一、二叉树基础
1.1 二叉排序树定义
二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree)又称二叉查找(搜索)树(Binary Search Tree)。它是一颗空树,或者具有下列性质:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树分别为二叉排序树。
上述性质简称二叉排序树性质(BST性质),故二叉排序树实际上是满足BST性质的二叉树。
注意:
当用线性表作为表的组织形式时,可以有三种查找法。其中以二分查找效率最高。但由于二分查找要求表中结点按关键字有序,且不能用链表作存储结构,因此,当表的插入或删除操作频繁时,为维护表的有序性,势必要移动表中很多结点。这种由移动结点引起的额外时间开销,就会抵消二分查找的优点。也就是说,二分查找只适用于静态查找表。若要对动态查找表进行高效率的查找,可采用下二叉树或树作为表的组织形式。不妨将它们统称为树表。
1.2 特点
由BST性质可得:
(1) 二叉排序树中任一结点x,其左(右)子树中任一结点y(若存在)的关键字必小(大)于x的关键字。
(2) 二叉排序树中,各结点关键字是惟一的。
注意:
实际应用中,不能保证被查找的数据集中各元素的关键字互不相同,所以可将二叉排序树定义中BST性质(1)里的"小于"改为"大于等于",或将BST性质(2)里的"大于"改为"小于等于",甚至可同时修改这两个性质。
(3) 按中序遍历该树所得到的中序序列是一个递增有序序列。
【例】下图所示的两棵树均是二叉排序树,它们的中序序列均为有序序列:2,3,4,5,7,8。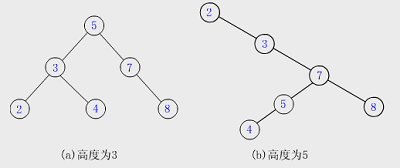
2、二叉树操作
二叉树TreeNode节点定义:
class TreeNode{ public int data; public TreeNode left; public TreeNode right; TreeNode(int data){ this.data=data; } } 2.1 二叉树的插入
2.1.1 递归实现
//添加节点(递归模式) public static boolean AddTreeNode1(TreeNode root, int data){ TreeNode treeNode=new TreeNode(data); //树为空 if(root==null){ root=treeNode; return true; } //比根节点小,插入到左子树 if(root.data>data){ if(root.left==null){ root.left=treeNode; return true; }else return AddTreeNode1(root.left, data); }else if(root.data<data){ //比根节点大,插入到右子树 if(root.right==null){ root.right=treeNode; return true; }else return AddTreeNode1(root.right,data); }else return false; } 2.1.2 非递归模式
//增加节点非递归模式 public static boolean AddTreeNode2(TreeNode root, int data){ //树为空 if(root==null){ root=new TreeNode(data); return true; } TreeNode treeNode=new TreeNode(data); TreeNode currNode=root; while(true){ if(currNode.data>data){ if(currNode.left!=null) currNode=currNode.left; else{ currNode.left=treeNode; return true; } }else if(currNode.data<treeNode.data){ if(currNode.right!=null) currNode=currNode.right; else { currNode.right=treeNode; return true; } }else return false; } } 2.2 二叉树的查找
public static boolean search(TreeNode root, int data){ if(root==null){ return false; }else if(root.data==data){ return true; }else if(root.data>data){ return search(root.left,data); }else{ return search(root.right,data); } } 2.3 二叉树的删除
删除可为BST问题最为复杂的一部分,需要考虑一下要删除的节点的四种情况:
- 该节点为叶子节点,删除即可
- 该节点只有左子树,没有右子树,删除后将该节点的左子树连接到该节点的父节点即可
- 该节点只有右子树,没有左子树,删除后将该节点的右子树连接到该节点的父节点即可
- 该节点既有左子树,也有右子树,这时候删除比较复杂,可以分为两种情况:
首先,我们知道二叉排序树经过中序遍历后得到的是一个递增有序序列,该节点的前一个即为直接前驱,后一个为直接后继。我们要得到直接前驱和直接后继的节点。
方法一:
- 得到该删除节点的左节点,如果此左节点没有右节点,则该左节点即为直接前驱;
- 左节点有右节点,则一直沿最右侧右节点迭代下去,最后面的那个即为直接前驱;
方法二:
- 得到该删除节点的右节点,如果此右节点没有左节点,则该右节点即为直接后继;
- 右节点有左节点,则一直沿最左侧左节点迭代下去,最后面的那个即为直接后继。
以上四种情况均要考虑要删除的节点为根节点root的情况。
代码实现如下:
//删除 public static boolean delete(TreeNode root, int data){ //current为查找得到的节点 TreeNode current=root; //parent为时刻更新父节点 TreeNode parent=root; //tempParent为同时存在左右子树的迭代临时父节点 TreeNode tempParent=root; //isLeft记录current节点的左右属性 boolean isLeft=true; while(current.data!=data){ parent=current; //到左子树查找 if(current.data>data){ isLeft=true; current=current.left; }else if(current.data<data){ //到右子树查找 isLeft=false; current=current.right; } //查不到,返回false if(current==null) return false; } //第一种情况:删除节点为叶节点 if(current.left==null && current.right==null){ if(current==root) root=null; if(isLeft) { parent.left = null; }else{ parent.right = null; } return true; }else if(current.right==null){ //第二种情况:删除节点只有左节点 if(current==root) root=current.left; else if(isLeft) parent.left=current.left; else parent.right=current.left; return true; }else if(current.left==null){ //第三种情况:删除节点只有右节点 if(current==root) root=current.right; else if(isLeft) parent.left=current.right; else parent.right=current.right; return true; }else{ //第四种情况:删除节点均存在左节点和右节点 if(current==root){ root=root.left; } TreeNode tempNode=current.left; //没有左节点 if(tempNode.right==null){ if(isLeft) parent.left=tempNode; else parent.right=tempNode; }else{ //存在左节点,迭代到最右侧子节点,即直接前驱 while(tempNode.right!=null){ tempParent=tempNode; tempNode=tempNode.right; } if(isLeft){ //为左节点,连接 parent.left=tempNode; parent.left.left=current.left; }else{ //为右节点,连接 parent.right=tempNode; parent.right.left=current.left; } //删除前驱节点,连接 if(tempNode.left==null) tempParent.right=null; else tempParent.right=tempNode.left; } return true; } } 2.4 二叉树的遍历
//二叉树中序遍历 public static void midSort(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } midSort(root.left); System.out.print(root.data+" "); midSort(root.right); } 2.5 测试代码
public static void main(String[] args){ int[] a=new int[]{62,88,58,47,35,73,51,99,37,93}; TreeNode root=new TreeNode(a[0]); for(int i=1; i<a.length; i++){ AddTreeNode1(root, a[i]); } System.out.println("中序遍历结果为:"); midSort(root); System.out.println("47存在:"+SearchTreeNode(root,47)); AddTreeNode1(root,100); System.out.println("添加100后,中序遍历结果为:"); midSort(root); System.out.println("添加100后,100存在:"+SearchTreeNode(root,100)); } 输出结果:
中序遍历结果为: 35 37 47 51 58 62 73 88 93 99 47存在:true 添加100后,中序遍历结果为: 35 37 47 51 58 62 73 88 93 99 100 添加100后,100存在:true 删除100后,中序遍历结果为: 35 37 47 51 58 62 73 88 93 99 删除100后,100存在:false 3、二叉排序树拓展
平衡二叉排序树:https://blog.csdn.net/zhaohong_bo/article/details/90311112
文章来源: https://blog.csdn.net/zhaohong_bo/article/details/90339684