图论——邻接表
邻接表表示
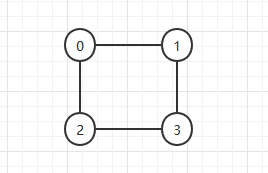
对于上图的邻接表如下
0:1->2 意思是顶点0保持着一个链表,链表里存放顶点0的邻接顶点
1:0->3 意思是顶点1保持着一个链表,链表里存放顶点1的邻接顶点
2:0->3
3:1->2
代码
public class AdjList {
private int V;//顶点数
private int E;//边数
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;//邻接表,链表数组存储
public AdjList(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();//顶点数
if(V<=0) throw new RuntimeException("顶点个数必须大于0");
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
adj[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt();//边数
if(E<0) throw new RuntimeException("边数不能为负数");
for(int i=0;i<E;i++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
//自环边检测
if(a==b){
throw new RuntimeException("简单图不能包含自环边");
}
//平行边检测
if(adj[a].contains(b)){
throw new RuntimeException("简单图不能包含平行边");
}
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v<0||v>=V){
throw new RuntimeException("顶点下标溢出");
}
}
public int vertexNum(){
return V;
}
public int edgeNum(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v,int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
//邻接顶点
public List<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
//度
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d,E = %d\n",V,E));
for(int i=0;i<adj.length;i++){
sb.append(i+":");
for (Iterator<Integer> it = adj[i].iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
sb.append(it.next()+" ");
}
sb.append("\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjList adjList = new AdjList("graph.txt");
System.out.println(adjList);
System.out.println(adjList.degree(6));
}
graph.txt
7 6
0 1
0 2
1 3
2 6
2 3
1 4
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
建图:O(E*V) 这个V是平行边检测消耗的时间
判断两个顶点是否有边:O(degree(v))
求一个顶点的邻接顶点:O(degree(v)) 返回list给用户,用户也得遍历,所以这里不是O(1)
求一个顶点的度:O(1)
空间复杂度:O(V+E)
对于时间复杂度建图过程需要花费V的时间检测平行边,这是因为我们用的数据结构是LinkedList,如果改为TreeSet,建图只需要O(E*logV),甚至改为HashSet只需要O(E),下一节介绍
来源:CSDN
作者:酒醉梦醒
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/LiuRenyou/article/details/104028415