1、什么是 随机访问文件流 RandomAccessFile?
该类的实例支持读取和写入随机访问文件。 随机访问文件的行为类似于存储在文件系统中的大量字节。 有一种游标,或索引到隐含的数组,称为文件指针 ; 输入操作读取从文件指针开始的字节,并使文件指针超过读取的字节。 如果在读/写模式下创建随机访问文件,则输出操作也可用; 输出操作从文件指针开始写入字节,并将文件指针提前到写入的字节。 写入隐式数组的当前端的输出操作会导致扩展数组。 文件指针可以通过读取getFilePointer方法和由设置seek方法。
通俗来讲:我们以前讲的 IO 字节流,包装流等都是按照文件内容的顺序来读取和写入的。而这个随机访问文件流我们可以再文件的任意地方写入数据,也可以读取任意地方的字节。
我们查看 底层源码,可以看到:
|
1
|
public class RandomAccessFile implements DataOutput, DataInput, Closeable { |
实现了 DataOutput类,DataInput类,那么这两个类是什么呢?
2、数据流:DataOutput,DataInput
①、DataOutput:提供将数据从任何Java基本类型转换为一系列字节,并将这些字节写入二进制流。 还有一种将String转换为modified UTF-8格式(这种格式会在写入的数据之前默认增加两个字节的长度)并编写结果字节系列的功能。
②、DataInput:提供从二进制流读取字节并从其中重建任何Java原语类型的数据。 还有,为了重建设施String从数据modified UTF-8格式。
下面我们以其典型实现:DataOutputSteam、DataInputStream 来看看它的用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
//数据输出流 File file = new File("io"+File.separator+"a.txt"); DataOutputStream dop = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file)); //写入三种类型的数据 dop.write(65); dop.writeChar('哥'); dop.writeUTF("帅锅"); dop.close(); //数据输入流 DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)); System.out.println(dis.read()); //65 System.out.println(dis.readChar()); //哥 System.out.println(dis.readUTF()); //帅锅 dis.close(); |
3、通过上面的例子,我们可以看到因为 RandomAccessFile 实现了数据输入输出流,那么 RandomAccessFile 这一个类就可以完成 输入输出的功能了。

这里面第二个参数:String mode 有以下几种形式:(ps:为什么这里的值是固定的而不弄成枚举形式,不然很容易写错,这是因为随机访问流出现在枚举类型之前,属于Java 历史遗留问题)

第一种:用 随机流顺序读取数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class RandomAccessFileTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file = new File("io"+File.separator+"a.txt"); write(file); read(file); } /** * 随机流读数据 */ private static void read(File file) throws Exception { //以 r 即只读的方法读取数据 RandomAccessFile ras = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"); byte b = ras.readByte(); System.out.println(b); //65 int i = ras.readInt(); System.out.println(i); //97 String str = ras.readUTF(); //帅锅 System.out.println(str); ras.close(); } /** * 随机流写数据 */ private static void write(File file) throws Exception{ //以 rw 即读写的方式写入数据 RandomAccessFile ras = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); ras.writeByte(65); ras.writeInt(97); ras.writeUTF("帅锅"); ras.close(); }} |
第二种:随机读取,那么我们先介绍这两个方法


这里所说的偏移量,也就是字节数。一个文件是有N个字节数组成,那么我们可以通过设置读取或者写入的偏移量,来达到随机读取或写入的目的。
我们先看看Java 各数据类型所占字节数:
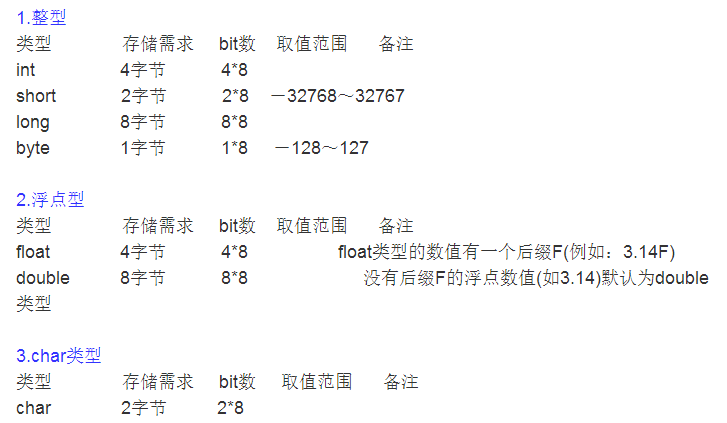
下面是 随机读取数据例子:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/** * 随机流读数据 */ private static void read(File file) throws Exception { //以 r 即只读的方法读取数据 RandomAccessFile ras = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"); byte b = ras.readByte(); System.out.println(b); //65 //我们已经读取了一个字节的数据,那么当前偏移量为 1 System.out.println(ras.getFilePointer()); //1 //这时候我们设置 偏移量为 5,那么可以直接读取后面的字符串(前面是一个字节+一个整型数据=5个字节) ras.seek(5); String str = ras.readUTF(); //帅锅 System.out.println(str); //这时我们设置 偏移量为 0,那么从头开始 ras.seek(0); System.out.println(ras.readByte()); //65 //需要注意的是:UTF 写入的数据默认会在前面增加两个字节的长度 ras.close(); } |
随机流复制文件:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
/** * 随机流复制文件 * @param fileA * @param B * @throws Exception */ private static void copyFile(File fileA,File fileB) throws Exception{ RandomAccessFile srcRA = new RandomAccessFile(fileA, "rw"); RandomAccessFile descRA = new RandomAccessFile(fileB, "rw"); //向 文件 a.txt 中写入数据 srcRA.writeByte(65); srcRA.writeInt(97); srcRA.writeUTF("帅锅"); //获取 a.txt 文件的字节长度 int len = (int) srcRA.length(); srcRA.seek(0); System.out.println(srcRA.readByte()+srcRA.readInt()+srcRA.readUTF()); //开始复制 srcRA.seek(0); //定义一个数组,用来存放 a.txt 文件的数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[len]; //将 a.txt 文件的内容读到 buffer 中 srcRA.readFully(buffer); //再将 buffer 写入到 b.txt文件中 descRA.write(buffer); //读取 b.txt 文件中的数据 descRA.seek(0); System.out.println(descRA.readByte()+descRA.readInt()+descRA.readUTF()); //关闭流资源 srcRA.close(); descRA.close(); } |
ps:一般多线程下载、断点下载都可以运用此随机流
来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/123hll/p/6903373.html