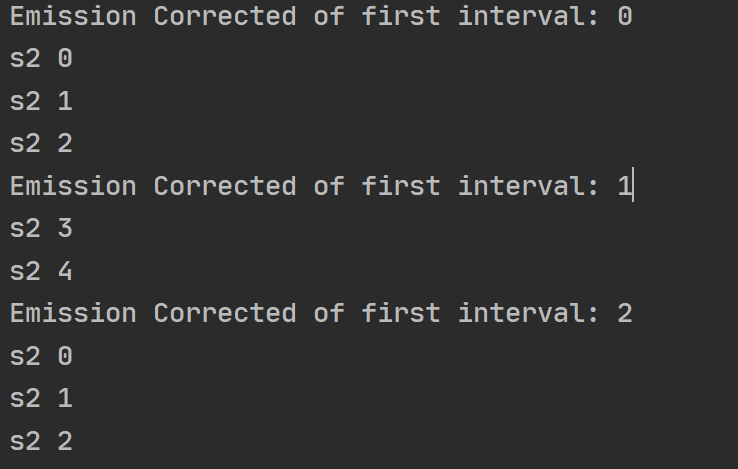
const {interval} = require('rxjs')
const {exhaustMap,exhaust, map, take} = require('rxjs/operators')
const firstInterval = interval(1000).pipe(take(10));
const secondInterval = interval(300).pipe(take(5), map(x => 's2 ' + x));
firstInterval
.pipe(
map(f => {
console.log(`Emission Corrected of first interval: ${f}`);
return secondInterval;
}),
exhaust()
)
.subscribe(s => console.log(s));
在第一个流没有执行完时, 获取第二个流, 但第二个流被忽视, 第一个流执行完成后, 开始第三个流
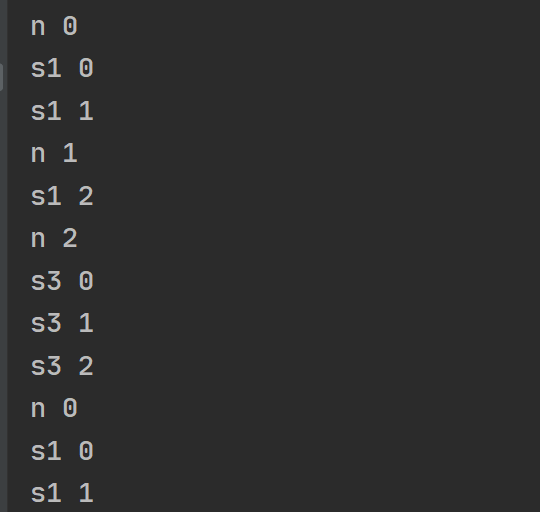
let s1$ = timer(0, 600).pipe(map(v => 's1 ' + v), take(3))
let s2$ = timer(0, 100).pipe(map(v => 's2 ' + v), take(3))
let s3$ = timer(0, 100).pipe(map(v => 's3 ' + v), take(3))
let s$ = [s1$, s2$, s3$]
function getSource(n) {
console.log('n', n)
return s$[n]
}
timer(0, 1000).pipe(
take(10),
map(v => getSource(v % 3)),
exhaust()
).subscribe(console.log)
exhaustMap
先做map再进行exhaust
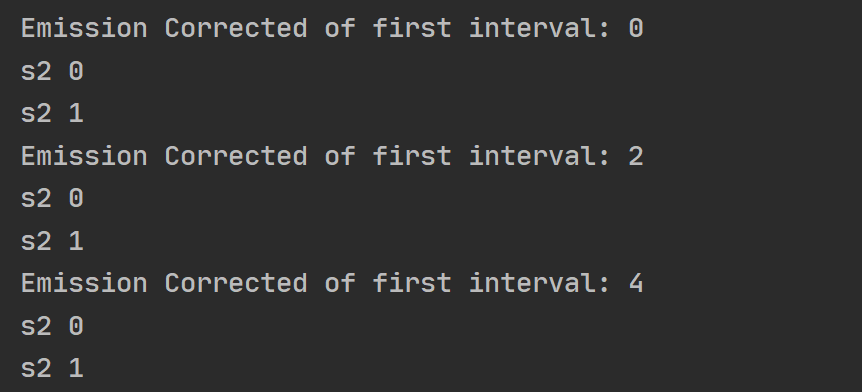
const {interval} = require('rxjs')
const {exhaustMap, map, take} = require('rxjs/operators')
const firstInterval = interval(1000).pipe(take(10));
const secondInterval = interval(1000).pipe(take(2), map(x => 's2 ' + x));
firstInterval
.pipe(
exhaustMap(f => {
console.log(`Emission Corrected of first interval: ${f}`);
return secondInterval;
})
)
.subscribe(s => console.log(s));
forkJoin
将异步数组或对象, 转化为数据流
数组和错误处理
const example = forkJoin(
//emit 'Hello' immediately
of('Hello'),
//emit 'World' after 1 second
of('World').pipe(delay(1000)),
// throw error
throwError('This will error').pipe(catchError(error => of(error)))
);
//output: ["Hello", "World", "This will error"]
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
const myPromise = val =>
new Promise(resolve =>
setTimeout(() => resolve(`Promise Resolved: ${val}`), 5000)
);
const source = of([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);
//emit array of all 5 results
const example = source.pipe(mergeMap(q => forkJoin(...q.map(myPromise))));
/*
output:
[
"Promise Resolved: 1",
"Promise Resolved: 2",
"Promise Resolved: 3",
"Promise Resolved: 4",
"Promise Resolved: 5"
]
*/
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
const observable = forkJoin({
foo: of(1, 2, 3, 4),
bar: Promise.resolve(8),
baz: timer(4000),
inv: interval(1000).pipe(
take(3)
),
});
observable.subscribe({
next: value => console.log(value),
complete: () => console.log('This is how it ends!'),
});
// Logs:
// { foo: 4, bar: 8, baz: 0 } after 4 seconds
// "This is how it ends!" immediately after
merge / mergeAll
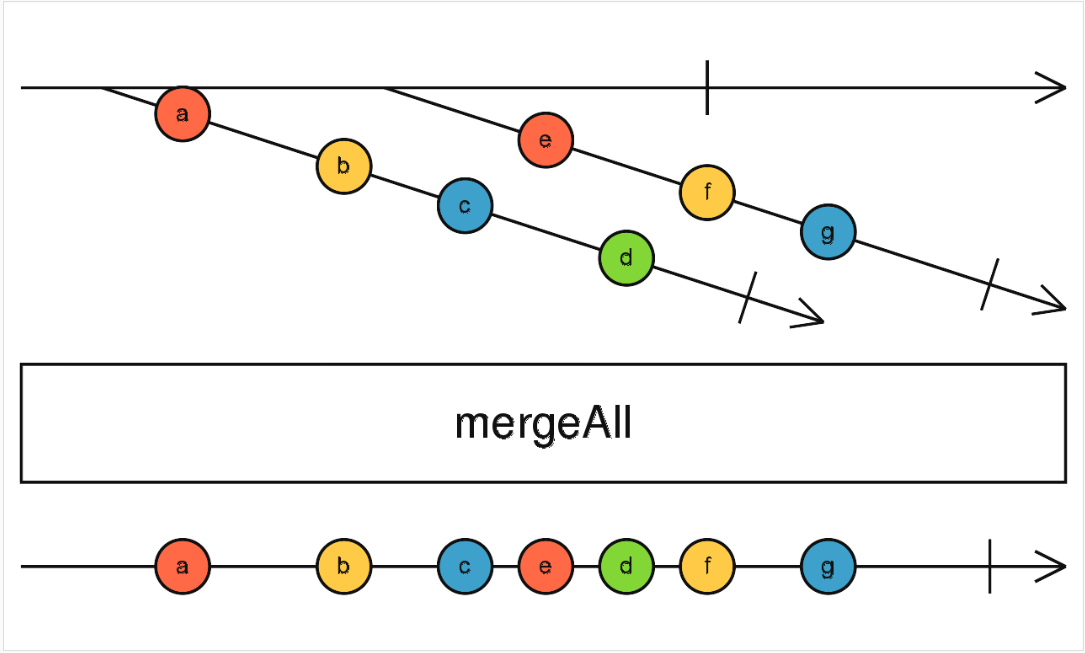
多个流, 每次将最新的数据输出
let s1 = interval(1000).pipe(map(v => '1000 ' + v))
let s2 = interval(600).pipe(map(v => '600 ' + v))
let s3 = interval(600).pipe(map(v => '300 ' + v))
merge(s1, s2, s3).subscribe(console.log)
mergeMap / mergeMapTo
用于在merge之前先进行映射
interval(100).pipe(
take(3),
mergeMap(x => {
let inv = (x + 1) * 100
return interval(inv).pipe(take(10), map(
i => x = inv + ' ' + i
))
}, 2)
).subscribe(console.log)
race
返回第一个返回数据的流, 会忽略其他流, 会在返回的流结束后结束
let s1 = interval(100).pipe(map(v => '100 ' + v), take(20))
let s2 = interval(200).pipe(map(v => '200 ' + v), take(10))
let s3 = interval(300).pipe(map(v => '300 ' + v), take(5))
race(s1, s2, s3).subscribe(
console.log,
)
startWith
用于在流的最开始添加数据, 多次使用时类似栈的数据结构
let s = of(1, 2, 3)
s.pipe(
startWith('a'),
startWith('b'),
).subscribe(console.log)
// b a 1 2 3
switchAll
每次新的流开始时, 取消之前订阅的流
200计时器和300计时器第二个数被新的流打断了

interval(400).pipe(
take(5),
map(v => (v + 1) * 100),
map(v => interval(v).pipe(map(x => v + ' ' + x), take(3))),
switchAll()
).subscribe(console.log)
switchMap
一般用switchMap的多一些, 第一个是映射函数, 第二个参数 resultSelector 用于修改结果
interval(400).pipe(
take(5),
switchMap(v => {
let inv = (v + 1) * 100
return interval(inv).pipe(map(x => inv + ' ' + x), take(3))
},
(outerValue, innerValue, outerIndex, innerIndex) => {
return [
outerValue,
innerValue,
outerIndex,
innerIndex
]
}
)
).subscribe(console.log)
switchMapTo
和switchMap类似, 将所有值映射为同样的流, 传递一个result和selector
withLatestFrom
只有当源发出值时, 才将最新的数据组合发出
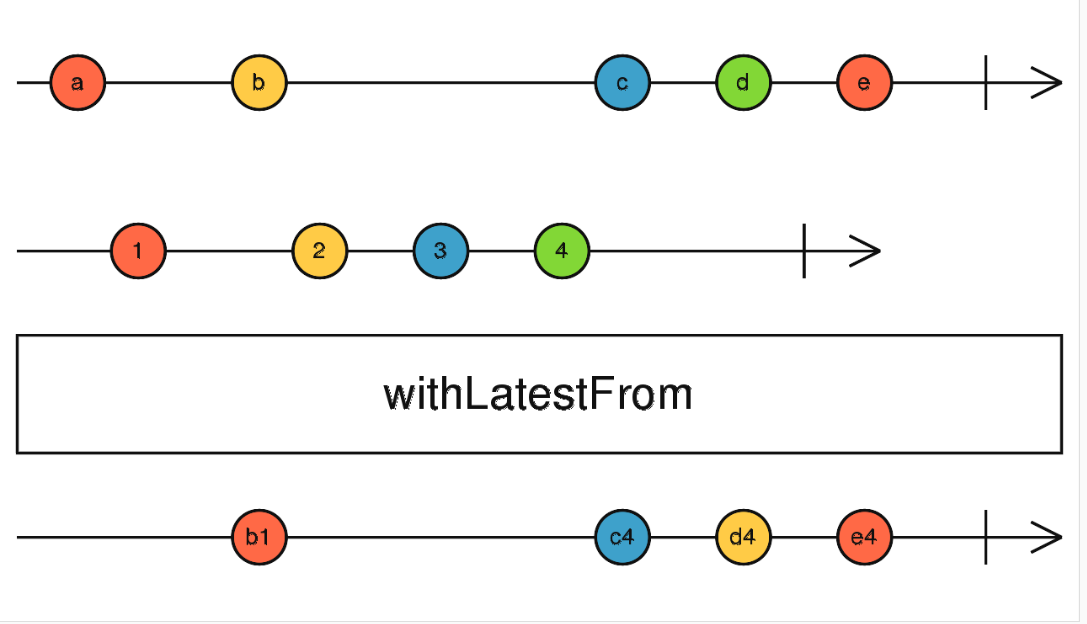

let source = interval(1000)
let t1 = interval(200)
let t2 = interval(400)
source.pipe(
withLatestFrom(t1, t2)
).subscribe(console.log)
zip / zipAll
和py中类似, 用于数据配对
const {interval, of, zip} = require('rxjs')
const {exhaustMap, exhaust, map, zipAll, take, delay} = require('rxjs/operators')
const s1$ = of(1, 2, 3)
const s2$ = interval(100).pipe(map(v => 'v ' + v))
// 效果和下面代码一样, 简写形式
// zip(s1$, s2$).subscribe(console.log)
of(s1$, s2$).pipe(
zipAll()
).subscribe(console.log)
来源:oschina
链接:https://my.oschina.net/ahaoboy/blog/3164711