关于 Envoy 线程模型,Envoy 作者的一遍文章写的很清楚,可以移步这里了解更多作者的设计思路,这是来自原文的线程模型图:
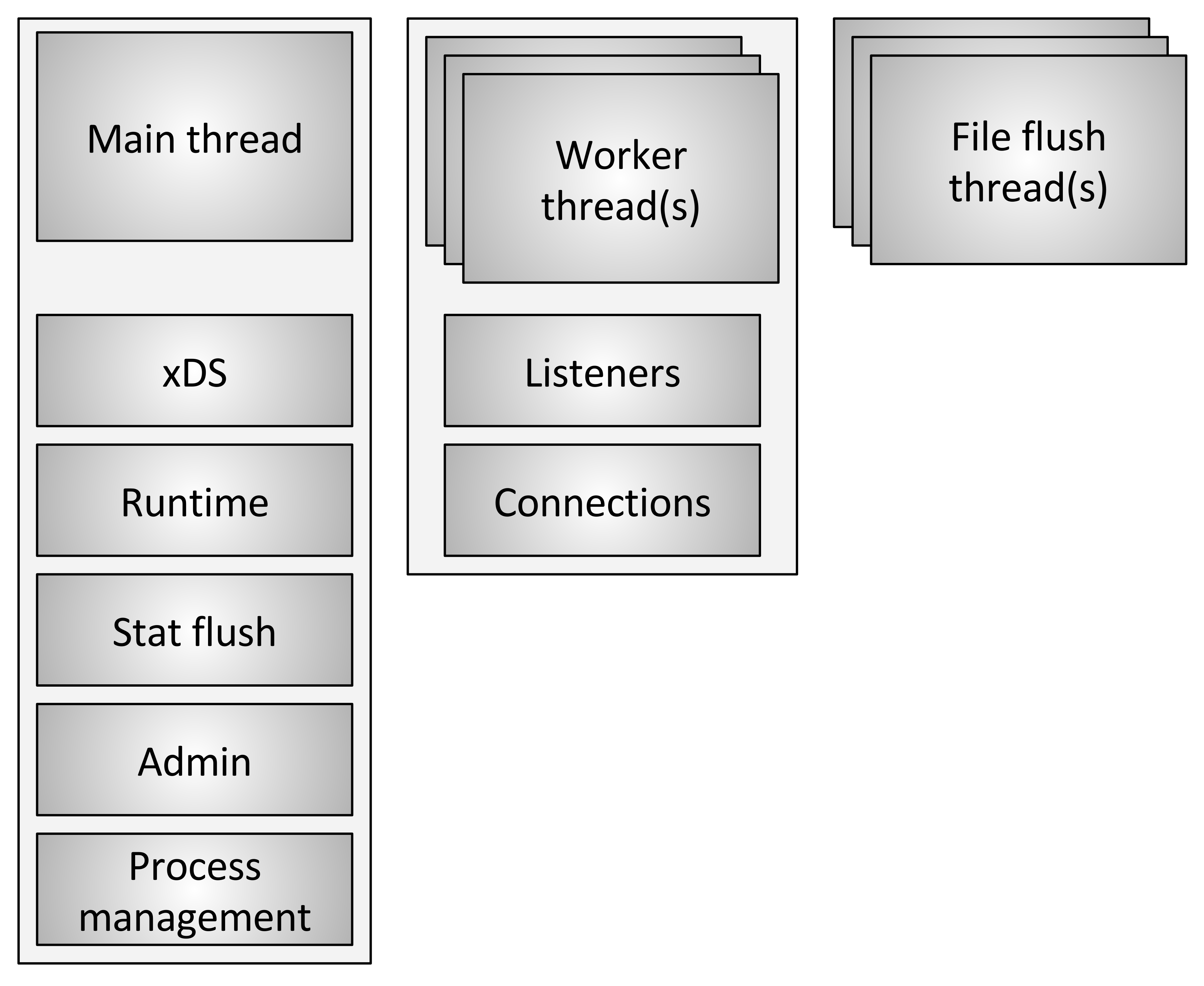
简而言之,Envoy 主线程(main thread)用来启动工作线程(worker thread)、管理 xDS 数据并同步至工作线程、统计数据 flush 等等;工作线程处理网络请求、路由、cluster 连接池等等。考虑到 xDS 会随时动态更新 listener/router/cluster 等信息,而实时处理数据的时候又会时刻查询此类信息,必然涉及到数据的线程安全问题,基于性能考虑,Envoy 做了无锁实现,主线程把需要同步的数据通过 Slot 推送给工作线程,由工作线程在沉寂期(quiescent period )完成数据更新,这样需要访问此类信息时就不需要加锁。以下是来自原文的 TLS 示意图: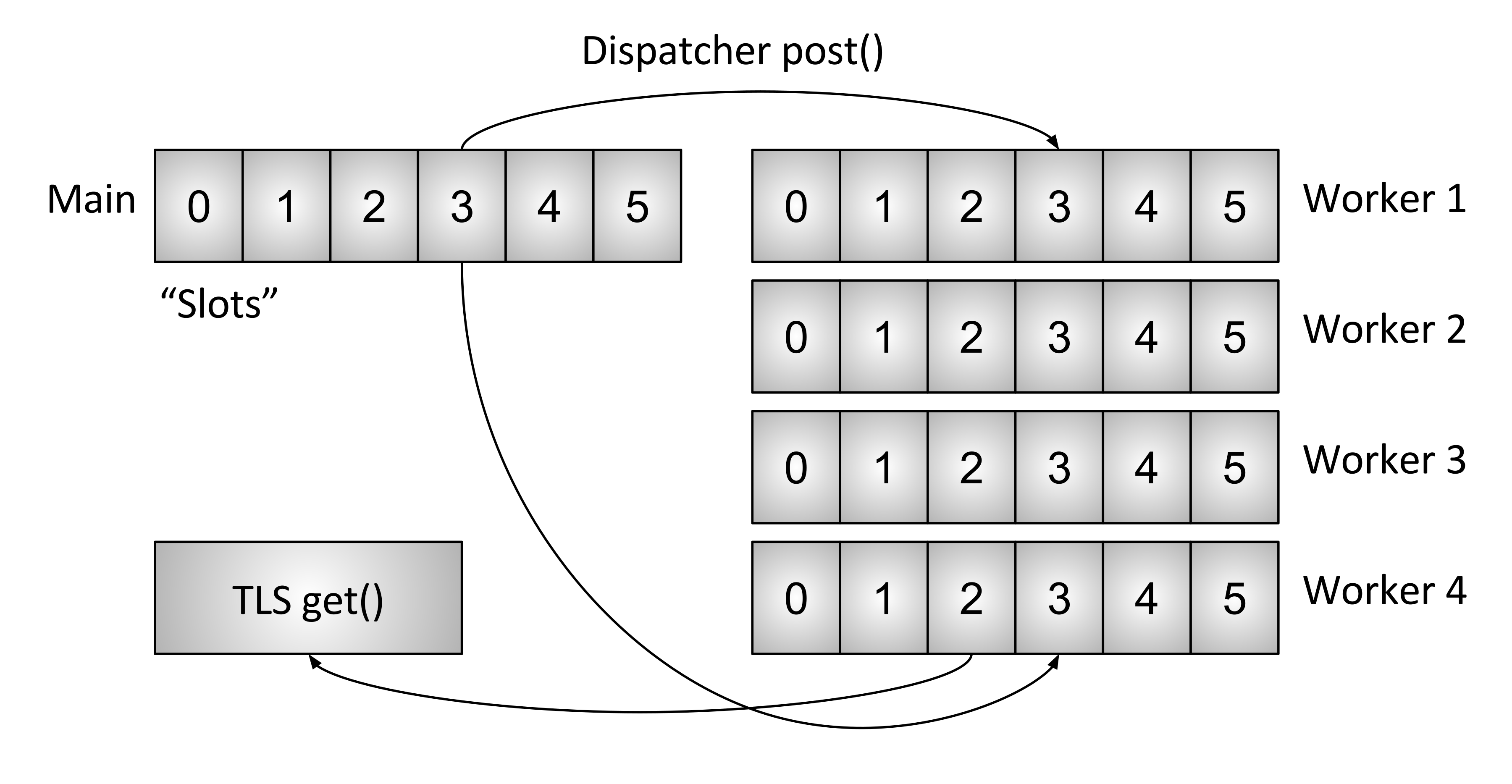
下面以 Cluster 信息为例,分析源代码实现,理解 TLS 是如何工作的。
Envoy::ThreadLocal::Slot and Envoy::ThreadLocal::SlotAllocator 接口
Envoy::ThreadLocal::Slot 定义了 TLS 存储的基本单元 Slot(槽),定义如下:
**
* An individual allocated TLS slot. When the slot is destroyed the stored thread local will
* be freed on each thread.
*/
class Slot {
public:
virtual ~Slot() = default;
/**
* @return ThreadLocalObjectSharedPtr a thread local object stored in the slot.
*/
virtual ThreadLocalObjectSharedPtr get() PURE;
/**
* This is a helper on top of get() that casts the object stored in the slot to the specified
* type. Since the slot only stores pointers to the base interface, dynamic_cast provides some
* level of protection via RTTI.
*/
template <class T> T& getTyped() { return *std::dynamic_pointer_cast<T>(get()); }
/**
* Run a callback on all registered threads.
* @param cb supplies the callback to run.
*/
virtual void runOnAllThreads(Event::PostCb cb) PURE;
/**
* Run a callback on all registered threads with a barrier. A shutdown initiated during the
* running of the PostCBs may prevent all_threads_complete_cb from being called.
* @param cb supplies the callback to run on each thread.
* @param all_threads_complete_cb supplies the callback to run on main thread after cb has
* been run on all registered threads.
*/
virtual void runOnAllThreads(Event::PostCb cb, Event::PostCb all_threads_complete_cb) PURE;
/**
* Set thread local data on all threads previously registered via registerThread().
* @param initializeCb supplies the functor that will be called *on each thread*. The functor
* returns the thread local object which is then stored. The storage is via
* a shared_ptr. Thus, this is a flexible mechanism that can be used to share
* the same data across all threads or to share different data on each thread.
*/
using InitializeCb = std::function<ThreadLocalObjectSharedPtr(Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher)>;
virtual void set(InitializeCb cb) PURE;
};
槽内存储的是实现了 Envoy::ThreadLocal:ThreadLocalObject 虚类的对象。runOnAllThreads 方法将 Envoy::Event::PostCb 方法通过 Slot 对象分发给所有工作线程执行。
Envoy::ThreadLocal::SlotAllocator 接口比较简单,定义了分配槽的接口:
/**
* Interface used to allocate thread local slots.
*/
class SlotAllocator {
public:
virtual ~SlotAllocator() = default;
/**
* @return SlotPtr a dedicated slot for use in further calls to get(), set(), etc.
*/
virtual SlotPtr allocateSlot() PURE;
};
对于需要将数据分发到所有工作线程的类来说,首先它要通过 Envoy::ThreadLocal::SlotAllocator 实现类分配存储数据的 Slot,将自己的 Envoy::ThreadLocal::ThreadLocalObject 数据存入该 Slot,然后通过 Slot::runOnAllThreads 在所有线程里执行数据存取和相关处理逻辑。
Envoy::ThreadLocal::Instance 接口
Envoy::ThreadLocal::Instace 提供了 TLS 系统需要实现的接口,定义如下:
// include/envoy/thread_local/thread_local.h
/**
* Interface for getting and setting thread local data as well as registering a thread
*/
class Instance : public SlotAllocator {
public:
/**
* A thread (via its dispatcher) must be registered before set() is called on any allocated slots
* to receive thread local data updates.
* @param dispatcher supplies the thread's dispatcher.
* @param main_thread supplies whether this is the main program thread or not. (The only
* difference is that callbacks fire immediately on the main thread when posted
* from the main thread).
*/
virtual void registerThread(Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher, bool main_thread) PURE;
/**
* This should be called by the main thread before any worker threads start to exit. This will
* block TLS removal during slot destruction, given that worker threads are about to call
* shutdownThread(). This avoids having to implement de-registration of threads.
*/
virtual void shutdownGlobalThreading() PURE;
/**
* The owning thread is about to exit. This will free all thread local variables. It must be
* called on the thread that is shutting down.
*/
virtual void shutdownThread() PURE;
/**
* @return Event::Dispatcher& the thread local dispatcher.
*/
virtual Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher() PURE;
};
在 Envoy::ThreadLocal::SlotAllocator 基础智商,主要提供了注册工作线程的方法:registerThread,工作线程 Envoy::Server::WorkerImpl 初始化的时候,会把自己的 Envoy::Event::Dispatcher 对象通过该方法注册进来,Slot 使用方需要分发的数据和逻辑,最终都是通过各自的 Dispatcher::post 来完成的。
Envoy::ThreadLocal::InstanceImpl 和 Envoy::ThreadLocal::SlotImpl
Envoy::ThreadLocal::InstanceImpl 是 Envoy 的 Thread Local Storage (tls) 的实现,具体依赖于 static thread_local 变量来存储线程共享的数据:
// source/common/thread_local/thread_local_impl.cc
namespace Envoy {
namespace ThreadLocal {
thread_local InstanceImpl::ThreadLocalData InstanceImpl::thread_local_data_;
}}
槽分配算法比较简单,SlotImpl 会分配一个唯一的 index,并存在 std::vector 里,SlotImpl 删除后空出来的位置会被重复利用 :
// slots_ 定义
std::vector<SlotImpl*> slots_;
SlotPtr InstanceImpl::allocateSlot() {
ASSERT(std::this_thread::get_id() == main_thread_id_);
ASSERT(!shutdown_);
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < slots_.size(); i++) {
if (slots_[i] == nullptr) {
std::unique_ptr<SlotImpl> slot(new SlotImpl(*this, i));
slots_[i] = slot.get();
return slot;
}
}
std::unique_ptr<SlotImpl> slot(new SlotImpl(*this, slots_.size()));
slots_.push_back(slot.get());
return slot;
}
SlotImpl 有了自己的 index,会将真实数据按照 index 保存在 thread_local_data_ 里面:
void InstanceImpl::SlotImpl::set(InitializeCb cb) {
ASSERT(std::this_thread::get_id() == parent_.main_thread_id_);
ASSERT(!parent_.shutdown_);
for (Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher : parent_.registered_threads_) {
const uint32_t index = index_;
dispatcher.post([index, cb, &dispatcher]() -> void { setThreadLocal(index, cb(dispatcher)); });
}
// Handle main thread.
setThreadLocal(index_, cb(*parent_.main_thread_dispatcher_));
}
void InstanceImpl::setThreadLocal(uint32_t index, ThreadLocalObjectSharedPtr object) {
if (thread_local_data_.data_.size() <= index) {
thread_local_data_.data_.resize(index + 1);
}
thread_local_data_.data_[index] = object;
}
从上面第 7 行代码可以看到,Slot 在设置数据的时候,会同时分发到所有线程执行数据设置逻辑,这样所有的线程的 Slot 数据异步保证最终一致性,Envoy 到处都在实践最终一致的架构哲学。
注册工作线程的 Dispather 逻辑也很简单,用一个 std::list 来存储:
// registered_threads_ 定义
std::list<std::reference_wrapper<Event::Dispatcher>> registered_threads_;
void InstanceImpl::registerThread(Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher, bool main_thread) {
ASSERT(std::this_thread::get_id() == main_thread_id_);
ASSERT(!shutdown_);
if (main_thread) {
main_thread_dispatcher_ = &dispatcher;
thread_local_data_.dispatcher_ = &dispatcher;
} else {
ASSERT(!containsReference(registered_threads_, dispatcher));
registered_threads_.push_back(dispatcher);
dispatcher.post([&dispatcher] { thread_local_data_.dispatcher_ = &dispatcher; });
}
}
Slot 数据同步逻辑
以 Cluster 信息为例,Envoy 实现了Envoy::Upstream::ClusterManagerImpl::ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl 放入 Slot:
/**
* Thread local cached cluster data. Each thread local cluster gets updates from the parent
* central dynamic cluster (if applicable). It maintains load balancer state and any created
* connection pools.
*/
struct ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl : public ThreadLocal::ThreadLocalObject
Envoy 在启动时解析到 static_resources 时会初始化 Envoy::Upstream::ClusterManagerImpl 对象,ClusterManagerImpl 对象初始化的时候拿到一个 Slot,用来存储 ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl:
// Once the initial set of static bootstrap clusters are created (including the local cluster),
// we can instantiate the thread local cluster manager.
tls_->set([this, local_cluster_name](
Event::Dispatcher& dispatcher) -> ThreadLocal::ThreadLocalObjectSharedPtr {
return std::make_shared<ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl>(*this, dispatcher, local_cluster_name);
});
继续解析到 cluster 定义后,会将 cluster 信息解析逻辑通过 slot 分发到所有线程执行:
void ClusterManagerImpl::createOrUpdateThreadLocalCluster(ClusterData& cluster) {
tls_->runOnAllThreads([this, new_cluster = cluster.cluster_->info(),
thread_aware_lb_factory = cluster.loadBalancerFactory()]() -> void {
ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl& cluster_manager =
tls_->getTyped<ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl>();
if (cluster_manager.thread_local_clusters_.count(new_cluster->name()) > 0) {
ENVOY_LOG(debug, "updating TLS cluster {}", new_cluster->name());
} else {
ENVOY_LOG(debug, "adding TLS cluster {}", new_cluster->name());
}
auto thread_local_cluster = new ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl::ClusterEntry(
cluster_manager, new_cluster, thread_aware_lb_factory);
cluster_manager.thread_local_clusters_[new_cluster->name()].reset(thread_local_cluster);
for (auto& cb : cluster_manager.update_callbacks_) {
cb->onClusterAddOrUpdate(*thread_local_cluster);
}
});
}
注意代码第 4 行,每个线程拿到的是各自不同的 ThreadLocalClusterManagerImpl 对象,因此做到了数据读写的无锁实现。
来源:CSDN
作者:zhangpin04
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangpin04/article/details/104500266