版权声明:原创文章,未经允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/shengqianfeng/article/details/91458482
openresty输出helloworld的两种方式
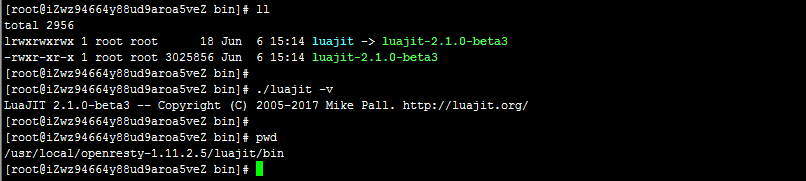
- 进入luajit目录,查看luajit版本 信息:
- 使用luajit执行lua脚本,我们编写一个hello.lua,输出hello world!
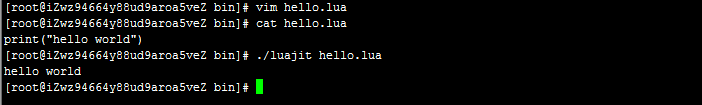
./luajit -v - 使用resty命令来执行打印hello world,因为resty最终也是调用luajit的。

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print("hello world")' openresty打印Lua的数据类型

输出:string

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print(type(print))' 输出:function

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print(type(true))' 输出:boolean

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print(type(0.1))' 输出:number

输出:table

输出:nil
数据类型案例
字符串拼接

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'local s = "" for i = 1, 10 do s=s..tostring(i) end print(s)' 结果:12345678910
在lua中表达字符串有三种方式:单引号、双引号、长括号[[]],接着演示下长括号的使用例子。

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print([[string has \r and \n]])' 结果:string has \r and \n
说明在lua中使用长括号表示的字符串不会做任何的转移处理!
那如果长括号字符串中又含有长括号呢?

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print([=[string has [[]] over ]=])' 结果:string has [[]] over
区别就是[=[ 和]=].
布尔值演示
判断0和“”是true还是false。

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'local a=0 if a then print('true') end a="" if a then print("true") end' 输出:true true
解释:其实在lua中,只有nil和false为假,0和空串都是真。
数值演示

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'print(9223372036854775807LL - 1)' 结果:9223372036854775806LL
Lua 的 number 类型,是用双精度浮点数来实现的。luaJit支持双数模式,即可以根据上下文,使用整型来存放整数,使用双精度浮点数来存放浮点数。上边例子是长整数的演示。
table演示

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'local color={first="red"} print(color["first"])' 结果:red
nil类型

/usr/local/openresty-1.11.2.5/bin/resty -e 'local a print(type(a))' 结果:nil
常用标准库
string标准库
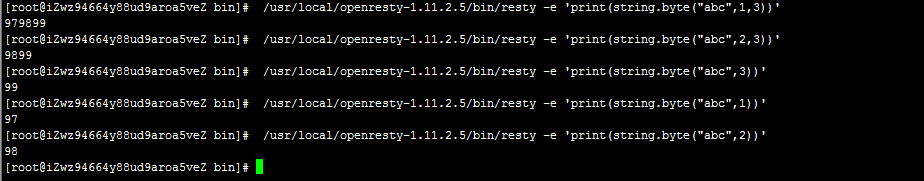
在 OpenResty 的环境中,Lua 标准库的优先级是很低的,优先级顺序:
OpenResty的API > LuaJIT的库函数 > 标准lua的函数
以上例子中,表示的是使用lua函数string.bytes,返回字符串 指定下标的ascii码值,结果如图所示。
math库

使用lua的math库生成随机 字符串。
虚变量

也就是使用下划线_,去代替那些不希望接收的返回值。
文章来源: https://blog.csdn.net/shengqianfeng/article/details/91458482