一、什么是原型模式:
传统的创建的对象,可以用new直接新建对象,但是如果某些类的属性太多,这样构造起来会相对复杂;这里提供了一种不用通过构造方法,创建对象的方法;通过Jdk自带的Cloneable接口,实现对象的拷贝,创建新的对象;
二、何时使用原型模式:
原型模式其实就是一个对象在创建另一个可定制的对象,而且不需要指定任何创建的细节。Java提供了Cloneable接口,其中有一个唯一方法Clone(),实现这个接口就可以完成原型模式了。
一般在初始化的信息不发生变化的情况下,克隆是最好的办法。既隐藏了对象创建的细节,又对性能是大大的提高。不用重新初始化对象,而是动态地获得对象运行时的状态。
三、原型模式大概分为潜拷贝和深度拷贝:
1)潜拷贝:
代码示例:
package com.jason.study.design.prototype.simple;
import com.jason.study.design.prototype.Teacher;
public class School implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private int id;
private Teacher teacher;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
package com.jason.study.design.prototype.simple;
import com.jason.study.design.prototype.Teacher;
public class TestSimpleCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School school=new School();
school.setId(1);
school.setName("红小");
Teacher teacher=new Teacher();
teacher.setName("zhang lao shi");
school.setTeacher(teacher);
System.out.println("school"+school);
System.out.println("school.getTeacher()"+teacher);
School school1=null;
try{
school1= (School) school.clone();
System.out.println("school1"+school1);
System.out.println("school1.getTeacher()"+school1.getTeacher());
school1.getTeacher().setName("wanglaoshi");
System.out.println("school.getTeacher().getName()="+school.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("school1.getTeacher().getName()="+school1.getTeacher().getName());
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
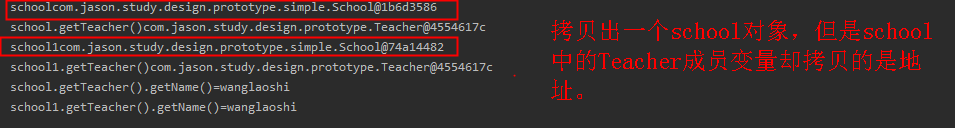
2)深度拷贝:
代码示例:
package com.jason.study.design.prototype.deep;
import com.jason.study.design.prototype.Teacher;
import java.io.*;
public class School implements Cloneable ,Serializable{
private String name;
private int id;
private Teacher teacher;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Teacher getTeacher() {
return teacher;
}
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
this.teacher = teacher;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
School school=(School)super.clone();
School s1=null;
try
{
//先将实例串行化到文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("sersingleton.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(school);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
fos.close();
//从文件读出原有的单例类
FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("Sersingleton.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
s1=(School)ois.readObject();
ois.close();
fis.close();
System.out.println(s1==school);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return s1;
}
}
package com.jason.study.design.prototype.deep;
import com.jason.study.design.prototype.Teacher;
import com.jason.study.design.prototype.deep.School;
public class TestDeepCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School school=new School();
school.setId(1);
school.setName("红小");
Teacher teacher=new Teacher();
teacher.setName("zhang lao shi");
school.setTeacher(teacher);
System.out.println("school"+school);
System.out.println("school.getTeacher()"+teacher);
School school1=null;
try{
school1= (School) school.clone();
System.out.println("school1"+school1);
System.out.println("school1.getTeacher()"+school1.getTeacher());
school1.getTeacher().setName("wanglaoshi");
System.out.println("school.getTeacher().getName()="+school.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("school1.getTeacher().getName()="+school1.getTeacher().getName());
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
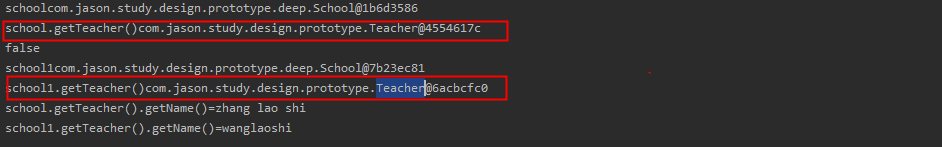
运行结果:
通过序列化的方式,完成了深度拷贝,school中Teacher引用也重新创建了对象;
四、总结一下:
通过上面的代码演示,大家可以看到原型模式和我们之前学习的单例模式,是相互对立的。在合适的场景选择合适的设计模式。
来源:CSDN
作者:石头城程序猿
链接:https://blog.csdn.net/jason_jiahongfei/article/details/104213230