原文地址:http://blog.163.com/net_worm/blog/static/127702419201002842553382/
首先对Windows下的网络编程总结一下:
如果是服务器,其WinSDK调用分别为:
1 WSAStartup() -> socket() -> htons() / htonl() -> bind() -> listen() -> accept() -> recv() / send() -> closesocket() -> WSACleanup()
如果是客户端程序,其调用序列为:
1 WSAStartup() -> socket() -> htons() / htonl() -> connect() -> recv() / send() -> closesocket() -> WSACleanup()
前面转贴的客户端(WinSocket温习)程序中,收到信息就在console打印出来然后退出了;在一般的应用中,通常是要一直等待收发消息的,直到程序确认退出才关闭socket。如果用一个轮询就会占用很多的CPU资源,所以很多嵌入式设计中会用一个WaitForMultiObject调用,等待退出命令或者超时,然后退出或进行下一轮信息接受。在Windows平台下也有一些比较高明的设计,使用异步socket,然后用异步选择的办法,实现多线程和事件的并发。在WinSocket中,同样也有一套异步Socket函数,那就是使用WSAAsyncSelect()及其配合函数。具体可以参考MSDN。QT在Windows平台上的实现,肯定也跟这些SDK调用有关。
按照这个思路,果然在QT代码里面找到了Qnativesocketengine_win.cpp,WSAStartup(),WSASocket()等序列WSA函数都有。QNativeSocketEnginePrivate类把这些SDK封装成:createNewSocket()、option()、setOption()、nativeConnect()、nativeBind()、nativeListen()、nativeAccept()、nativeWrite()、nativeRead()、nativeSelect()、nativeClose()等。按照QT的设计,QPrivate类是数据类;Q类应该是主类。接着看QNativeSocket类的继承:
1 QNativeSocketEngine : public QAbstractSocketEngine : public QObject
QAbstractSocketEngine类是使用了大量纯虚函数的定义。继续深入查看,发现大量有关的类:QAbstractSocket,SocketAsyncHandler,QTcpSocket,QUdpSocket等,看来我要先了解下QT网络编程体系再进一步分析之
之前没有看QT自带的文档,看了doc之后对QT的网络体系有一个大致的了解:
QNatvieSocketEnginePrivate是OS相关的API封装,和QNativeSocketEngine一起构成具体平台SOCKET实现;
QTcpSocket、QUdpSocket、QTcpServer构成底层的应用API;QSslSocket是SSL加密相关API;
QHttp、QFtp构成高层次应该API;
QNetworkAccessManager、QNetworkRequest、QNetworkReply是高度抽象的网络层。
分析TCP的例子fortuneclient,运行起来按了[Get
Fortune]按钮之后,调用的是Client::requestNewFortune()。
1 void Client::requestNewFortune()
2 {
3 getFortuneButton->setEnabled(false);
4 blockSize = 0;
5 tcpSocket->abort();
6 tcpSocket->connectToHost(hostLineEdit->text(), portLineEdit->text().toInt());
7 }
具体看QTcpSocket::connectToHost()的代码
1 void QAbstractSocket::connectToHost(const QString &hostName, quint16 port,
2 OpenMode openMode)
3 {
4 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "connectToHostImplementation",
5 Qt::DirectConnection,
6 Q_ARG(QString, hostName),
7 Q_ARG(quint16, port),
8 Q_ARG(OpenMode, openMode));
9 }
调用的是QAbstractSocket::connectToHostImplementation()。
1 void QAbstractSocket::connectToHostImplementation(const QString &hostName, quint16 port,
2 OpenMode openMode)
3 {
4 Q_D(QAbstractSocket);
5 if (d->state == ConnectedState || d->state == ConnectingState || d->state == ClosingState) {
6 qWarning("QAbstractSocket::connectToHost() called when already connecting/connected to \"%s\"", qPrintable(hostName));
7 return;
8 }
9
10 d->hostName = hostName;
11 d->port = port;
12 d->state = UnconnectedState;
13 d->readBuffer.clear();
14 d->writeBuffer.clear();
15 d->abortCalled = false;
16 d->closeCalled = false;
17 d->pendingClose = false;
18 d->localPort = 0;
19 d->peerPort = 0;
20 d->localAddress.clear();
21 d->peerAddress.clear();
22 d->peerName = hostName;
23 if (d->hostLookupId != -1) {
24 QHostInfo::abortHostLookup(d->hostLookupId);
25 d->hostLookupId = -1;
26 }
27
28 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
29 // Get the proxy information
30 d->resolveProxy(hostName, port);
31 if (d->proxyInUse.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy) {
32 // failed to setup the proxy
33 d->socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError;
34 setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Operation on socket is not supported"));
35 emit error(d->socketError);
36 return;
37 }
38 #endif
39
40 if (!d_func()->isBuffered)
41 openMode |= QAbstractSocket::Unbuffered;
42 QIODevice::open(openMode); // ??
43 d->state = HostLookupState;
44 emit stateChanged(d->state);
45
46 QHostAddress temp;
47 if (temp.setAddress(hostName)) {
48 QHostInfo info;
49 info.setAddresses(QList<QHostAddress>() << temp);
50 d->_q_startConnecting(info);
51 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
52 } else if (d->proxyInUse.capabilities() & QNetworkProxy::HostNameLookupCapability) {
53 // the proxy supports connection by name, so use it
54 d->startConnectingByName(hostName);
55 return;
56 #endif
57 } else {
58 if (d->threadData->eventDispatcher)
59 d->hostLookupId = QHostInfo::lookupHost(hostName, this, SLOT(_q_startConnecting(QHostInfo)));
60 }
61 }
继续调用QAbstractSocket::_q_startConnecting(),是QAbstractSocket的私有信号。简单来说,_q_startConnecting()就是调用了_q_connectToNextAddress()而已。
1 void QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_connectToNextAddress()
2 {
3 Q_Q(QAbstractSocket);
4 do {
5 // Check for more pending addresses
6 if (addresses.isEmpty()) {
7 state = QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState;
8 if (socketEngine) {
9 if ((socketEngine->error() == QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketError
10 ) && socketEngine->state() == QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState) {
11 socketError = QAbstractSocket::ConnectionRefusedError;
12 q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Connection refused"));
13 } else {
14 socketError = socketEngine->error();
15 q->setErrorString(socketEngine->errorString());
16 }
17 } else {
18 // socketError = QAbstractSocket::ConnectionRefusedError;
19 // q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Connection refused"));
20 }
21 emit q->stateChanged(state);
22 emit q->error(socketError);
23 return;
24 }
25
26 // Pick the first host address candidate
27 host = addresses.takeFirst();
28
29 #if defined(QT_NO_IPV6)
30 if (host.protocol() == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) {
31 // If we have no IPv6 support, then we will not be able to
32 // connect. So we just pretend we didn't see this address.
33 continue;
34 }
35 #endif
36
37 if (!initSocketLayer(host.protocol())) {
38 // hope that the next address is better
39 continue;
40 }
41
42 // Tries to connect to the address. If it succeeds immediately
43 // (localhost address on BSD or any UDP connect), emit
44 // connected() and return.
45 if (socketEngine->connectToHost(host, port)) {
46 //_q_testConnection();
47 fetchConnectionParameters();
48 return;
49 }
50
51 // cache the socket descriptor even if we're not fully connected yet
52 cachedSocketDescriptor = socketEngine->socketDescriptor();
53
54 // Check that we're in delayed connection state. If not, try
55 // the next address
56 if (socketEngine->state() != QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState) {
57 continue;
58 }
59
60 // Start the connect timer.
61 if (threadData->eventDispatcher) {
62 if (!connectTimer) {
63 connectTimer = new QTimer(q);
64 QObject::connect(connectTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()),
65 q, SLOT(_q_abortConnectionAttempt()),
66 Qt::DirectConnection);
67 }
68 connectTimer->start(QT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
69 }
70
71 // Wait for a write notification that will eventually call
72 // _q_testConnection().
73 socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true);
74 break;
75 } while (state != QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState);
76 }
上面关键的三句,实际是把WinSocket编程中的简单过程分成三个阶段:socket初始化;connect到远程目标;设定Timer定时查看并处理Select的情况(收发数据或者关闭socket)。这里主要看前面两个:初始化和连接,select的处理放到明天分析。
1、初始化
1 bool QAbstractSocketPrivate::initSocketLayer(QAbstractSocket::NetworkLayerProtocol protocol)
2 {
3 #ifdef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
4 // this is here to avoid a duplication of the call to createSocketEngine below
5 static const QNetworkProxy &proxyInUse = *(QNetworkProxy *)0;
6 #endif
7
8 Q_Q(QAbstractSocket);
9
10 resetSocketLayer();
11 socketEngine = QAbstractSocketEngine::createSocketEngine(q->socketType(), proxyInUse, q);
12 if (!socketEngine) {
13 socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError;
14 q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Operation on socket is not supported"));
15 return false;
16 }
17 if (!socketEngine->initialize(q->socketType(), protocol)) {
18 socketError = socketEngine->error();
19 q->setErrorString(socketEngine->errorString());
20 return false;
21 }
22
23 if (threadData->eventDispatcher)
24 socketEngine->setReceiver(this);
25
26 return true;
27 }
28
29 QAbstractSocketEngine *QAbstractSocketEngine::createSocketEngine(QAbstractSocket::SocketType socketType, const QNetworkProxy &proxy, QObject *parent)
30 {
31 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
32 // proxy type must have been resolved by now
33 if (proxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy)
34 return 0;
35 #endif
36
37 QMutexLocker locker(&socketHandlers()->mutex);
38 for (int i = 0; i < socketHandlers()->size(); i++) {
39 if (QAbstractSocketEngine *ret = socketHandlers()->at(i)->createSocketEngine(socketType, proxy, parent))
40 return ret;
41 }
42
43 return new QNativeSocketEngine(parent);
44 }
上面可以知道socketEngine->initialize()实际调用的是QNativeSocketEngine::initialize()
1 bool QNativeSocketEngine::initialize(QAbstractSocket::SocketType socketType, QAbstractSocket::NetworkLayerProtocol protocol)
2 {
3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine);
4 if (isValid())
5 close();
6
7 #if defined(QT_NO_IPV6)
8 if (protocol == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) {
9 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError,
10 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NoIpV6ErrorString);
11 return false;
12 }
13 #endif
14
15 // Create the socket
16 if (!d->createNewSocket(socketType, protocol)) {
17 return false;
18 }
19
20 // Make the socket nonblocking.
21 if (!setOption(NonBlockingSocketOption, 1)) {
22 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError,
23 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NonBlockingInitFailedErrorString);
24 close();
25 return false;
26 }
27
28 // Set the broadcasting flag if it's a UDP socket.
29 if (socketType == QAbstractSocket::UdpSocket
30 && !setOption(BroadcastSocketOption, 1)) {
31 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError,
32 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::BroadcastingInitFailedErrorString);
33 close();
34 return false;
35 }
36
37 // Make sure we receive out-of-band data
38 if (socketType == QAbstractSocket::TcpSocket
39 && !setOption(ReceiveOutOfBandData, 1)) {
40 qWarning("QNativeSocketEngine::initialize unable to inline out-of-band data");
41 }
42
43 // Set the send and receive buffer sizes to a magic size, found
44 // most optimal for our platforms.
45 setReceiveBufferSize(49152);
46 setSendBufferSize(49152);
47
48 d->socketType = socketType;
49 d->socketProtocol = protocol;
50 return true;
51 }
至此,初始化过程完成,socket被设定为非阻塞模式(也就是Select会超时方式)。
2、connect到远程目标
1 bool QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(const QHostAddress &address, quint16 port)
2 {
3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine);
4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(), false);
5
6 #if defined (QT_NO_IPV6)
7 if (address.protocol() == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) {
8 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError,
9 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NoIpV6ErrorString);
10 return false;
11 }
12 #endif
13 if (!d->checkProxy(address))
14 return false;
15
16 Q_CHECK_STATES(QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(),
17 QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState, QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState, false);
18
19 d->peerAddress = address;
20 d->peerPort = port;
21 bool connected = d->nativeConnect(address, port);
22 if (connected)
23 d->fetchConnectionParameters();
24
25 return connected;
26 }
连接相对简单。
3、读取信息
在QAbstractSocket中,有两个成员是收发数据用的:readData()、writeData()
readData()有两种读取方式:有缓冲和无缓冲方式。基本原理是一致的,简单其见只分析无缓冲直接读取方式。
1 qint64 QAbstractSocket::readData(char *data, qint64 maxSize)
2 {
3 Q_D(QAbstractSocket);
4 if (d->socketEngine && !d->socketEngine->isReadNotificationEnabled() && d->socketEngine->isValid())
5 d->socketEngine->setReadNotificationEnabled(true);
6
7 if (!d->isBuffered) {
8 if (!d->socketEngine)
9 return -1; // no socket engine is probably EOF
10 qint64 readBytes = d->socketEngine->read(data, maxSize);
11 if (readBytes < 0) {
12 d->socketError = d->socketEngine->error();
13 setErrorString(d->socketEngine->errorString());
14 }
15 if (!d->socketEngine->isReadNotificationEnabled())
16 d->socketEngine->setReadNotificationEnabled(true);
17 return readBytes;
18 }
19
20 if (d->readBuffer.isEmpty())
21 // if we're still connected, return 0 indicating there may be more data in the future
22 // if we're not connected, return -1 indicating EOF
23 return d->state == QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState ? qint64(0) : qint64(-1);
24
25 // If readFromSocket() read data, copy it to its destination.
26 if (maxSize == 1) {
27 *data = d->readBuffer.getChar();
28 return 1;
29 }
30
31 qint64 bytesToRead = qMin(qint64(d->readBuffer.size()), maxSize);
32 qint64 readSoFar = 0;
33 while (readSoFar < bytesToRead) {
34 const char *ptr = d->readBuffer.readPointer();
35 int bytesToReadFromThisBlock = qMin(int(bytesToRead - readSoFar),
36 d->readBuffer.nextDataBlockSize());
37 memcpy(data + readSoFar, ptr, bytesToReadFromThisBlock);
38 readSoFar += bytesToReadFromThisBlock;
39 d->readBuffer.free(bytesToReadFromThisBlock);
40 }
41
42 return readSoFar;
43 }
从前面(二)可以知道,socketEngine->read()实际调用的是QNativeSocketEngine::read()
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEngine::read(char *data, qint64 maxSize)
2 {
3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine);
4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::read(), -1);
5 Q_CHECK_STATES(QNativeSocketEngine::read(), QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState, QAbstractSocket::BoundState, -1);
6
7 qint64 readBytes = d->nativeRead(data, maxSize);
8
9 // Handle remote close
10 if (readBytes == 0 && d->socketType == QAbstractSocket::TcpSocket) {
11 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::RemoteHostClosedError,
12 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::RemoteHostClosedErrorString);
13 close();
14 return -1;
15 }
16 return readBytes;
17 }
除了一些相关的检查,就是调用QNativeSocketPrivate::nativeRead()
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::nativeRead(char *data, qint64 maxLength)
2 {
3 qint64 ret = -1;
4 WSABUF buf;
5 buf.buf = data;
6 buf.len = maxLength;
7 DWORD flags = 0;
8 DWORD bytesRead = 0;
9 #if defined(Q_OS_WINCE)
10 WSASetLastError(0);
11 #endif
12 if (::WSARecv(socketDescriptor, &buf, 1, &bytesRead, &flags, 0,0) == SOCKET_ERROR) {
13 int err = WSAGetLastError();
14 WS_ERROR_DEBUG(err);
15 switch (err) {
16 case WSAEWOULDBLOCK:
17 ret = -2;
18 break;
19 case WSAEBADF:
20 case WSAEINVAL:
21 setError(QAbstractSocket::NetworkError, ReadErrorString);
22 break;
23 case WSAECONNRESET:
24 case WSAECONNABORTED:
25 // for tcp sockets this will be handled in QNativeSocketEngine::read
26 ret = 0;
27 break;
28 default:
29 break;
30 }
31 } else {
32 if (WSAGetLastError() == WSAEWOULDBLOCK)
33 ret = -2;
34 else
35 ret = qint64(bytesRead);
36 }
37
38 return ret;
39 }
至此,调用Windows API读取数据。
4、发送数据
同样分有缓存与无缓存方式,对无缓存方式:
1 qint64 QAbstractSocket::writeData(const char *data, qint64 size)
2 {
3 Q_D(QAbstractSocket);
4 if (d->state == QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState) {
5 d->socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketError;
6 setErrorString(tr("Socket is not connected"));
7 return -1;
8 }
9
10 if (!d->isBuffered) {
11 qint64 written = d->socketEngine->write(data, size);
12 if (written < 0) {
13 d->socketError = d->socketEngine->error();
14 setErrorString(d->socketEngine->errorString());
15 } else if (!d->writeBuffer.isEmpty()) {
16 d->socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true);
17 }
18 if (written >= 0)
19 emit bytesWritten(written);
20 return written;
21 }
22
23 char *ptr = d->writeBuffer.reserve(size);
24 if (size == 1)
25 *ptr = *data;
26 else
27 memcpy(ptr, data, size);
28
29 qint64 written = size;
30
31 if (d->socketEngine && !d->writeBuffer.isEmpty())
32 d->socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true);
33 return written;
34 }
查看QNativeSocketEngine::write():
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEngine::write(const char *data, qint64 size)
2 {
3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine);
4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::write(), -1);
5 Q_CHECK_STATE(QNativeSocketEngine::write(), QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState, -1);
6 return d->nativeWrite(data, size);
7 }
8
9 qint64 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::nativeWrite(const char *data, qint64 len)
10 {
11 Q_Q(QNativeSocketEngine);
12 qint64 ret = 0;
13 // don't send more than 49152 per call to WSASendTo to avoid getting a WSAENOBUFS
14 for (;;) {
15 qint64 bytesToSend = qMin<qint64>(49152, len - ret);
16 WSABUF buf;
17 buf.buf = (char*)data + ret;
18 buf.len = bytesToSend;
19 DWORD flags = 0;
20 DWORD bytesWritten = 0;
21
22 int socketRet = ::WSASend(socketDescriptor, &buf, 1, &bytesWritten, flags, 0,0);
23
24 ret += qint64(bytesWritten);
25
26 if (socketRet != SOCKET_ERROR) {
27 if (ret == len)
28 break;
29 else
30 continue;
31 } else if (WSAGetLastError() == WSAEWOULDBLOCK) {
32 break;
33 } else {
34 int err = WSAGetLastError();
35 WS_ERROR_DEBUG(err);
36 switch (err) {
37 case WSAECONNRESET:
38 case WSAECONNABORTED:
39 ret = -1;
40 setError(QAbstractSocket::NetworkError, WriteErrorString);
41 q->close();
42 break;
43 default:
44 break;
45 }
46 break;
47 }
48 }
49 return ret;
50 }
至此分析完毕。
前面分析中,一个问题一直没有解决:新生成的SOCKET是什么时候加入WSASelect()的?另外还有一个不是很大的问题,close流程。
在
1 QEventDispatcherWin32Private::doWsaAsyncSelect()
中WSAAsyncSelect()设置一个断点,观察call stack:
1 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32Private::doWsaAsyncSelect(int socket=0x00001628) 行633 C++
2 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32::registerSocketNotifier(QSocketNotifier * notifier=0x00c6f248) 行829 C++
3 QtCored4.dll!QSocketNotifier::QSocketNotifier(int socket=0x00001628, QSocketNotifier::Type type=Write, QObject * parent=0x00c66228) 行185 C++
4 QtNetworkd4.dll!QWriteNotifier::QWriteNotifier(int fd=0x00001628, QNativeSocketEngine * parent=0x00c66228) 行1053 + 0x1a 字节 C++
5 QtNetworkd4.dll!QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled(bool enable=true) 行1118 + 0x2d 字节 C++
6 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_connectToNextAddress() 行996 C++
7 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_startConnecting(const QHostInfo & hostInfo={...}) 行890 C++
8 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocket::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c=InvokeMetaMethod, int _id=0x0000000a, void * * _a=0x00c6e510) 行104 + 0x16 字节 C++
9 QtNetworkd4.dll!QTcpSocket::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c=InvokeMetaMethod, int _id=0x00000012, void * * _a=0x00c6e510) 行58 + 0x14 字节 C++
10 QtCored4.dll!QMetaCallEvent::placeMetaCall(QObject * object=0x00c4f790) 行478 C++
11 QtCored4.dll!QObject::event(QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行1102 + 0x14 字节 C++
12 QtGuid4.dll!QApplicationPrivate::notify_helper(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行4065 + 0x11 字节 C++
13 QtGuid4.dll!QApplication::notify(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行3605 + 0x10 字节 C++
14 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplication::notifyInternal(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * event=0x00c4d8a0) 行610 + 0x15 字节 C++
15 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplication::sendEvent(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * event=0x00c4d8a0) 行213 + 0x39 字节 C++
16 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplicationPrivate::sendPostedEvents(QObject * receiver=0x00000000, int event_type=0x00000000, QThreadData * data=0x00bc8890) 行1247 + 0xd 字节 C++
17 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行679 + 0x10 字节 C++
18 QtGuid4.dll!QGuiEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行1182 + 0x15 字节 C++
19 QtCored4.dll!QEventLoop::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行150 C++
20 QtCored4.dll!QEventLoop::exec(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行201 + 0x2d 字节 C++
21 QtGuid4.dll!QDialog::exec() 行499 C++
22 fortuneclient.exe!main(int argc=0x00000001, char * * argv=0x00bc8750) 行51 + 0x9 字节 C++
23 fortuneclient.exe!WinMain(HINSTANCE__ * instance=0x00400000, HINSTANCE__ * prevInstance=0x00000000, char * __formal=0x001520e2, int cmdShow=0x00000001) 行137 + 0x12 字节 C++
24 fortuneclient.exe!__tmainCRTStartup() 行574 + 0x35 字节 C
25 fortuneclient.exe!WinMainCRTStartup() 行399 C
26 kernel32.dll!7c82f23b()
[下面的框架可能不正确和/或缺失,没有为 kernel32.dll 加载符号]
看QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled()的代码实现:
1 void QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled(bool enable)
2 {
3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine);
4 if (d->writeNotifier) {
5 d->writeNotifier->setEnabled(enable);
6 } else if (enable && d->threadData->eventDispatcher) {
7 d->writeNotifier = new QWriteNotifier(d->socketDescriptor, this);
8 d->writeNotifier->setEnabled(true);
9 }
10 }
在QWriteNotifier对象新建的时候,引起其父类的构建:QSocketNotifier
1 QSocketNotifier::QSocketNotifier(int socket, Type type, QObject *parent)
2 : QObject(parent)
3 {
4 if (socket < 0)
5 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Invalid socket specified");
6 sockfd = socket;
7 sntype = type;
8 snenabled = true;
9
10 Q_D(QObject);
11 if (!d->threadData->eventDispatcher) {
12 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Can only be used with threads started with QThread");
13 } else {
14 d->threadData->eventDispatcher->registerSocketNotifier(this);
15 }
16 }
原来是通过获取当前线程数据得到Dispatcher的指针(QEventDispatcherWin32),通过其注册QNativeSocketEngine对象自己本身。
1 void QEventDispatcherWin32::registerSocketNotifier(QSocketNotifier *notifier)
2 {
3 Q_ASSERT(notifier);
4 int sockfd = notifier->socket();
5 int type = notifier->type();
6
7 Q_D(QEventDispatcherWin32);
8 QSNDict *sn_vec[3] = { &d->sn_read, &d->sn_write, &d->sn_except };
9 QSNDict *dict = sn_vec[type];
10
11 if (QCoreApplication::closingDown()) // ### d->exitloop?
12 return; // after sn_cleanup, don't reinitialize.
13
14 if (dict->contains(sockfd)) {
15 const char *t[] = { "Read", "Write", "Exception" };
16 /* Variable "socket" below is a function pointer. */
17 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Multiple socket notifiers for "
18 "same socket %d and type %s", sockfd, t[type]);
19 }
20
21 QSockNot *sn = new QSockNot;
22 sn->obj = notifier;
23 sn->fd = sockfd;
24 dict->insert(sn->fd, sn);
25
26 if (d->internalHwnd)
27 d->doWsaAsyncSelect(sockfd);
28 }
在这里跟前面分析的QEventDispatcherWin32消息处理搭上关系了,把QWriteNotifier对象加入到系统的列表中;在QApplication::exec()的消息循环中,就能够获取目标对象了。
今天分析QNetworkAccessManager、QNetworkRequest和QNetworkReply组成的高级抽象API序列。在动手之前,把doc中有关QNetworkAccessManager的介绍看了一遍。其使用方法大致是:
1 QNetworkAccessManager * manager = new QNetworkAccessManager(this);
2 QNetworkRequest request;
3 request.setUrl(QUrl("http://www.baidu.com"));
4 QNetworkReply * reply = manager->get(request);
5 connect(reply, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(slotReadyRead()));
关键是后面的三行:设定URL、发送并获取响应、读取数据。
在QT自带的例子中也有QNetworkAccessManager的应用:downloadmanager
单步跟踪就用downloadmanager这个例子。
在动手跟踪之前,总结了几个问题:
1、QNetworkAccessManager是更高级的抽象,那么怎么跟QTcpSocket/QUdpSocket联系起来的呢?
2、如果没有跟QTcpSocket联系起来,那么又是怎么跟WSA序列WinAPI联系起来的呢?
3、整个逻辑过程是怎么的呢?
4、获取的(图片或者网页)数据保存在什么地方?
5、跟HTTP或者FTP有关的Cookie、认证等怎么实现的?
6、HTTP的Session相关功能实现了吗?怎么实现的?
在动手分析前,简单介绍一下HTTP协议。HTTP协议是一种为分布式,合作式,超媒体信息系统。它是一种通用的,无状态(stateless)的协议,除了应用于超文本传输外,它也可以应用于诸如名称服务器和分布对象管理系统之类的系统,这可以通过扩展它的请求方法,错误代码和报头来实现。HTTP的一个特点是数据表现形式是可输入的和可协商性的,这就允许系统能被建立而独立于数据传输。HTTP在1990年WWW全球信息刚刚起步的时候就得到了应用。该规范定义的协议用“HTTP/1.1”表示,是对RFC2608[33]的更新。 HTTP协议是通过定义一序列的动作(协议文本中称为方法),来完成数据的传输通信。HTTP1.1版本中有这些方法:get、post、head、options、put、delete、trace、connect。
get方法用于获取URI资源,是最为常用的一种方法。
post方法用于向指定URI提交内容,服务器端响应其行为,该方法也极为常用。
head方法向URI发送请求,仅仅只需要获得响应的协议头。
put方法用于向URI发送请求,若URI不存在,则要求服务器端根据请求创建资源。当URI存在时,服务器端必须接受请求内容,将其作为URI资源的修改后版本。
delete方法用于删除URI标识的指定资源。
trace方法用于激活服务器端对请求的循环反馈,反馈作为http响应的正文内容被传输回客户端。
connect方法通常被用于使用代理连接。
更详细的内容请查看相关资料。
回到QT系统,manager->get()调用其实就是HTTP/1.1协议中get方法的实现。
1 QNetworkReply *QNetworkAccessManager::get(const QNetworkRequest &request)
2 {
3 return d_func()->postProcess(createRequest(QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation, request));
4 }
上面的一行程序中有两个调用
1 QNetworkAccessManager::createRequest() 2 QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::postProcess()
先来看createRequest(),两个参数:第一个参数表示使用Get方法;第二个参数是目标网址。
1 QNetworkReply *QNetworkAccessManager::createRequest(QNetworkAccessManager::Operation op,
2 const QNetworkRequest &req,
3 QIODevice *outgoingData)
4 {
5 Q_D(QNetworkAccessManager);
6
7 bool isLocalFile = req.url().isLocalFile();
8 QString scheme = req.url().scheme().toLower();
9
10 // fast path for GET on file:// URLs
11 // The QNetworkAccessFileBackend will right now only be used for PUT
12 if ((op == QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation || op == QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation)
13 && (isLocalFile || scheme == QLatin1String("qrc"))) {
14 return new QNetworkReplyFileImpl(this, req, op);
15 }
16
17 if ((op == QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation || op == QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation)
18 && scheme == QLatin1String("data")) {
19 return new QNetworkReplyDataImpl(this, req, op);
20 }
21
22 // A request with QNetworkRequest::AlwaysCache does not need any bearer management
23 QNetworkRequest::CacheLoadControl mode =
24 static_cast<QNetworkRequest::CacheLoadControl>(
25 req.attribute(QNetworkRequest::CacheLoadControlAttribute,
26 QNetworkRequest::PreferNetwork).toInt());
27 if (mode == QNetworkRequest::AlwaysCache
28 && (op == QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation
29 || op == QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation)) {
30 // FIXME Implement a QNetworkReplyCacheImpl instead, see QTBUG-15106
31 QNetworkReplyImpl *reply = new QNetworkReplyImpl(this);
32 QNetworkReplyImplPrivate *priv = reply->d_func();
33 priv->manager = this;
34 priv->backend = new QNetworkAccessCacheBackend();
35 priv->backend->manager = this->d_func();
36 priv->backend->setParent(reply);
37 priv->backend->reply = priv;
38 priv->setup(op, req, outgoingData);
39 return reply;
40 }
41
42 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
43 // Return a disabled network reply if network access is disabled.
44 // Except if the scheme is empty or file://.
45 if (!d->networkAccessible && !isLocalFile) {
46 return new QDisabledNetworkReply(this, req, op);
47 }
48
49 if (!d->networkSessionStrongRef && (d->initializeSession || !d->networkConfiguration.isEmpty())) {
50 QNetworkConfigurationManager manager;
51 if (!d->networkConfiguration.isEmpty()) {
52 d->createSession(manager.configurationFromIdentifier(d->networkConfiguration));
53 } else {
54 if (manager.capabilities() & QNetworkConfigurationManager::NetworkSessionRequired)
55 d->createSession(manager.defaultConfiguration());
56 else
57 d->initializeSession = false;
58 }
59 }
60 #endif
61
62 QNetworkRequest request = req;
63 if (!request.header(QNetworkRequest::ContentLengthHeader).isValid() &&
64 outgoingData && !outgoingData->isSequential()) {
65 // request has no Content-Length
66 // but the data that is outgoing is random-access
67 request.setHeader(QNetworkRequest::ContentLengthHeader, outgoingData->size());
68 }
69
70 if (static_cast<QNetworkRequest::LoadControl>
71 (request.attribute(QNetworkRequest::CookieLoadControlAttribute,
72 QNetworkRequest::Automatic).toInt()) == QNetworkRequest::Automatic) {
73 if (d->cookieJar) {
74 QList<QNetworkCookie> cookies = d->cookieJar->cookiesForUrl(request.url());
75 if (!cookies.isEmpty())
76 request.setHeader(QNetworkRequest::CookieHeader, QVariant::fromValue(cookies));
77 }
78 }
79
80 // first step: create the reply
81 QUrl url = request.url();
82 QNetworkReplyImpl *reply = new QNetworkReplyImpl(this);
83 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
84 if (!isLocalFile) {
85 connect(this, SIGNAL(networkSessionConnected()),
86 reply, SLOT(_q_networkSessionConnected()));
87 }
88 #endif
89 QNetworkReplyImplPrivate *priv = reply->d_func();
90 priv->manager = this;
91
92 // second step: fetch cached credentials
93 // This is not done for the time being, we should use signal emissions to request
94 // the credentials from cache.
95
96 // third step: find a backend
97 priv->backend = d->findBackend(op, request);
98
99 if (priv->backend) {
100 priv->backend->setParent(reply);
101 priv->backend->reply = priv;
102 }
103
104 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
105 reply->setSslConfiguration(request.sslConfiguration());
106 #endif
107
108 // fourth step: setup the reply
109 priv->setup(op, request, outgoingData);
110
111 return reply;
112 }
代码比较长,主要做了这些事情:
1、设定HTTP请求的头信息(例如客户端请求内容的长度、Cookie等)
2、生成并初始化Reply对象(实际是QNetworkReplyImpl对象)
3、获取本地缓存的认证信息(如果有的话)
4、设定Reply
5、获取一个backend实体
6、如果支持OPENSSL的话,设定SSL的配置
暂时先放一边后面再对createRequest()做进一步的分析,再来看postProcess()
1 QNetworkReply *QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::postProcess(QNetworkReply *reply)
2 {
3 Q_Q(QNetworkAccessManager);
4 QNetworkReplyPrivate::setManager(reply, q);
5 q->connect(reply, SIGNAL(finished()), SLOT(_q_replyFinished()));
6 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
7 /* In case we're compiled without SSL support, we don't have this signal and we need to
8 * avoid getting a connection error. */
9 q->connect(reply, SIGNAL(sslErrors(QList<QSslError>)), SLOT(_q_replySslErrors(QList<QSslError>)));
10 #endif
11 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
12 activeReplyCount++;
13 #endif
14
15 return reply;
16 }
简单来说就做了一件事情,把QNetworkReply的信号(finished、sslErrors)与QNetworkAccessManager的槽连接起来
接上面,进一步分析QNetworkAccessManager::createRequest()的实现。去除不重要的分支末节,看其调用的QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::setup()和QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::findBackend()的代码
1 void QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::setup(QNetworkAccessManager::Operation op, const QNetworkRequest &req,
2 QIODevice *data)
3 {
4 Q_Q(QNetworkReplyImpl);
5
6 outgoingData = data; //outgoingData实际就是QNetworkRequest对象
7 request = req;
8 url = request.url();
9 operation = op;
10
11 q->QIODevice::open(QIODevice::ReadOnly);
12 // Internal code that does a HTTP reply for the synchronous Ajax
13 // in QtWebKit.
14 QVariant synchronousHttpAttribute = req.attribute(
15 static_cast<QNetworkRequest::Attribute>(QNetworkRequest::SynchronousRequestAttribute));
16 // The synchronous HTTP is a corner case, we will put all upload data in one big QByteArray in the outgoingDataBuffer.
17 // Yes, this is not the most efficient thing to do, but on the other hand synchronous XHR needs to die anyway.
18 if (synchronousHttpAttribute.toBool() && outgoingData) {
19 outgoingDataBuffer = QSharedPointer<QRingBuffer>(new QRingBuffer());
20 qint64 previousDataSize = 0;
21 do {
22 previousDataSize = outgoingDataBuffer->size();
23 outgoingDataBuffer->append(outgoingData->readAll());
24 } while (outgoingDataBuffer->size() != previousDataSize);
25 }
26
27 if (backend)
28 backend->setSynchronous(synchronousHttpAttribute.toBool());
29
30
31 if (outgoingData && backend && !backend->isSynchronous()) {
32 // there is data to be uploaded, e.g. HTTP POST.
33
34 if (!backend->needsResetableUploadData() || !outgoingData->isSequential()) {
35 // backend does not need upload buffering or
36 // fixed size non-sequential
37 // just start the operation
38 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_startOperation", Qt::QueuedConnection);
39 } else {
40 bool bufferingDisallowed =
41 req.attribute(QNetworkRequest::DoNotBufferUploadDataAttribute,
42 false).toBool();
43
44 if (bufferingDisallowed) {
45 // if a valid content-length header for the request was supplied, we can disable buffering
46 // if not, we will buffer anyway
47 if (req.header(QNetworkRequest::ContentLengthHeader).isValid()) {
48 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_startOperation", Qt::QueuedConnection);
49 } else {
50 state = Buffering;
51 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_bufferOutgoingData", Qt::QueuedConnection);
52 }
53 } else {
54 // _q_startOperation will be called when the buffering has finished.
55 state = Buffering;
56 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_bufferOutgoingData", Qt::QueuedConnection);
57 }
58 }
59 } else {
60 // for HTTP, we want to send out the request as fast as possible to the network, without
61 // invoking methods in a QueuedConnection
62 #ifndef QT_NO_HTTP
63 if (qobject_cast<QNetworkAccessHttpBackend *>(backend) || (backend && backend->isSynchronous())) {
64 _q_startOperation();
65 } else {
66 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_startOperation", Qt::QueuedConnection);
67 }
68 #else
69 if (backend && backend->isSynchronous())
70 _q_startOperation();
71 else
72 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(q, "_q_startOperation", Qt::QueuedConnection);
73 #endif // QT_NO_HTTP
74 }
75 }
发现调用_q_startOperation函数和_q_bufferOutgoingData函数,代码如下
1 void QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::_q_startOperation()
2 {
3 // ensure this function is only being called once
4 if (state == Working || state == Finished) {
5 qDebug("QNetworkReplyImpl::_q_startOperation was called more than once");
6 return;
7 }
8 state = Working;
9
10 // note: if that method is called directly, it cannot happen that the backend is 0,
11 // because we just checked via a qobject_cast that we got a http backend (see
12 // QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::setup())
13 if (!backend) {
14 error(QNetworkReplyImpl::ProtocolUnknownError,
15 QCoreApplication::translate("QNetworkReply", "Protocol \"%1\" is unknown").arg(url.scheme())); // not really true!;
16 finished();
17 return;
18 }
19
20 if (!backend->start()) {
21 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
22 // backend failed to start because the session state is not Connected.
23 // QNetworkAccessManager will call _q_startOperation again for us when the session
24 // state changes.
25 state = WaitingForSession;
26
27 QSharedPointer<QNetworkSession> session(manager->d_func()->getNetworkSession());
28
29 if (session) {
30 Q_Q(QNetworkReplyImpl);
31
32 QObject::connect(session.data(), SIGNAL(error(QNetworkSession::SessionError)),
33 q, SLOT(_q_networkSessionFailed()), Qt::QueuedConnection);
34
35 if (!session->isOpen())
36 session->open();
37 } else {
38 qWarning("Backend is waiting for QNetworkSession to connect, but there is none!");
39 state = Working;
40 error(QNetworkReplyImpl::UnknownNetworkError,
41 QCoreApplication::translate("QNetworkReply", "Network session error."));
42 finished();
43 }
44 #else
45 qWarning("Backend start failed");
46 state = Working;
47 error(QNetworkReplyImpl::UnknownNetworkError,
48 QCoreApplication::translate("QNetworkReply", "backend start error."));
49 finished();
50 #endif
51 return;
52 }
53
54 if (backend && backend->isSynchronous()) {
55 state = Finished;
56 q_func()->setFinished(true);
57 } else {
58 if (state != Finished) {
59 if (operation == QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation)
60 pendingNotifications.append(NotifyDownstreamReadyWrite);
61
62 handleNotifications();
63 }
64 }
65 }
1 void QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::_q_bufferOutgoingData()
2 {
3 Q_Q(QNetworkReplyImpl);
4
5 if (!outgoingDataBuffer) {
6 // first call, create our buffer
7 outgoingDataBuffer = QSharedPointer<QRingBuffer>(new QRingBuffer());
8
9 QObject::connect(outgoingData, SIGNAL(readyRead()), q, SLOT(_q_bufferOutgoingData()));
10 QObject::connect(outgoingData, SIGNAL(readChannelFinished()), q, SLOT(_q_bufferOutgoingDataFinished()));
11 }
12
13 qint64 bytesBuffered = 0;
14 qint64 bytesToBuffer = 0;
15
16 // read data into our buffer
17 forever {
18 bytesToBuffer = outgoingData->bytesAvailable();
19 // unknown? just try 2 kB, this also ensures we always try to read the EOF
20 if (bytesToBuffer <= 0)
21 bytesToBuffer = 2*1024;
22
23 char *dst = outgoingDataBuffer->reserve(bytesToBuffer);
24 bytesBuffered = outgoingData->read(dst, bytesToBuffer);
25
26 if (bytesBuffered == -1) {
27 // EOF has been reached.
28 outgoingDataBuffer->chop(bytesToBuffer);
29
30 _q_bufferOutgoingDataFinished();
31 break;
32 } else if (bytesBuffered == 0) {
33 // nothing read right now, just wait until we get called again
34 outgoingDataBuffer->chop(bytesToBuffer);
35
36 break;
37 } else {
38 // don't break, try to read() again
39 outgoingDataBuffer->chop(bytesToBuffer - bytesBuffered);
40 }
41 }
42 }
连接两个信号与槽之后,是打开QIODevice,暂未深入分析。然后是呼叫q->_q_startOperation(),实际就是调用QNetworkReplyImpl::_q_startOperation(),使用的是队列等待方式(也就是发送一个消息进入系统消息队列,这个setup函数以及全部后续执行完毕,主动权交回给Windows后,再根据进入队列的消息来触发)。
_q_startOperation就是做了一些简单的判断,然后调用 handleNotifications
1 void QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::handleNotifications()
2 {
3 if (notificationHandlingPaused)
4 return;
5
6 NotificationQueue current = pendingNotifications;
7 pendingNotifications.clear();
8
9 if (state != Working)
10 return;
11
12 while (state == Working && !current.isEmpty()) {
13 InternalNotifications notification = current.dequeue();
14 switch (notification) {
15 case NotifyDownstreamReadyWrite:
16 if (copyDevice)
17 _q_copyReadyRead();
18 else
19 backend->downstreamReadyWrite();
20 break;
21
22 case NotifyCloseDownstreamChannel:
23 backend->closeDownstreamChannel();
24 break;
25
26 case NotifyCopyFinished: {
27 QIODevice *dev = copyDevice;
28 copyDevice = 0;
29 backend->copyFinished(dev);
30 break;
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 }
该函数主要用于处理各种socket相关事件
因此我们先看QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::findBackend()的代码实现
1 QNetworkAccessBackend *QNetworkAccessManagerPrivate::findBackend(QNetworkAccessManager::Operation op,
2 const QNetworkRequest &request)
3 {
4 if (QNetworkAccessBackendFactoryData::valid) {
5 QMutexLocker locker(&factoryData()->mutex);
6 QNetworkAccessBackendFactoryData::ConstIterator it = factoryData()->constBegin(),
7 end = factoryData()->constEnd();
8 while (it != end) {
9 QNetworkAccessBackend *backend = (*it)->create(op, request);
10 if (backend) {
11 backend->manager = this;
12 return backend; // found a factory that handled our request
13 }
14 ++it;
15 }
16 }
17 return 0;
18 }
这段代码有一点复杂,先看红色标记的第一句,factoryData()是用宏来定义的函数:
1 Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(QNetworkAccessBackendFactoryData, factoryData)
宏定义如下:
1 #define Q_GLOBAL_STATIC(TYPE, NAME) \
2 static TYPE *NAME() \
3 { \
4 static TYPE thisVariable; \
5 static QGlobalStatic<TYPE > thisGlobalStatic(&thisVariable); \
6 return thisGlobalStatic.pointer; \
7 }
如果对STD比较熟悉,第一感觉这是一个模板List操作。在这里constBegin()和constEnd()组合起来是一个遍历,那么在什么地方设定值呢?良好代码的命名是很规范的,我试了试全局查找factoryData(),找到了我所希望看到的东西:
1 QNetworkAccessBackendFactory::QNetworkAccessBackendFactory()
2 {
3 QMutexLocker locker(&factoryData()->mutex);
4 factoryData()->append(this);
5 }
6
7 QNetworkAccessBackendFactory::~QNetworkAccessBackendFactory()
8 {
9 if (QNetworkAccessBackendFactoryData::valid) {
10 QMutexLocker locker(&factoryData()->mutex);
11 factoryData()->removeAll(this);
12 }
13 }
里prepend()应该是把对象添加到列表;而removeAll()就是清空全部数据了。
factoryData()里面包含的对象序列,应该是从QNetworkAccessBackendFactory衍生出来的。
一共有哪些子类呢?继续全局查找
1 class QNetworkAccessDataBackendFactory: public QNetworkAccessBackendFactory 2 class QNetworkAccessDebugPipeBackendFactory: public QNetworkAccessBackendFactory 3 class QNetworkAccessFileBackendFactory: public QNetworkAccessBackendFactory 4 class QNetworkAccessFtpBackendFactory: public QNetworkAccessBackendFactory 5 class QNetworkAccessHttpBackendFactory : public QNetworkAccessBackendFactory
去除暂时不关心的DebugPipe,一共有四种:DataBackend、FileBackend、FtpBackend、HttpBackend。媒体的种类原来是在这里实现的。看其中QNetworkAccessHttpBackendFactory::create()
1 QNetworkAccessBackend *
2 QNetworkAccessHttpBackendFactory::create(QNetworkAccessManager::Operation op,
3 const QNetworkRequest &request) const
4 {
5 // check the operation
6 switch (op) {
7 case QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation:
8 case QNetworkAccessManager::PostOperation:
9 case QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation:
10 case QNetworkAccessManager::PutOperation:
11 case QNetworkAccessManager::DeleteOperation:
12 case QNetworkAccessManager::CustomOperation:
13 break;
14
15 default:
16 // no, we can't handle this request
17 return 0;
18 }
19
20 QUrl url = request.url();
21 QString scheme = url.scheme().toLower();
22 if (scheme == QLatin1String("http") || scheme == QLatin1String("https"))
23 return new QNetworkAccessHttpBackend;
24
25 return 0;
26 }
如果是能够处理的OP标记并且URL的前缀是http或者是https,则创建一个QNetworkAccessHttpBackend对象。
前面QNetworkAccessManager::get()代码中,调用的参数是QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation,所以在我们分析的这个应用中,创建的是QNetworkAccessHttpBackend对象。
findBackend()到此分析完毕;由于factoryData()的具体实现跟我们分析网络通信的目标没有太大关系,未深入分析,有谁分析了的话请转告一声,值得一看。
回到前面暂停的QNetworkReplyImpl::_q_startOperation(),又实现了什么动作呢?
首先调用了刚刚创建的QNetworkAccessHttpBackend::start(),然后是添加通知消息、调用_q_sourceReadyRead()、最后处理通知消息
1 bool QNetworkAccessBackend::start()
2 {
3 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
4 // For bearer, check if session start is required
5 QSharedPointer<QNetworkSession> networkSession(manager->getNetworkSession());
6 if (networkSession) {
7 // session required
8 if (networkSession->isOpen() &&
9 networkSession->state() == QNetworkSession::Connected) {
10 // Session is already open and ready to use.
11 // copy network session down to the backend
12 setProperty("_q_networksession", QVariant::fromValue(networkSession));
13 } else {
14 // Session not ready, but can skip for loopback connections
15
16 // This is not ideal.
17 const QString host = reply->url.host();
18
19 if (host == QLatin1String("localhost") ||
20 QHostAddress(host) == QHostAddress::LocalHost ||
21 QHostAddress(host) == QHostAddress::LocalHostIPv6) {
22 // Don't need an open session for localhost access.
23 } else {
24 // need to wait for session to be opened
25 return false;
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 #endif
30
31 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
32 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
33 // Get the proxy settings from the network session (in the case of service networks,
34 // the proxy settings change depending which AP was activated)
35 QNetworkSession *session = networkSession.data();
36 QNetworkConfiguration config;
37 if (session) {
38 QNetworkConfigurationManager configManager;
39 // The active configuration tells us what IAP is in use
40 QVariant v = session->sessionProperty(QLatin1String("ActiveConfiguration"));
41 if (v.isValid())
42 config = configManager.configurationFromIdentifier(qvariant_cast<QString>(v));
43 // Fallback to using the configuration if no active configuration
44 if (!config.isValid())
45 config = session->configuration();
46 // or unspecified configuration if that is no good either
47 if (!config.isValid())
48 config = QNetworkConfiguration();
49 }
50 reply->proxyList = manager->queryProxy(QNetworkProxyQuery(config, url()));
51 #else // QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
52 // Without bearer management, the proxy depends only on the url
53 reply->proxyList = manager->queryProxy(QNetworkProxyQuery(url()));
54 #endif
55 #endif
56
57 // now start the request
58 open();
59 return true;
60 }
start函数很简单,主要是打开QNetworkAccessBackend
话说昨日走到QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::_q_startOperation(),勾引出QNetworkAccessHttpBackend::open(),今日接着欣赏QT之美丽
1 void QNetworkAccessHttpBackend::open()
2 {
3 postRequest();
4 }
open函数仅仅是调用postRequest()
1 etworkAccessHttpBackend::postRequest()
2 {
3 QThread *thread = 0;
4 if (isSynchronous()) {
5 // A synchronous HTTP request uses its own thread
6 thread = new QThread();
7 QObject::connect(thread, SIGNAL(finished()), thread, SLOT(deleteLater()));
8 thread->start();
9 } else if (!manager->httpThread) {
10 // We use the manager-global thread.
11 // At some point we could switch to having multiple threads if it makes sense.
12 manager->httpThread = new QThread();
13 QObject::connect(manager->httpThread, SIGNAL(finished()), manager->httpThread, SLOT(deleteLater()));
14 manager->httpThread->start();
15 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
16 qRegisterMetaType<QNetworkProxy>("QNetworkProxy");
17 #endif
18 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
19 qRegisterMetaType<QList<QSslError> >("QList<QSslError>");
20 qRegisterMetaType<QSslConfiguration>("QSslConfiguration");
21 #endif
22 qRegisterMetaType<QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> > >("QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >");
23 qRegisterMetaType<QHttpNetworkRequest>("QHttpNetworkRequest");
24 qRegisterMetaType<QNetworkReply::NetworkError>("QNetworkReply::NetworkError");
25 qRegisterMetaType<QSharedPointer<char> >("QSharedPointer<char>");
26
27 thread = manager->httpThread;
28 } else {
29 // Asynchronous request, thread already exists
30 thread = manager->httpThread;
31 }
32
33 QUrl url = request().url();
34 httpRequest.setUrl(url);
35
36 bool ssl = url.scheme().toLower() == QLatin1String("https");
37 setAttribute(QNetworkRequest::ConnectionEncryptedAttribute, ssl);
38 httpRequest.setSsl(ssl);
39
40
41 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
42 QNetworkProxy transparentProxy, cacheProxy;
43
44 foreach (const QNetworkProxy &p, proxyList()) {
45 // use the first proxy that works
46 // for non-encrypted connections, any transparent or HTTP proxy
47 // for encrypted, only transparent proxies
48 if (!ssl
49 && (p.capabilities() & QNetworkProxy::CachingCapability)
50 && (p.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpProxy ||
51 p.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpCachingProxy)) {
52 cacheProxy = p;
53 transparentProxy = QNetworkProxy::NoProxy;
54 break;
55 }
56 if (p.isTransparentProxy()) {
57 transparentProxy = p;
58 cacheProxy = QNetworkProxy::NoProxy;
59 break;
60 }
61 }
62
63 // check if at least one of the proxies
64 if (transparentProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy &&
65 cacheProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy) {
66 // unsuitable proxies
67 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "error", isSynchronous() ? Qt::DirectConnection : Qt::QueuedConnection,
68 Q_ARG(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, QNetworkReply::ProxyNotFoundError),
69 Q_ARG(QString, tr("No suitable proxy found")));
70 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "finished", isSynchronous() ? Qt::DirectConnection : Qt::QueuedConnection);
71 return;
72 }
73 #endif
74
75
76 bool loadedFromCache = false;
77 httpRequest.setPriority(convert(request().priority()));
78
79 switch (operation()) {
80 case QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation:
81 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Get);
82 loadedFromCache = loadFromCacheIfAllowed(httpRequest);
83 break;
84
85 case QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation:
86 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Head);
87 loadedFromCache = loadFromCacheIfAllowed(httpRequest);
88 break;
89
90 case QNetworkAccessManager::PostOperation:
91 invalidateCache();
92 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Post);
93 createUploadByteDevice();
94 break;
95
96 case QNetworkAccessManager::PutOperation:
97 invalidateCache();
98 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Put);
99 createUploadByteDevice();
100 break;
101
102 case QNetworkAccessManager::DeleteOperation:
103 invalidateCache();
104 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Delete);
105 break;
106
107 case QNetworkAccessManager::CustomOperation:
108 invalidateCache(); // for safety reasons, we don't know what the operation does
109 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Custom);
110 createUploadByteDevice();
111 httpRequest.setCustomVerb(request().attribute(
112 QNetworkRequest::CustomVerbAttribute).toByteArray());
113 break;
114
115 default:
116 break; // can't happen
117 }
118
119 if (loadedFromCache) {
120 // commented this out since it will be called later anyway
121 // by copyFinished()
122 //QNetworkAccessBackend::finished();
123 return; // no need to send the request! :)
124 }
125
126 QList<QByteArray> headers = request().rawHeaderList();
127 if (resumeOffset != 0) {
128 if (headers.contains("Range")) {
129 // Need to adjust resume offset for user specified range
130
131 headers.removeOne("Range");
132
133 // We've already verified that requestRange starts with "bytes=", see canResume.
134 QByteArray requestRange = request().rawHeader("Range").mid(6);
135
136 int index = requestRange.indexOf('-');
137
138 quint64 requestStartOffset = requestRange.left(index).toULongLong();
139 quint64 requestEndOffset = requestRange.mid(index + 1).toULongLong();
140
141 requestRange = "bytes=" + QByteArray::number(resumeOffset + requestStartOffset) +
142 '-' + QByteArray::number(requestEndOffset);
143
144 httpRequest.setHeaderField("Range", requestRange);
145 } else {
146 httpRequest.setHeaderField("Range", "bytes=" + QByteArray::number(resumeOffset) + '-');
147 }
148 }
149
150 foreach (const QByteArray &header, headers)
151 httpRequest.setHeaderField(header, request().rawHeader(header));
152
153 if (request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::HttpPipeliningAllowedAttribute).toBool() == true)
154 httpRequest.setPipeliningAllowed(true);
155
156 if (static_cast<QNetworkRequest::LoadControl>
157 (request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::AuthenticationReuseAttribute,
158 QNetworkRequest::Automatic).toInt()) == QNetworkRequest::Manual)
159 httpRequest.setWithCredentials(false);
160
161
162 // Create the HTTP thread delegate
163 QHttpThreadDelegate *delegate = new QHttpThreadDelegate;
164 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
165 QVariant v(property("_q_networksession"));
166 if (v.isValid())
167 delegate->networkSession = qvariant_cast<QSharedPointer<QNetworkSession> >(v);
168 #endif
169
170 // For the synchronous HTTP, this is the normal way the delegate gets deleted
171 // For the asynchronous HTTP this is a safety measure, the delegate deletes itself when HTTP is finished
172 connect(thread, SIGNAL(finished()), delegate, SLOT(deleteLater()));
173
174 // Set the properties it needs
175 delegate->httpRequest = httpRequest;
176 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
177 delegate->cacheProxy = cacheProxy;
178 delegate->transparentProxy = transparentProxy;
179 #endif
180 delegate->ssl = ssl;
181 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
182 if (ssl)
183 delegate->incomingSslConfiguration = request().sslConfiguration();
184 #endif
185
186 // Do we use synchronous HTTP?
187 delegate->synchronous = isSynchronous();
188
189 // The authentication manager is used to avoid the BlockingQueuedConnection communication
190 // from HTTP thread to user thread in some cases.
191 delegate->authenticationManager = manager->authenticationManager;
192
193 if (!isSynchronous()) {
194 // Tell our zerocopy policy to the delegate
195 delegate->downloadBufferMaximumSize =
196 request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::MaximumDownloadBufferSizeAttribute).toLongLong();
197
198 // These atomic integers are used for signal compression
199 delegate->pendingDownloadData = pendingDownloadDataEmissions;
200 delegate->pendingDownloadProgress = pendingDownloadProgressEmissions;
201
202 // Connect the signals of the delegate to us
203 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadData(QByteArray)),
204 this, SLOT(replyDownloadData(QByteArray)),
205 Qt::QueuedConnection);
206 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadFinished()),
207 this, SLOT(replyFinished()),
208 Qt::QueuedConnection);
209 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadMetaData(QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >,int,QString,bool,QSharedPointer<char>,qint64)),
210 this, SLOT(replyDownloadMetaData(QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >,int,QString,bool,QSharedPointer<char>,qint64)),
211 Qt::QueuedConnection);
212 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadProgress(qint64,qint64)),
213 this, SLOT(replyDownloadProgressSlot(qint64,qint64)),
214 Qt::QueuedConnection);
215 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(error(QNetworkReply::NetworkError,QString)),
216 this, SLOT(httpError(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, const QString)),
217 Qt::QueuedConnection);
218 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
219 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(sslConfigurationChanged(QSslConfiguration)),
220 this, SLOT(replySslConfigurationChanged(QSslConfiguration)),
221 Qt::QueuedConnection);
222 #endif
223 // Those need to report back, therefire BlockingQueuedConnection
224 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(authenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
225 this, SLOT(httpAuthenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
226 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
227 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
228 connect (delegate, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
229 this, SLOT(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
230 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
231 #endif
232 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
233 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(sslErrors(QList<QSslError>,bool*,QList<QSslError>*)),
234 this, SLOT(replySslErrors(const QList<QSslError> &, bool *, QList<QSslError> *)),
235 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
236 #endif
237 // This signal we will use to start the request.
238 connect(this, SIGNAL(startHttpRequest()), delegate, SLOT(startRequest()));
239 connect(this, SIGNAL(abortHttpRequest()), delegate, SLOT(abortRequest()));
240
241 // To throttle the connection.
242 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(readBufferSizeChanged(qint64)), delegate, SLOT(readBufferSizeChanged(qint64)));
243 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(readBufferFreed(qint64)), delegate, SLOT(readBufferFreed(qint64)));
244
245 if (uploadByteDevice) {
246 QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl *forwardUploadDevice =
247 new QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl(uploadByteDevice->atEnd(), uploadByteDevice->size());
248 if (uploadByteDevice->isResetDisabled())
249 forwardUploadDevice->disableReset();
250 forwardUploadDevice->setParent(delegate); // needed to make sure it is moved on moveToThread()
251 delegate->httpRequest.setUploadByteDevice(forwardUploadDevice);
252
253 // From main thread to user thread:
254 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(haveUploadData(QByteArray, bool, qint64)),
255 forwardUploadDevice, SLOT(haveDataSlot(QByteArray, bool, qint64)), Qt::QueuedConnection);
256 QObject::connect(uploadByteDevice.data(), SIGNAL(readyRead()),
257 forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(readyRead()),
258 Qt::QueuedConnection);
259
260 // From http thread to user thread:
261 QObject::connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(wantData(qint64)),
262 this, SLOT(wantUploadDataSlot(qint64)));
263 QObject::connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(processedData(qint64)),
264 this, SLOT(sentUploadDataSlot(qint64)));
265 connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(resetData(bool*)),
266 this, SLOT(resetUploadDataSlot(bool*)),
267 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection); // this is the only one with BlockingQueued!
268 }
269 } else if (isSynchronous()) {
270 connect(this, SIGNAL(startHttpRequestSynchronously()), delegate, SLOT(startRequestSynchronously()), Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
271
272 if (uploadByteDevice) {
273 // For the synchronous HTTP use case the use thread (this one here) is blocked
274 // so we cannot use the asynchronous upload architecture.
275 // We therefore won't use the QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl but directly
276 // use the uploadByteDevice provided to us by the QNetworkReplyImpl.
277 // The code that is in QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::setup() makes sure it is safe to use from a thread
278 // since it only wraps a QRingBuffer
279 delegate->httpRequest.setUploadByteDevice(uploadByteDevice.data());
280 }
281 }
282
283
284 // Move the delegate to the http thread
285 delegate->moveToThread(thread);
286 // This call automatically moves the uploadDevice too for the asynchronous case.
287
288 // Send an signal to the delegate so it starts working in the other thread
289 if (isSynchronous()) {
290 emit startHttpRequestSynchronously(); // This one is BlockingQueuedConnection, so it will return when all work is done
291
292 if (delegate->incomingErrorCode != QNetworkReply::NoError) {
293 replyDownloadMetaData
294 (delegate->incomingHeaders,
295 delegate->incomingStatusCode,
296 delegate->incomingReasonPhrase,
297 delegate->isPipeliningUsed,
298 QSharedPointer<char>(),
299 delegate->incomingContentLength);
300 replyDownloadData(delegate->synchronousDownloadData);
301 httpError(delegate->incomingErrorCode, delegate->incomingErrorDetail);
302 } else {
303 replyDownloadMetaData
304 (delegate->incomingHeaders,
305 delegate->incomingStatusCode,
306 delegate->incomingReasonPhrase,
307 delegate->isPipeliningUsed,
308 QSharedPointer<char>(),
309 delegate->incomingContentLength);
310 replyDownloadData(delegate->synchronousDownloadData);
311 }
312
313 // End the thread. It will delete itself from the finished() signal
314 thread->quit();
315 thread->wait(5000);
316
317 finished();
318 } else {
319 emit startHttpRequest(); // Signal to the HTTP thread and go back to user.
320 }
321 }
主要是链接槽函数,看槽函数代码startRequest
1 void QHttpThreadDelegate::startRequest()
2 {
3 #ifdef QHTTPTHREADDELEGATE_DEBUG
4 qDebug() << "QHttpThreadDelegate::startRequest() thread=" << QThread::currentThreadId();
5 #endif
6 // Check QThreadStorage for the QNetworkAccessCache
7 // If not there, create this connection cache
8 if (!connections.hasLocalData()) {
9 connections.setLocalData(new QNetworkAccessCache());
10 }
11
12 // check if we have an open connection to this host
13 QUrl urlCopy = httpRequest.url();
14 urlCopy.setPort(urlCopy.port(ssl ? 443 : 80));
15
16 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
17 if (transparentProxy.type() != QNetworkProxy::NoProxy)
18 cacheKey = makeCacheKey(urlCopy, &transparentProxy);
19 else if (cacheProxy.type() != QNetworkProxy::NoProxy)
20 cacheKey = makeCacheKey(urlCopy, &cacheProxy);
21 else
22 #endif
23 cacheKey = makeCacheKey(urlCopy, 0);
24
25
26 // the http object is actually a QHttpNetworkConnection
27 httpConnection = static_cast<QNetworkAccessCachedHttpConnection *>(connections.localData()->requestEntryNow(cacheKey));
28 if (httpConnection == 0) {
29 // no entry in cache; create an object
30 // the http object is actually a QHttpNetworkConnection
31 #ifdef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
32 httpConnection = new QNetworkAccessCachedHttpConnection(urlCopy.host(), urlCopy.port(), ssl);
33 #else
34 httpConnection = new QNetworkAccessCachedHttpConnection(urlCopy.host(), urlCopy.port(), ssl, networkSession);
35 #endif
36 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
37 // Set the QSslConfiguration from this QNetworkRequest.
38 if (ssl && incomingSslConfiguration != QSslConfiguration::defaultConfiguration()) {
39 httpConnection->setSslConfiguration(incomingSslConfiguration);
40 }
41 #endif
42
43 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
44 httpConnection->setTransparentProxy(transparentProxy);
45 httpConnection->setCacheProxy(cacheProxy);
46 #endif
47
48 // cache the QHttpNetworkConnection corresponding to this cache key
49 connections.localData()->addEntry(cacheKey, httpConnection);
50 }
51
52
53 // Send the request to the connection
54 httpReply = httpConnection->sendRequest(httpRequest);
55 httpReply->setParent(this);
56
57 // Connect the reply signals that we need to handle and then forward
58 if (synchronous) {
59 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(headerChanged()), this, SLOT(synchronousHeaderChangedSlot()));
60 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(finished()), this, SLOT(synchronousFinishedSlot()));
61 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(finishedWithError(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, const QString)),
62 this, SLOT(synchronousFinishedWithErrorSlot(QNetworkReply::NetworkError,QString)));
63
64 connect(httpReply, SIGNAL(authenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
65 this, SLOT(synchronousAuthenticationRequiredSlot(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)));
66 connect(httpReply, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
67 this, SLOT(synchronousProxyAuthenticationRequiredSlot(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)));
68
69 // Don't care about ignored SSL errors for now in the synchronous HTTP case.
70 } else if (!synchronous) {
71 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(headerChanged()), this, SLOT(headerChangedSlot()));
72 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(finished()), this, SLOT(finishedSlot()));
73 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(finishedWithError(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, const QString)),
74 this, SLOT(finishedWithErrorSlot(QNetworkReply::NetworkError,QString)));
75 // some signals are only interesting when normal asynchronous style is used
76 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(readyReadSlot()));
77 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(dataReadProgress(int, int)), this, SLOT(dataReadProgressSlot(int,int)));
78 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
79 connect(httpReply,SIGNAL(sslErrors(const QList<QSslError>)), this, SLOT(sslErrorsSlot(QList<QSslError>)));
80 #endif
81
82 // In the asynchronous HTTP case we can just forward those signals
83 // Connect the reply signals that we can directly forward
84 connect(httpReply, SIGNAL(authenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
85 this, SIGNAL(authenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)));
86 connect(httpReply, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
87 this, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)));
88 }
89
90 connect(httpReply, SIGNAL(cacheCredentials(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
91 this, SLOT(cacheCredentialsSlot(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)));
92 }
先查缓冲,没用的话新建连接,然后调用其sendRequest
1 QHttpNetworkReply* QHttpNetworkConnection::sendRequest(const QHttpNetworkRequest &request)
2 {
3 Q_D(QHttpNetworkConnection);
4 return d->queueRequest(request);
5 }
sendRequest()调用queueRequest()函数
1 QHttpNetworkReply* QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::queueRequest(const QHttpNetworkRequest &request)
2 {
3 Q_Q(QHttpNetworkConnection);
4
5 // The reply component of the pair is created initially.
6 QHttpNetworkReply *reply = new QHttpNetworkReply(request.url());
7 reply->setRequest(request);
8 reply->d_func()->connection = q;
9 reply->d_func()->connectionChannel = &channels[0]; // will have the correct one set later
10 HttpMessagePair pair = qMakePair(request, reply);
11
12 switch (request.priority()) {
13 case QHttpNetworkRequest::HighPriority:
14 highPriorityQueue.prepend(pair);
15 break;
16 case QHttpNetworkRequest::NormalPriority:
17 case QHttpNetworkRequest::LowPriority:
18 lowPriorityQueue.prepend(pair);
19 break;
20 }
21
22 // this used to be called via invokeMethod and a QueuedConnection
23 // It is the only place _q_startNextRequest is called directly without going
24 // through the event loop using a QueuedConnection.
25 // This is dangerous because of recursion that might occur when emitting
26 // signals as DirectConnection from this code path. Therefore all signal
27 // emissions that can come out from this code path need to
28 // be QueuedConnection.
29 // We are currently trying to fine-tune this.
30 _q_startNextRequest();
31
32
33 return reply;
34 }
在这里整个消息处理(或者是初始化动作)完成之后,按消息序列调用_q_startNextRequest
循环多通道处理请求,类似于connect流程
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::_q_startNextRequest()
2 {
3 // If the QHttpNetworkConnection is currently paused then bail out immediately
4 if (state == PausedState)
5 return;
6
7 //resend the necessary ones.
8 for (int i = 0; i < channelCount; ++i) {
9 if (channels[i].resendCurrent && (channels[i].state != QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::ClosingState)) {
10 channels[i].resendCurrent = false;
11 channels[i].state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::IdleState;
12
13 // if this is not possible, error will be emitted and connection terminated
14 if (!channels[i].resetUploadData())
15 continue;
16 channels[i].sendRequest();
17 }
18 }
19
20 // dequeue new ones
21
22 // return fast if there is nothing to do
23 if (highPriorityQueue.isEmpty() && lowPriorityQueue.isEmpty())
24 return;
25 // try to get a free AND connected socket
26 for (int i = 0; i < channelCount; ++i) {
27 if (!channels[i].reply && !channels[i].isSocketBusy() && channels[i].socket->state() == QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState) {
28 if (dequeueRequest(channels[i].socket))
29 channels[i].sendRequest();
30 }
31 }
32
33 // try to push more into all sockets
34 // ### FIXME we should move this to the beginning of the function
35 // as soon as QtWebkit is properly using the pipelining
36 // (e.g. not for XMLHttpRequest or the first page load)
37 // ### FIXME we should also divide the requests more even
38 // on the connected sockets
39 //tryToFillPipeline(socket);
40 // return fast if there is nothing to pipeline
41 if (highPriorityQueue.isEmpty() && lowPriorityQueue.isEmpty())
42 return;
43 for (int i = 0; i < channelCount; i++)
44 if (channels[i].socket->state() == QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState)
45 fillPipeline(channels[i].socket);
46
47 // If there is not already any connected channels we need to connect a new one.
48 // We do not pair the channel with the request until we know if it is
49 // connected or not. This is to reuse connected channels before we connect new once.
50 int queuedRequest = highPriorityQueue.count() + lowPriorityQueue.count();
51 for (int i = 0; i < channelCount; ++i) {
52 if (channels[i].socket->state() == QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState)
53 queuedRequest--;
54 if ( queuedRequest <=0 )
55 break;
56 if (!channels[i].reply && !channels[i].isSocketBusy() && (channels[i].socket->state() == QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState)) {
57 channels[i].ensureConnection();
58 queuedRequest--;
59 }
60 }
61 }
接着调用看代码
1 bool QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::dequeueRequest(QAbstractSocket *socket)
2 {
3 Q_ASSERT(socket);
4
5 int i = indexOf(socket);
6
7 if (!highPriorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
8 // remove from queue before sendRequest! else we might pipeline the same request again
9 HttpMessagePair messagePair = highPriorityQueue.takeLast();
10 if (!messagePair.second->d_func()->requestIsPrepared)
11 prepareRequest(messagePair);
12 channels[i].request = messagePair.first;
13 channels[i].reply = messagePair.second;
14 return true;
15 }
16
17 if (!lowPriorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
18 // remove from queue before sendRequest! else we might pipeline the same request again
19 HttpMessagePair messagePair = lowPriorityQueue.takeLast();
20 if (!messagePair.second->d_func()->requestIsPrepared)
21 prepareRequest(messagePair);
22 channels[i].request = messagePair.first;
23 channels[i].reply = messagePair.second;
24 return true;
25 }
26 return false;
27 }
看看prepareReuest
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::prepareRequest(HttpMessagePair &messagePair)
2 {
3 QHttpNetworkRequest &request = messagePair.first;
4 QHttpNetworkReply *reply = messagePair.second;
5
6 // add missing fields for the request
7 QByteArray value;
8 // check if Content-Length is provided
9 QNonContiguousByteDevice* uploadByteDevice = request.uploadByteDevice();
10 if (uploadByteDevice) {
11 if (request.contentLength() != -1 && uploadByteDevice->size() != -1) {
12 // both values known, take the smaller one.
13 request.setContentLength(qMin(uploadByteDevice->size(), request.contentLength()));
14 } else if (request.contentLength() == -1 && uploadByteDevice->size() != -1) {
15 // content length not supplied by user, but the upload device knows it
16 request.setContentLength(uploadByteDevice->size());
17 } else if (request.contentLength() != -1 && uploadByteDevice->size() == -1) {
18 // everything OK, the user supplied us the contentLength
19 } else if (request.contentLength() == -1 && uploadByteDevice->size() == -1) {
20 qFatal("QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate: Neither content-length nor upload device size were given");
21 }
22 }
23 // set the Connection/Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive headers
24 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
25 if (networkProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpCachingProxy) {
26 value = request.headerField("proxy-connection");
27 if (value.isEmpty())
28 request.setHeaderField("Proxy-Connection", "Keep-Alive");
29 } else {
30 #endif
31 value = request.headerField("connection");
32 if (value.isEmpty())
33 request.setHeaderField("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
34 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
35 }
36 #endif
37
38 // If the request had a accept-encoding set, we better not mess
39 // with it. If it was not set, we announce that we understand gzip
40 // and remember this fact in request.d->autoDecompress so that
41 // we can later decompress the HTTP reply if it has such an
42 // encoding.
43 value = request.headerField("accept-encoding");
44 if (value.isEmpty()) {
45 #ifndef QT_NO_COMPRESS
46 request.setHeaderField("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
47 request.d->autoDecompress = true;
48 #else
49 // if zlib is not available set this to false always
50 request.d->autoDecompress = false;
51 #endif
52 }
53
54 // some websites mandate an accept-language header and fail
55 // if it is not sent. This is a problem with the website and
56 // not with us, but we work around this by setting
57 // one always.
58 value = request.headerField("accept-language");
59 if (value.isEmpty()) {
60 QString systemLocale = QLocale::system().name().replace(QChar::fromAscii('_'),QChar::fromAscii('-'));
61 QString acceptLanguage;
62 if (systemLocale == QLatin1String("C"))
63 acceptLanguage = QString::fromAscii("en,*");
64 else if (systemLocale.startsWith(QLatin1String("en-")))
65 acceptLanguage = QString::fromAscii("%1,*").arg(systemLocale);
66 else
67 acceptLanguage = QString::fromAscii("%1,en,*").arg(systemLocale);
68 request.setHeaderField("Accept-Language", acceptLanguage.toAscii());
69 }
70
71 // set the User Agent
72 value = request.headerField("user-agent");
73 if (value.isEmpty())
74 request.setHeaderField("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0");
75 // set the host
76 value = request.headerField("host");
77 if (value.isEmpty()) {
78 QHostAddress add;
79 QByteArray host;
80 if(add.setAddress(hostName)) {
81 if(add.protocol() == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) {
82 host = "[" + hostName.toAscii() + "]";//format the ipv6 in the standard way
83 } else {
84 host = QUrl::toAce(hostName);
85 }
86 } else {
87 host = QUrl::toAce(hostName);
88 }
89
90 int port = request.url().port();
91 if (port != -1) {
92 host += ':';
93 host += QByteArray::number(port);
94 }
95
96 request.setHeaderField("Host", host);
97 }
98
99 reply->d_func()->requestIsPrepared = true;
100 }
按优先级次序发送请求。prepareRequest()设定HTTP请求的Header信息;关键是sendRequest()
1 bool QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::sendRequest()
2 {
3 if (!reply) {
4 // heh, how should that happen!
5 qWarning() << "QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::sendRequest() called without QHttpNetworkReply";
6 state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::IdleState;
7 return false;
8 }
9
10 switch (state) {
11 case QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::IdleState: { // write the header
12 if (!ensureConnection()) {
13 // wait for the connection (and encryption) to be done
14 // sendRequest will be called again from either
15 // _q_connected or _q_encrypted
16 return false;
17 }
18 written = 0; // excluding the header
19 bytesTotal = 0;
20
21 QHttpNetworkReplyPrivate *replyPrivate = reply->d_func();
22 replyPrivate->clear();
23 replyPrivate->connection = connection;
24 replyPrivate->connectionChannel = this;
25 replyPrivate->autoDecompress = request.d->autoDecompress;
26 replyPrivate->pipeliningUsed = false;
27
28 // if the url contains authentication parameters, use the new ones
29 // both channels will use the new authentication parameters
30 if (!request.url().userInfo().isEmpty() && request.withCredentials()) {
31 QUrl url = request.url();
32 QAuthenticator &auth = authenticator;
33 if (url.userName() != auth.user()
34 || (!url.password().isEmpty() && url.password() != auth.password())) {
35 auth.setUser(url.userName());
36 auth.setPassword(url.password());
37 connection->d_func()->copyCredentials(connection->d_func()->indexOf(socket), &auth, false);
38 }
39 // clear the userinfo, since we use the same request for resending
40 // userinfo in url can conflict with the one in the authenticator
41 url.setUserInfo(QString());
42 request.setUrl(url);
43 }
44 // Will only be false if QtWebKit is performing a cross-origin XMLHttpRequest
45 // and withCredentials has not been set to true.
46 if (request.withCredentials())
47 connection->d_func()->createAuthorization(socket, request);
48 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
49 QByteArray header = QHttpNetworkRequestPrivate::header(request,
50 (connection->d_func()->networkProxy.type() != QNetworkProxy::NoProxy));
51 #else
52 QByteArray header = QHttpNetworkRequestPrivate::header(request, false);
53 #endif
54 socket->write(header);
55 // flushing is dangerous (QSslSocket calls transmit which might read or error)
56 // socket->flush();
57 QNonContiguousByteDevice* uploadByteDevice = request.uploadByteDevice();
58 if (uploadByteDevice) {
59 // connect the signals so this function gets called again
60 QObject::connect(uploadByteDevice, SIGNAL(readyRead()),this, SLOT(_q_uploadDataReadyRead()));
61
62 bytesTotal = request.contentLength();
63
64 state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WritingState; // start writing data
65 sendRequest(); //recurse
66 } else {
67 state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WaitingState; // now wait for response
68 sendRequest(); //recurse
69 }
70
71 break;
72 }
73 case QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WritingState:
74 {
75 // write the data
76 QNonContiguousByteDevice* uploadByteDevice = request.uploadByteDevice();
77 if (!uploadByteDevice || bytesTotal == written) {
78 if (uploadByteDevice)
79 emit reply->dataSendProgress(written, bytesTotal);
80 state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WaitingState; // now wait for response
81 sendRequest(); // recurse
82 break;
83 }
84
85 // only feed the QTcpSocket buffer when there is less than 32 kB in it
86 const qint64 socketBufferFill = 32*1024;
87 const qint64 socketWriteMaxSize = 16*1024;
88
89
90 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
91 QSslSocket *sslSocket = qobject_cast<QSslSocket*>(socket);
92 // if it is really an ssl socket, check more than just bytesToWrite()
93 while ((socket->bytesToWrite() + (sslSocket ? sslSocket->encryptedBytesToWrite() : 0))
94 <= socketBufferFill && bytesTotal != written)
95 #else
96 while (socket->bytesToWrite() <= socketBufferFill
97 && bytesTotal != written)
98 #endif
99 {
100 // get pointer to upload data
101 qint64 currentReadSize = 0;
102 qint64 desiredReadSize = qMin(socketWriteMaxSize, bytesTotal - written);
103 const char *readPointer = uploadByteDevice->readPointer(desiredReadSize, currentReadSize);
104
105 if (currentReadSize == -1) {
106 // premature eof happened
107 connection->d_func()->emitReplyError(socket, reply, QNetworkReply::UnknownNetworkError);
108 return false;
109 break;
110 } else if (readPointer == 0 || currentReadSize == 0) {
111 // nothing to read currently, break the loop
112 break;
113 } else {
114 qint64 currentWriteSize = socket->write(readPointer, currentReadSize);
115 if (currentWriteSize == -1 || currentWriteSize != currentReadSize) {
116 // socket broke down
117 connection->d_func()->emitReplyError(socket, reply, QNetworkReply::UnknownNetworkError);
118 return false;
119 } else {
120 written += currentWriteSize;
121 uploadByteDevice->advanceReadPointer(currentWriteSize);
122
123 emit reply->dataSendProgress(written, bytesTotal);
124
125 if (written == bytesTotal) {
126 // make sure this function is called once again
127 state = QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WaitingState;
128 sendRequest();
129 break;
130 }
131 }
132 }
133 }
134 break;
135 }
136
137 case QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::WaitingState:
138 {
139 QNonContiguousByteDevice* uploadByteDevice = request.uploadByteDevice();
140 if (uploadByteDevice) {
141 QObject::disconnect(uploadByteDevice, SIGNAL(readyRead()), this, SLOT(_q_uploadDataReadyRead()));
142 }
143
144 // HTTP pipelining
145 //connection->d_func()->fillPipeline(socket);
146 //socket->flush();
147
148 // ensure we try to receive a reply in all cases, even if _q_readyRead_ hat not been called
149 // this is needed if the sends an reply before we have finished sending the request. In that
150 // case receiveReply had been called before but ignored the server reply
151 if (socket->bytesAvailable())
152 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "_q_receiveReply", Qt::QueuedConnection);
153 break;
154 }
155 case QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::ReadingState:
156 // ignore _q_bytesWritten in these states
157 // fall through
158 default:
159 break;
160 }
161 return true;
162 }
进行的底层的socket调用,不详细分析
QHttpNetworkConnection的构造中,有些我们感兴趣的东西:
1 QHttpNetworkConnection::QHttpNetworkConnection(const QString &hostName, quint16 port, bool encrypt, QObject *parent, QSharedPointer<QNetworkSession> networkSession)
2 : QObject(*(new QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate(hostName, port, encrypt)), parent)
3 {
4 Q_D(QHttpNetworkConnection);
5 d->networkSession = networkSession;
6 d->init();
7 }
继续跟进 init函数:
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::init()
2 {
3 for (int i = 0; i < channelCount; i++) {
4 channels[i].setConnection(this->q_func());
5 channels[i].ssl = encrypt;
6 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
7 //push session down to channels
8 channels[i].networkSession = networkSession;
9 #endif
10 channels[i].init();
11 }
12 }
接下来看channels的init函数
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionChannel::init()
2 {
3 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
4 if (connection->d_func()->encrypt)
5 socket = new QSslSocket;
6 else
7 socket = new QTcpSocket;
8 #else
9 socket = new QTcpSocket;
10 #endif
11 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
12 //push session down to socket
13 if (networkSession)
14 socket->setProperty("_q_networksession", QVariant::fromValue(networkSession));
15 #endif
16 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
17 // Set by QNAM anyway, but let's be safe here
18 socket->setProxy(QNetworkProxy::NoProxy);
19 #endif
20
21 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(bytesWritten(qint64)),
22 this, SLOT(_q_bytesWritten(qint64)),
23 Qt::DirectConnection);
24 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(connected()),
25 this, SLOT(_q_connected()),
26 Qt::DirectConnection);
27 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(readyRead()),
28 this, SLOT(_q_readyRead()),
29 Qt::DirectConnection);
30
31 // The disconnected() and error() signals may already come
32 // while calling connectToHost().
33 // In case of a cached hostname or an IP this
34 // will then emit a signal to the user of QNetworkReply
35 // but cannot be caught because the user did not have a chance yet
36 // to connect to QNetworkReply's signals.
37 qRegisterMetaType<QAbstractSocket::SocketError>("QAbstractSocket::SocketError");
38 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(disconnected()),
39 this, SLOT(_q_disconnected()),
40 Qt::QueuedConnection);
41 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(error(QAbstractSocket::SocketError)),
42 this, SLOT(_q_error(QAbstractSocket::SocketError)),
43 Qt::QueuedConnection);
44
45
46 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
47 QObject::connect(socket, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
48 this, SLOT(_q_proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
49 Qt::DirectConnection);
50 #endif
51
52 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
53 QSslSocket *sslSocket = qobject_cast<QSslSocket*>(socket);
54 if (sslSocket) {
55 // won't be a sslSocket if encrypt is false
56 QObject::connect(sslSocket, SIGNAL(encrypted()),
57 this, SLOT(_q_encrypted()),
58 Qt::DirectConnection);
59 QObject::connect(sslSocket, SIGNAL(sslErrors(QList<QSslError>)),
60 this, SLOT(_q_sslErrors(QList<QSslError>)),
61 Qt::DirectConnection);
62 QObject::connect(sslSocket, SIGNAL(encryptedBytesWritten(qint64)),
63 this, SLOT(_q_encryptedBytesWritten(qint64)),
64 Qt::DirectConnection);
65 }
66 #endif
67 }
看到了我们熟悉的QTcpSocket类,该类继承于QAbstractSocket,封装了平台socket
回到前面,继续看postRequst又做了哪些事情呢?再看代码
1 void QNetworkAccessHttpBackend::postRequest()
2 {
3 QThread *thread = 0;
4 if (isSynchronous()) {
5 // A synchronous HTTP request uses its own thread
6 thread = new QThread();
7 QObject::connect(thread, SIGNAL(finished()), thread, SLOT(deleteLater()));
8 thread->start();
9 } else if (!manager->httpThread) {
10 // We use the manager-global thread.
11 // At some point we could switch to having multiple threads if it makes sense.
12 manager->httpThread = new QThread();
13 QObject::connect(manager->httpThread, SIGNAL(finished()), manager->httpThread, SLOT(deleteLater()));
14 manager->httpThread->start();
15 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
16 qRegisterMetaType<QNetworkProxy>("QNetworkProxy");
17 #endif
18 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
19 qRegisterMetaType<QList<QSslError> >("QList<QSslError>");
20 qRegisterMetaType<QSslConfiguration>("QSslConfiguration");
21 #endif
22 qRegisterMetaType<QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> > >("QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >");
23 qRegisterMetaType<QHttpNetworkRequest>("QHttpNetworkRequest");
24 qRegisterMetaType<QNetworkReply::NetworkError>("QNetworkReply::NetworkError");
25 qRegisterMetaType<QSharedPointer<char> >("QSharedPointer<char>");
26
27 thread = manager->httpThread;
28 } else {
29 // Asynchronous request, thread already exists
30 thread = manager->httpThread;
31 }
32
33 QUrl url = request().url();
34 httpRequest.setUrl(url);
35
36 bool ssl = url.scheme().toLower() == QLatin1String("https");
37 setAttribute(QNetworkRequest::ConnectionEncryptedAttribute, ssl);
38 httpRequest.setSsl(ssl);
39
40
41 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
42 QNetworkProxy transparentProxy, cacheProxy;
43
44 foreach (const QNetworkProxy &p, proxyList()) {
45 // use the first proxy that works
46 // for non-encrypted connections, any transparent or HTTP proxy
47 // for encrypted, only transparent proxies
48 if (!ssl
49 && (p.capabilities() & QNetworkProxy::CachingCapability)
50 && (p.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpProxy ||
51 p.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpCachingProxy)) {
52 cacheProxy = p;
53 transparentProxy = QNetworkProxy::NoProxy;
54 break;
55 }
56 if (p.isTransparentProxy()) {
57 transparentProxy = p;
58 cacheProxy = QNetworkProxy::NoProxy;
59 break;
60 }
61 }
62
63 // check if at least one of the proxies
64 if (transparentProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy &&
65 cacheProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy) {
66 // unsuitable proxies
67 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "error", isSynchronous() ? Qt::DirectConnection : Qt::QueuedConnection,
68 Q_ARG(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, QNetworkReply::ProxyNotFoundError),
69 Q_ARG(QString, tr("No suitable proxy found")));
70 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "finished", isSynchronous() ? Qt::DirectConnection : Qt::QueuedConnection);
71 return;
72 }
73 #endif
74
75
76 bool loadedFromCache = false;
77 httpRequest.setPriority(convert(request().priority()));
78
79 switch (operation()) {
80 case QNetworkAccessManager::GetOperation:
81 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Get);
82 loadedFromCache = loadFromCacheIfAllowed(httpRequest);
83 break;
84
85 case QNetworkAccessManager::HeadOperation:
86 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Head);
87 loadedFromCache = loadFromCacheIfAllowed(httpRequest);
88 break;
89
90 case QNetworkAccessManager::PostOperation:
91 invalidateCache();
92 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Post);
93 createUploadByteDevice();
94 break;
95
96 case QNetworkAccessManager::PutOperation:
97 invalidateCache();
98 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Put);
99 createUploadByteDevice();
100 break;
101
102 case QNetworkAccessManager::DeleteOperation:
103 invalidateCache();
104 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Delete);
105 break;
106
107 case QNetworkAccessManager::CustomOperation:
108 invalidateCache(); // for safety reasons, we don't know what the operation does
109 httpRequest.setOperation(QHttpNetworkRequest::Custom);
110 createUploadByteDevice();
111 httpRequest.setCustomVerb(request().attribute(
112 QNetworkRequest::CustomVerbAttribute).toByteArray());
113 break;
114
115 default:
116 break; // can't happen
117 }
118
119 if (loadedFromCache) {
120 // commented this out since it will be called later anyway
121 // by copyFinished()
122 //QNetworkAccessBackend::finished();
123 return; // no need to send the request! :)
124 }
125
126 QList<QByteArray> headers = request().rawHeaderList();
127 if (resumeOffset != 0) {
128 if (headers.contains("Range")) {
129 // Need to adjust resume offset for user specified range
130
131 headers.removeOne("Range");
132
133 // We've already verified that requestRange starts with "bytes=", see canResume.
134 QByteArray requestRange = request().rawHeader("Range").mid(6);
135
136 int index = requestRange.indexOf('-');
137
138 quint64 requestStartOffset = requestRange.left(index).toULongLong();
139 quint64 requestEndOffset = requestRange.mid(index + 1).toULongLong();
140
141 requestRange = "bytes=" + QByteArray::number(resumeOffset + requestStartOffset) +
142 '-' + QByteArray::number(requestEndOffset);
143
144 httpRequest.setHeaderField("Range", requestRange);
145 } else {
146 httpRequest.setHeaderField("Range", "bytes=" + QByteArray::number(resumeOffset) + '-');
147 }
148 }
149
150 foreach (const QByteArray &header, headers)
151 httpRequest.setHeaderField(header, request().rawHeader(header));
152
153 if (request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::HttpPipeliningAllowedAttribute).toBool() == true)
154 httpRequest.setPipeliningAllowed(true);
155
156 if (static_cast<QNetworkRequest::LoadControl>
157 (request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::AuthenticationReuseAttribute,
158 QNetworkRequest::Automatic).toInt()) == QNetworkRequest::Manual)
159 httpRequest.setWithCredentials(false);
160
161
162 // Create the HTTP thread delegate
163 QHttpThreadDelegate *delegate = new QHttpThreadDelegate;
164 #ifndef QT_NO_BEARERMANAGEMENT
165 QVariant v(property("_q_networksession"));
166 if (v.isValid())
167 delegate->networkSession = qvariant_cast<QSharedPointer<QNetworkSession> >(v);
168 #endif
169
170 // For the synchronous HTTP, this is the normal way the delegate gets deleted
171 // For the asynchronous HTTP this is a safety measure, the delegate deletes itself when HTTP is finished
172 connect(thread, SIGNAL(finished()), delegate, SLOT(deleteLater()));
173
174 // Set the properties it needs
175 delegate->httpRequest = httpRequest;
176 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
177 delegate->cacheProxy = cacheProxy;
178 delegate->transparentProxy = transparentProxy;
179 #endif
180 delegate->ssl = ssl;
181 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
182 if (ssl)
183 delegate->incomingSslConfiguration = request().sslConfiguration();
184 #endif
185
186 // Do we use synchronous HTTP?
187 delegate->synchronous = isSynchronous();
188
189 // The authentication manager is used to avoid the BlockingQueuedConnection communication
190 // from HTTP thread to user thread in some cases.
191 delegate->authenticationManager = manager->authenticationManager;
192
193 if (!isSynchronous()) {
194 // Tell our zerocopy policy to the delegate
195 delegate->downloadBufferMaximumSize =
196 request().attribute(QNetworkRequest::MaximumDownloadBufferSizeAttribute).toLongLong();
197
198 // These atomic integers are used for signal compression
199 delegate->pendingDownloadData = pendingDownloadDataEmissions;
200 delegate->pendingDownloadProgress = pendingDownloadProgressEmissions;
201
202 // Connect the signals of the delegate to us
203 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadData(QByteArray)),
204 this, SLOT(replyDownloadData(QByteArray)),
205 Qt::QueuedConnection);
206 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadFinished()),
207 this, SLOT(replyFinished()),
208 Qt::QueuedConnection);
209 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadMetaData(QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >,int,QString,bool,QSharedPointer<char>,qint64)),
210 this, SLOT(replyDownloadMetaData(QList<QPair<QByteArray,QByteArray> >,int,QString,bool,QSharedPointer<char>,qint64)),
211 Qt::QueuedConnection);
212 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(downloadProgress(qint64,qint64)),
213 this, SLOT(replyDownloadProgressSlot(qint64,qint64)),
214 Qt::QueuedConnection);
215 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(error(QNetworkReply::NetworkError,QString)),
216 this, SLOT(httpError(QNetworkReply::NetworkError, const QString)),
217 Qt::QueuedConnection);
218 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
219 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(sslConfigurationChanged(QSslConfiguration)),
220 this, SLOT(replySslConfigurationChanged(QSslConfiguration)),
221 Qt::QueuedConnection);
222 #endif
223 // Those need to report back, therefire BlockingQueuedConnection
224 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(authenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
225 this, SLOT(httpAuthenticationRequired(QHttpNetworkRequest,QAuthenticator*)),
226 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
227 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
228 connect (delegate, SIGNAL(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
229 this, SLOT(proxyAuthenticationRequired(QNetworkProxy,QAuthenticator*)),
230 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
231 #endif
232 #ifndef QT_NO_OPENSSL
233 connect(delegate, SIGNAL(sslErrors(QList<QSslError>,bool*,QList<QSslError>*)),
234 this, SLOT(replySslErrors(const QList<QSslError> &, bool *, QList<QSslError> *)),
235 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
236 #endif
237 // This signal we will use to start the request.
238 connect(this, SIGNAL(startHttpRequest()), delegate, SLOT(startRequest()));
239 connect(this, SIGNAL(abortHttpRequest()), delegate, SLOT(abortRequest()));
240
241 // To throttle the connection.
242 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(readBufferSizeChanged(qint64)), delegate, SLOT(readBufferSizeChanged(qint64)));
243 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(readBufferFreed(qint64)), delegate, SLOT(readBufferFreed(qint64)));
244
245 if (uploadByteDevice) {
246 QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl *forwardUploadDevice =
247 new QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl(uploadByteDevice->atEnd(), uploadByteDevice->size());
248 if (uploadByteDevice->isResetDisabled())
249 forwardUploadDevice->disableReset();
250 forwardUploadDevice->setParent(delegate); // needed to make sure it is moved on moveToThread()
251 delegate->httpRequest.setUploadByteDevice(forwardUploadDevice);
252
253 // From main thread to user thread:
254 QObject::connect(this, SIGNAL(haveUploadData(QByteArray, bool, qint64)),
255 forwardUploadDevice, SLOT(haveDataSlot(QByteArray, bool, qint64)), Qt::QueuedConnection);
256 QObject::connect(uploadByteDevice.data(), SIGNAL(readyRead()),
257 forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(readyRead()),
258 Qt::QueuedConnection);
259
260 // From http thread to user thread:
261 QObject::connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(wantData(qint64)),
262 this, SLOT(wantUploadDataSlot(qint64)));
263 QObject::connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(processedData(qint64)),
264 this, SLOT(sentUploadDataSlot(qint64)));
265 connect(forwardUploadDevice, SIGNAL(resetData(bool*)),
266 this, SLOT(resetUploadDataSlot(bool*)),
267 Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection); // this is the only one with BlockingQueued!
268 }
269 } else if (isSynchronous()) {
270 connect(this, SIGNAL(startHttpRequestSynchronously()), delegate, SLOT(startRequestSynchronously()), Qt::BlockingQueuedConnection);
271
272 if (uploadByteDevice) {
273 // For the synchronous HTTP use case the use thread (this one here) is blocked
274 // so we cannot use the asynchronous upload architecture.
275 // We therefore won't use the QNonContiguousByteDeviceThreadForwardImpl but directly
276 // use the uploadByteDevice provided to us by the QNetworkReplyImpl.
277 // The code that is in QNetworkReplyImplPrivate::setup() makes sure it is safe to use from a thread
278 // since it only wraps a QRingBuffer
279 delegate->httpRequest.setUploadByteDevice(uploadByteDevice.data());
280 }
281 }
282
283
284 // Move the delegate to the http thread
285 delegate->moveToThread(thread);
286 // This call automatically moves the uploadDevice too for the asynchronous case.
287
288 // Send an signal to the delegate so it starts working in the other thread
289 if (isSynchronous()) {
290 emit startHttpRequestSynchronously(); // This one is BlockingQueuedConnection, so it will return when all work is done
291
292 if (delegate->incomingErrorCode != QNetworkReply::NoError) {
293 replyDownloadMetaData
294 (delegate->incomingHeaders,
295 delegate->incomingStatusCode,
296 delegate->incomingReasonPhrase,
297 delegate->isPipeliningUsed,
298 QSharedPointer<char>(),
299 delegate->incomingContentLength);
300 replyDownloadData(delegate->synchronousDownloadData);
301 httpError(delegate->incomingErrorCode, delegate->incomingErrorDetail);
302 } else {
303 replyDownloadMetaData
304 (delegate->incomingHeaders,
305 delegate->incomingStatusCode,
306 delegate->incomingReasonPhrase,
307 delegate->isPipeliningUsed,
308 QSharedPointer<char>(),
309 delegate->incomingContentLength);
310 replyDownloadData(delegate->synchronousDownloadData);
311 }
312
313 // End the thread. It will delete itself from the finished() signal
314 thread->quit();
315 thread->wait(5000);
316
317 finished();
318 } else {
319 emit startHttpRequest(); // Signal to the HTTP thread and go back to user.
320 }
321 }
完了下面这些动作:
1、看Cache中是否保存有过去浏览的内容,如果有还要看是否超出生存时间(Expiration
Time);
2、设定Url、Header和数据内容(需要提交的数据);
3、调用QNetworkAccessHttpBackendCache::sendRequest()发送请求内容;
4、把QHttpNetworkReply的信号与QNetworkAccessHttpBackend的槽连接起来,完成后续处理。
分析QNetworkAccessManager的时候,有一段设定HTTP的请求包的Header,当时没进行深入的分析。
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::prepareRequest(HttpMessagePair &messagePair)
2 {
3 QHttpNetworkRequest &request = messagePair.first;
4 QHttpNetworkReply *reply = messagePair.second;
5
6 // add missing fields for the request
7 QByteArray value;
8 // check if Content-Length is provided
9 QIODevice *data = request.data();
10 if (data && request.contentLength() == -1) {
11 if (!data->isSequential())
12 request.setContentLength(data->size());
13 else
14 bufferData(messagePair); // ### or do chunked upload
15 }
16 // set the Connection/Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive headers
17 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
18 if (networkProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpCachingProxy) {
19 value = request.headerField("proxy-connection");
20 if (value.isEmpty())
21 request.setHeaderField("Proxy-Connection", "Keep-Alive");
22 } else {
23 #endif
24 value = request.headerField("connection");
25 if (value.isEmpty())
26 request.setHeaderField("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
27 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY
28 }
29 #endif
30
31 // If the request had a accept-encoding set, we better not mess
32 // with it. If it was not set, we announce that we understand gzip
33 // and remember this fact in request.d->autoDecompress so that
34 // we can later decompress the HTTP reply if it has such an
35 // encoding.
36 value = request.headerField("accept-encoding");
37 if (value.isEmpty()) {
38 #ifndef QT_NO_COMPRESS
39 request.setHeaderField("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
40 request.d->autoDecompress = true;
41 #else
42 // if zlib is not available set this to false always
43 request.d->autoDecompress = false;
44 #endif
45 }
46 // set the User Agent
47 value = request.headerField("user-agent");
48 if (value.isEmpty())
49 request.setHeaderField("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0");
50 // set the host
51 value = request.headerField("host");
52 if (value.isEmpty()) {
53 QByteArray host = QUrl::toAce(hostName);
54
55 int port = request.url().port();
56 if (port != -1) {
57 host += ':';
58 host += QByteArray::number(port);
59 }
60
61 request.setHeaderField("Host", host);
62 }
63
64 reply->d_func()->requestIsPrepared = true;
65 }
如果想模拟IE浏览器,或者想修改成任何你希望的信息,就是在这里修改。
在设定了这些请求信息之后,发送的请求信息包是什么样子的呢?我把工具拦截的信息包具体情况贴出来
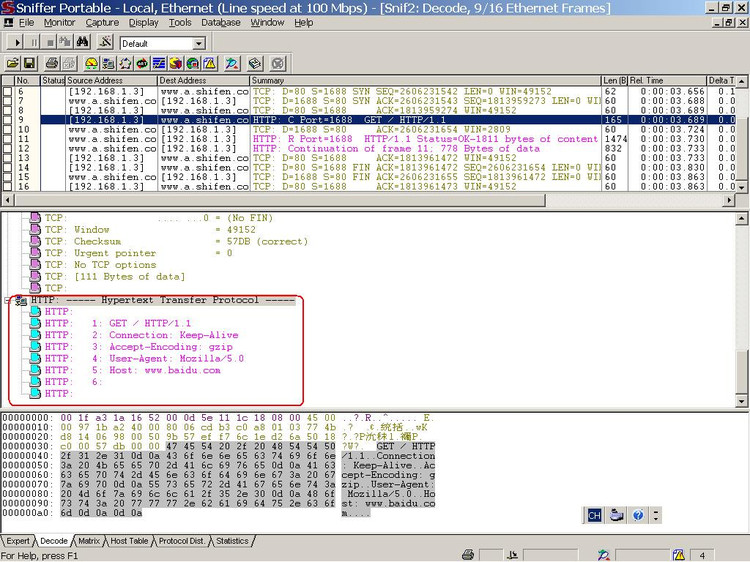
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/lfsblack/p/5279813.html