如果饿了就吃,困了就睡,渴了就喝,人生就太无趣了
1 定义
1.1 概念
在一个方法中定义一个算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以在改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法中的某些步骤。
1.2 类图
如图1,抽象类AbstractClass中的templateMethod方法定义了算法框架,将算法分步骤实现,每一步的定义为抽象方法primitiveOperation1()和primitiveOperation2()。由实现的AbstractClass的实例类进行重写该静态方法。

2 例子(咖啡店)
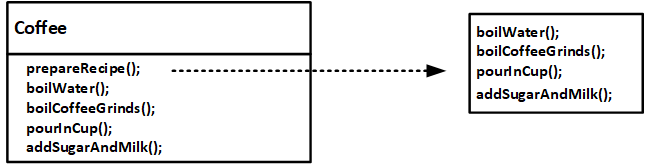
如图2:做咖啡的步骤,分为四步:烧水boilWater(),沸水冲咖啡boilCoffeeGrinds(),倒进杯子pourInCup(),加糖加奶addSugarAndMilk()。
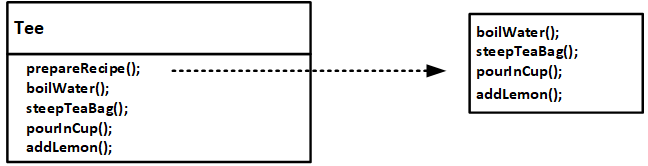
如图3:做茶的步骤,也分为四步:烧水boilWater(),沸水泡茶包steepTeaBag(),倒进杯子pourInCup(),加柠檬addLemon()。
可以发现这两种做法有两个相同的步骤:烧水boilWater()和倒进杯子pourInCup()。
2.1 改进设计
如图4:设计一个抽象类CoffeineBeverage,将刚刚发现的共同点抽象出来在该类中实现,将prepareRecipe()方法作为抽象方法。Coffee和Tea继承CoffeinBeverage,并重写prepareRecipe(),将不同的步骤进行实现。

2.2 再次改进
在看咖啡和茶的不同的步骤:
- 沸水冲咖啡
boilCoffeeGrinds()和沸水泡茶包steepTeaBag(),可以看出两个步骤的其实也是相同的动作,只是将不同的料放入沸水中。 - 加糖加奶
addSugarAndMilk()和加柠檬addLemon()。这两个步骤也是相同的动作,只不过是加的料不同。
再次进行改进,如图5:个抽象类CoffeineBeverage将不相同的两个步骤进行抽象化,生成两个抽象方法brew()和addCondiments(),由Coffee和Tee来实现这个抽象放方法,实现prepareRecipe()方法,做步骤进行固定化,将prepareRecipe()方法使用final关键字修饰,此时就应用了模板方法模式。

代码
public abstract class CaffeineBeverage {
final void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brew();
pourInCup();
addCondiments();
}
abstract void brew();
abstract void addCondiments();
void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
}
public class Coffee extends CaffeineBeverage {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Dripping Coffee through filter");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Sugar and Milk");
}
}
public class Tea extends CaffeineBeverage {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Steeping the tea");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Lemon");
}
}
public class BeverageTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tea tea = new Tea();
Coffee coffee = new Coffee();
System.out.println("\nMaking tea...");
tea.prepareRecipe();
System.out.println("\nMaking coffee...");
coffee.prepareRecipe();
}
}
2.3 人性化改进
有些人喝咖啡不需要糖和奶,喝茶不要柠檬,此时算法就需要进行改动,更加人性化。此时在抽象类中加入钩子方法,其实现只有空和默认方法。钩子方法对算法的不同点进行挂钩,对于要不要挂钩,由子类决定。(直接看类图吧,说不清啦)
如图6:在抽象类CoffeineBeverage中添加customerWantsCondiments()方法,此方法就是钩子方法,直接返回值,不做任何操作,但此方法却在perpareRecipe()起到决定是否至执行addCondiments()方法。此时子类就可以重写该方法,让顾客决定是否加料。
代码
public abstract class CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
final void prepareRecipe() {
boilWater();
brew();
pourInCup();
if (customerWantsCondiments()) {
addCondiments();
}
}
abstract void brew();
abstract void addCondiments();
void boilWater() {
System.out.println("Boiling water");
}
void pourInCup() {
System.out.println("Pouring into cup");
}
boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
return true;
}
}
public class CoffeeWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Dripping Coffee through filter");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Sugar and Milk");
}
public boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
String answer = getUserInput();
if (answer.toLowerCase().startsWith("y")) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private String getUserInput() {
String answer = null;
System.out.print("Would you like milk and sugar with your coffee (y/n)? ");
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
answer = in.readLine();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.err.println("IO error trying to read your answer");
}
if (answer == null) {
return "no";
}
return answer;
}
}
public class TeaWithHook extends CaffeineBeverageWithHook {
public void brew() {
System.out.println("Steeping the tea");
}
public void addCondiments() {
System.out.println("Adding Lemon");
}
public boolean customerWantsCondiments() {
String answer = getUserInput();
if (answer.toLowerCase().startsWith("y")) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private String getUserInput() {
// get the user's response
String answer = null;
System.out.print("Would you like lemon with your tea (y/n)? ");
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
answer = in.readLine();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
System.err.println("IO error trying to read your answer");
}
if (answer == null) {
return "no";
}
return answer;
}
}
public class BeverageTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TeaWithHook teaHook = new TeaWithHook();
CoffeeWithHook coffeeHook = new CoffeeWithHook();
System.out.println("\nMaking tea...");
teaHook.prepareRecipe();
System.out.println("\nMaking coffee...");
coffeeHook.prepareRecipe();
}
}
来源:CSDN
作者:###keer###
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41938180/article/details/104397782